
(a)
Interpretation:
Using the recommended daily dietary intake of calcium the amount of calcium required for adult men and premenopausal women should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Importance of Calcium in diet:
- 1. Calcium is required by human body for muscle contraction, hormones release and transmission of messages via nerves.
- 2. Correct intake of calcium helps one from osteoporosis which occurs as density of the bone decreases and results in structural defect and weakness of bones.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mass of calcium citrate required to attain the recommended daily intake of calcium should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Calcium citrate: It is recommended for calcium deficiency diseases namely rickets, tetany and osteoporosis. The molecular formula of Calcium citrate is
Importance of Calcium in diet:
- 1. Calcium is required by human body for muscle contraction, hormones release and transmission of messages via nerves.
- 2. Correct intake of calcium helps one from osteoporosis which occurs as density of the bone decreases and results in structural defect and weakness of bones.
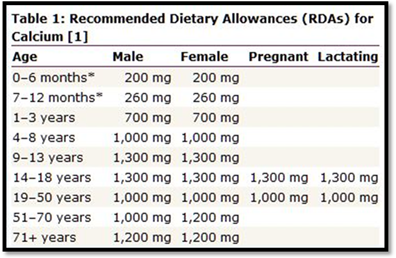
The table that depicts recommended daily intake of calcium is as follows,
Moles: One mole is equivalent to the mass of the substance consists same number of units equal to the atoms present in
The mole is actually quantity of particles that is
The sum of mass of all atoms present in formula of chemical substance is referred as molecular or formula weight of that substance.
Mass: It is the quantitative measure of a substance. The amount of matter present in substance is expressed as mass. The
Molar mass: It is obtained by dividing the mass of substance with the amount of substance and the S.I. unit of molar mass is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H H ⚫OH HO- -H H- -OH H- -OH CH2OH Ag*, NH4OH, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H₂O -OH H ⚫OH HO H HO- CH2OH Cu2+ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H、 H -OH H ⚫OH H -OH CH2OH Fehlings' solution ⑤ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning





