
Write the ground-state electron configurations for the following elements:
Interpretation:
The ground state electron configurations of the given elements are to be obtained.
Concept introduction:
Aufbau Principle states that every electron occupies the orbitals in the increasing of their energy.
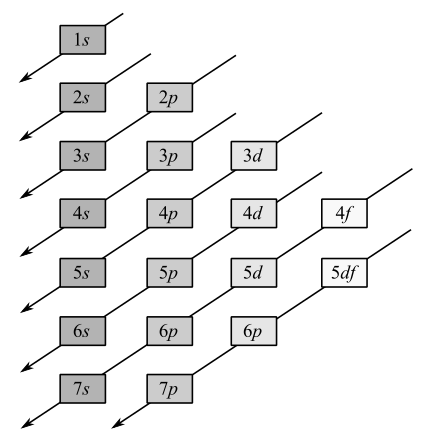
The four steps for writing the ground state electron configuration of an element are shown below:
An electron enters the lowest energy orbital.
A maximum of two electrons can occupy each orbital.
In a degenerate orbital, the electrons do not pair until all the orbitals are occupied with at least one electron.
Electrons occupy the orbitals in the following order:
Noble gas core is used to represent electron configuration of all the elements except hydrogen and helium.
Noble gas core is an abbreviation in an atom’s electron configuration. It replaces the electron configuration of noble gas element most recently precede the element.
Answer to Problem 97QP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Ge, Fe, Zn, Ni, W, and Tl elements.
Every electron occupies the orbitals in the increasing order of their energy
The atomic number of the element Ge is
Hence, the ground state electronic configuration is
The atomic number of the element Fe is
Hence, the ground state electronic configuration is
The atomic number of the element Zn is
Hence, the ground state electron configuration is
The atomic number of the element Ni is
Hence, the ground state electronic configuration is
The atomic number of the element W is
Hence, the ground state electronic configuration is
The atomic number of the element Tl is
Hence, the ground state electronic configuration is
The ground state electron configurations of elements (Ge, Fe, Zn, Ni, W, Tl) are as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry
MARINE BIOLOGY
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
- Draw a structural formula for the major product of the acid-base reaction shown. H 0 N + HCI (1 mole) CH3 N' (1 mole) CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. ● • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I, in your answer. . In those cases in which there are two reactants, draw only the product from 989 CH3 344 ? [Farrow_forwardQuestion 15 What is the major neutral organic product for the following sequence? 1. POCI₂ pyridine ? 2. OsO4 OH 3. NaHSO Major Organic Product ✓ OH OH 'OH OH 'OH 'CIarrow_forwardURGENT! PLEASE HELP!arrow_forward
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forwardCan you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning 
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





