
a)
To prove: The graph of the polar equation
It is proved that
Given information:
The given equation is
Formula used:
Odd-even identities:
Cosine of a difference identity:
Cosine of a sum identity:
Calculation:
Symmetry about the
-axis:
Case1: Replace
Case 2: Replace
Both replacements give the same original polar equation.
Thus, it is proved that
b)
To find: The graph of the polar equation
It is proved that
Given information:
The given equation is
Formula used:
Odd-even identities:
Cosine of a difference identity:
Cosine of a sum identity:
Calculation:
Symmetry about the
Case1: Replace
Case2: Replace
Both replacements do not give the same original polar equation.
Thus, it is proved that
c)
To find:The graph of the polar equation
It is proved that
Given information:
The given equation is
Formula used:
Odd-even identities:
Cosine of a difference identity:
Cosine of a sum identity:
Calculation:
Symmetry about the origin:
Case1: Replace
Case2: Replace
Both replacements do not give the same original polar equation.
Thus, it is proved that
d)
To prove:The maximum
It is proved that the maximum
Given information:
The given equation is
Formula used:
The range of
Calculation:
The maximum value of
The minimum value of
Therefore, it is proved that the maximum
e)
To analyze:The graph of the curve.
The polar equation represents a rose curve with
The domain of the graph is
The range of the polar equation is
The graph is symmetric about both the axes and the origin.
The graph is continuous and bounded between the minimum and maximum
The maximum value of
Given information:
The given equation is
Calculation:
Plot the graph for
Consider the value of
The graph of
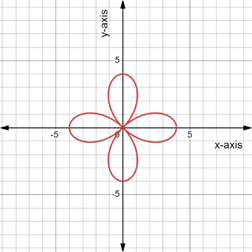
The graph of
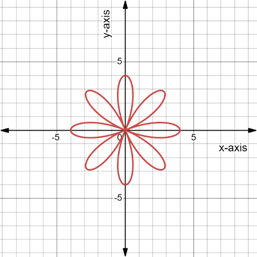
The graph of
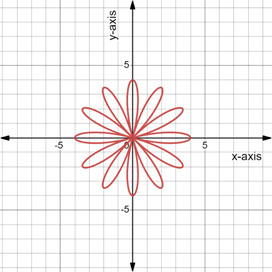
From the graphs for
The domain of the graph is
The range of
So, the range of the polar equation is
The graph is symmetric about both the axes and the origin.
The graph is continuous and bounded between the minimum and maximum
The maximum value of
Chapter 6 Solutions
PRECALCULUS:GRAPHICAL,...-NASTA ED.
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





