
Concept explainers
The truss shown consists of nine members and is support by a ball-and-socket at B, a short link at C, and two short links at D. (a) Check that this truss is a simple truss, that completely constrained, and that the reactions at its suppo are statically determinate. (b) Determine the force in each member for P = (−1200 N)j and Q = 0.
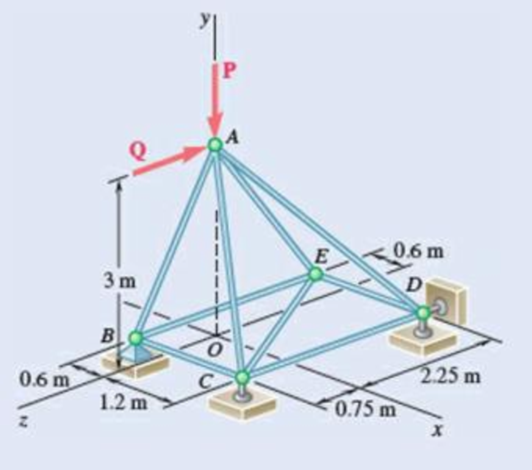
Fig. P6.39
(a)
Verify that the truss is a simple truss, completely constrained, and the reactions at the supports are statically determinate.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The reactions at supports B, C, and D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The value of the force P is
The value of the force Q is zero.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the truss as in Figure 1.
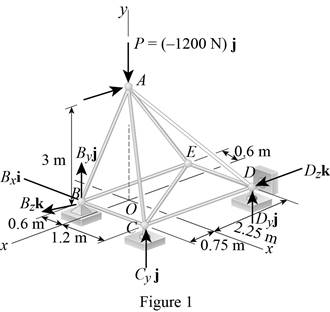
Find the vector coordinates by taking moment about point B.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute 300 N for
Resolve the force components in y-axis.
Substitute 300 N for
The unknown reactions can be calculated with the equilibrium equations. Therefore, the truss is statically determinate, completely constrained and simple truss.
Thus, the reactions at supports B, C, and D is
(b)
Find the force in each member of the truss.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The force in the member AB is
The force in the member BC is
The force in the member BE is
The force in the member AC is
The force in the member CE is
The force in the member CD is
The force in the member AD is
The force in the member DE is
The force in the member AE is
Explanation of Solution
Show the free-body diagram of the joint B as in Figure 2.
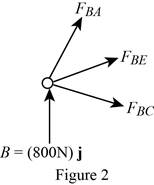
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of BA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AB as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member BC as follows;
Find the force in the member BE as follows;
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –840 N for
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute –840 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AB is
The force in the member BC is
The force in the member BE is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint C as in Figure 3.
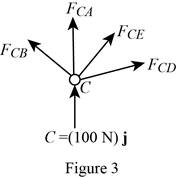
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of CA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AC as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member CB as follows;
Find the force in the member CD as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of CE using the relation.
Find the force in the member CE as follows;
Substitute
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –110.6 N for
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute –110.6 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AC is
The force in the member CE is
The force in the member CD is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint D as in Figure 4.
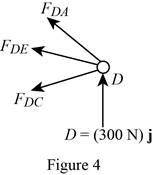
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of DA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AD as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member DC as follows;
Find the force in the member DE as follows;
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –394 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AD is
The force in the member DE is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint E as in figure 5.
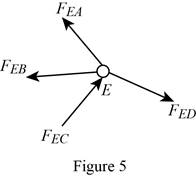
The member AE is not in the xz plane.
Therefore, the force in the member AE is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYNA.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Consider a large 6-cm-thick stainless steel plate (k = 15.1 W/m-K) in which heat is generated uniformly at a rate of 5 × 105 W/m³. Both sides of the plate are exposed to an environment at 30°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/m²K. Determine the value of the highest and lowest temperature. The highest temperature is The lowest temperature is °C. °C.arrow_forwardSketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel engine please, please explain into detail the difference bewteen the two and referance the a diagram. Please include a sketch or an image of each diagramarrow_forwardDraw left view of the first orthographic projectionarrow_forward
- Sketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel engine emphasis on the 2 stroke as my last answer explained 4 stroke please include a diagram or sketch.arrow_forwardA 4 ft 200 Ib 1000 Ib.ft C 2 ft 350 Ib - за в 2.5 ft 150 Ib 250 Ib 375 300 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame. shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ). ive submitted this question twice and have gotten two way different answers. looking for some help thanksarrow_forward
- 15 kg of steel ball bearings at 100 ° C is immersed in 25 kg of water at 20 ° C . Assuming no loss of heat to or from the container, calculate the final temperature of the water after equilibrium has been attained.Specific heat of steel: 0.4857 kJ / kg / ° KSpecific heat of water: 4.187 kJ / kg / ° Karrow_forwardSketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel enginearrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ).arrow_forward
- Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardanswer the fallowing Brake Specific Fuel Consumption - 0.3 kg/kwh, Mechanical Efficiency- 90% Calorific Value of Fuel -45 MJ/kg. Given these values, find the indicated power, indicated thermal efficiency and brake thermal efficiencyarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L