
Concept explainers
Ketene, C2H2O, is a reactant for synthesizing cellulose acetate, which is used to make films, fibers, and fashionable clothing.
- (a) Write the Lewis structure of ketene. Ketene does not contain an —OH bond.
- (b) Identify the electron-region geometry and the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and all the bond angles in the molecule.
- (c) Identify the hybridization of each carbon and oxygen atom.
- (d) Is the molecule polar or nonpolar? Use appropriate data to support your answer.
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
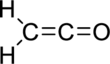
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The four electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
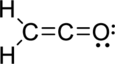
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron-region geometry and the molecular-geometry around each atom and the bond angles in the molecule have to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Electron geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs and lone pair of electrons.
Molecular geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering only bond pair of electrons
Geometry of different type of molecules with respect to the number of electron pairs are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure is given below:
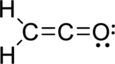 .
.
Consider the first carbon atom.
The molecular geometry and the electron-pair geometry will be trigonal planar because of the presence of three bond pairs around the carbon atom. The
Consider the second carbon atom.
The molecular geometry and the electron-pair geometry will be linear because of the presence of two bond pairs around the carbon atom. The
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of each carbon and oxygen has to be described.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure is given below:
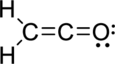 .
.
Consider the first carbon atom.
The molecular geometry and the electron-pair geometry will be trigonal planar because of the presence of three bond pairs around the carbon atom. Therefore, the hybridisation will be
Consider the second carbon atom.
The molecular geometry and the electron-pair geometry will be linear because of the presence of two bond pairs around the carbon atom. Therefore, the hybridisation will be will be
Consider the oxygen atom.
The electron-pair geometry around oxygen will be trigonal planar because of the presence of one bond pair and two lone pair around the oxygen atom. Therefore, the hybridisation will be
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the molecule is polar or non-polar has to be given.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure is given below:
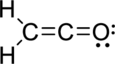 .
.
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
OWLV2 FOR MOORE/STANITSKI'S CHEMISTRY:
- If the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forward
- If the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forwardIndicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





