
Concept explainers
6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members act both in tension and in compression.)
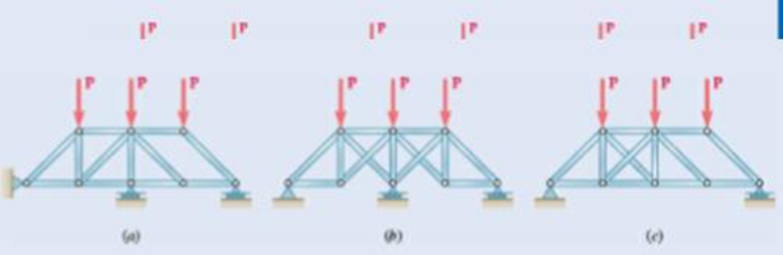
Fig. P6.74
(a)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (a). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 1.
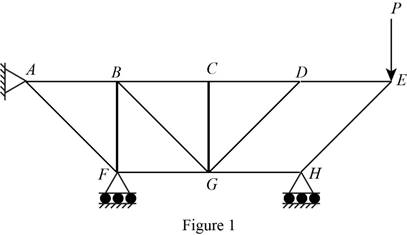
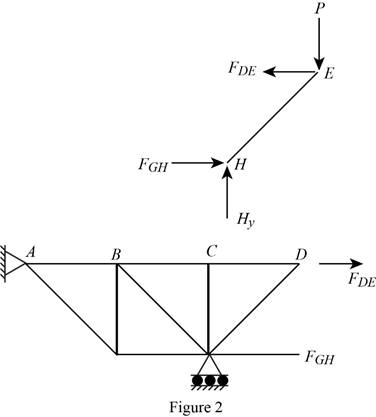
The free-body diagram of the section
Write the condition for a truss to be completely constrained.
Here,
Write the condition for a truss to be partially constrained.
Write the expression for a truss to be indeterminate.
Write the expression for the condition for equilibrium.
Here,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (IV) about point
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (V) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams given in Figure 2.
So, the truss
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
(b)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is partially constrained.
Explanation of Solution
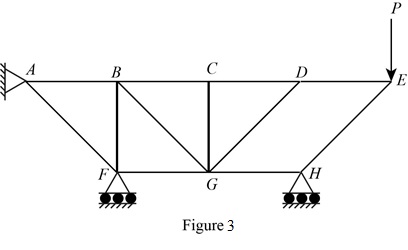
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (b). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 3.
From equations (I), (II), and (III), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is partially constrained.
(c)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is completely constrained and indeterminate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (c). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 4.
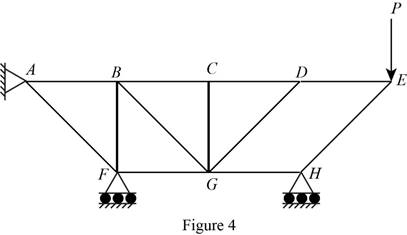
From equations (I), (II), and (III), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and indeterminate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STA
- 6.12 Determine the force in each member of the Howe roof truss shown. State whether each member is in tension (7) or compression (C). Answer FAB = FFH = Fig. P6.12 1500lbC;FAC = FCE = FEG = FGH = 1200lbT;FBc = Ffg = 0; Fbd = FCF = 1000lbC;Fbe = FeF = 500lbCFDE = 600lbT 300 lb A o 000 600 lb B C C O 600 lb D E 600 lb G O 300 lb 6 ft 8 ft· 8 ft 8 ft 8 ft →8 ft- H 4) 6 ftarrow_forward4. (20¹) Determine the force in each member of the truss in Fig. 4, and state if the members are in tension or compression. In Fig. 4, set 0= 25°, and F₁ = (12+ last 2 digits of your UTPB ID) (Hint: if your ID is 8000123456, then F1 =12+56= 79 kN) F₁ = 3 m 4 m B 1.3F, KN Fig. 4 F, KN F, 87 KN 4 m To asarrow_forwardmm.2arrow_forward
- Classify each of the structures shown as completely, partially, or improperly constrained; if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members can act both in tension and in compression.)arrow_forwardFig. P6.45 and P6.46 36 kips 36 kips Answer For = 60.0 kips C; FDG = 15.00 kips C. E G 4 panels at 10 ft = 40 ft 6.46 Determine the force in members DF and DG of the truss shown. 7.5 ftarrow_forward6.27 Determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression. 15 kips B F -10 ft- 5 ft Fig. P6.27 D E 40 kips -10 ft- C Go 5 ft 4 ft ↑ 6 ft 10 ftarrow_forward
- using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. state wether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardUsing the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwarduse attached imagearrow_forward
- Problem 1 (a) (b) compression. Answers: (a) RAx= Rcx = . For the given truss structure below: Determine the reactions and their directions. Determine the forces, FBC, FBE, and FEF. Specify whether the member is in tension or (b) FBC = 45° You ( - 4 m (direction: (direction: ) FBE = B + ) ) 12kN 4 m Ray = Rcy= E 12 kN () 4 m FEF= 8 kN D 3 m (direction: ) (direction: ) ()arrow_forwardUsing the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the trussshown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardProblem 4.30 While the stiffness of an elastic cord can be quite constant (i.e., the force versus displace- ment curve is a straight line) over a large range of stretch, as a bungee cord is stretched, it softens; that is, the cord tends to get less stiff as it gets longer. Assuming a soften- ing force-displacement relation of the form k8 - B83, where 8 (measured in ft) is the displacement of the cord from its unstretched length, considering a bungee cord whose unstretched length is 150 ft, and letting k = 2.58 lb/ft, determine the value of the con- stant B such that a bungee jumper weighing 170 lb and starting from rest gets to the bottom of a 400 ft tower with zero speed.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





