
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.5.8P
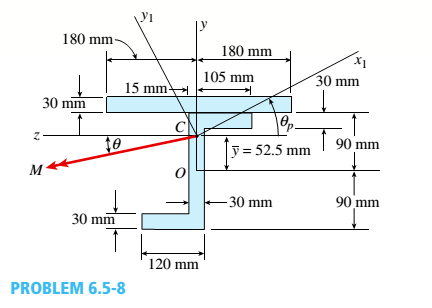
The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the figure. This beam is subjected to a bending moment M having its
Determine the orientation of the neutral axis and calculate the maximum tensile stress tiand maximum compressive stress tcin the beam. Assume that e = 22.5° and M = 4.5 kN · m. Use cross-sectional properties Ix=93.14 × 106 mm4, Iy= 152.7 X 10e mm4, and 9 = 27.3º.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Research and select different values for the R ratio from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphs.
Qu. 7 The v -t graph of a car while travelling along a road is shown. Draw the s -t and a -t graphs for the motion.
I need to draw a graph and I need to show all work step by step please do not get short cut from dtna
An unpressurized cylindrical tank with a 100-foot diameter holds a 40-foot column of water. What is total force acting against the bottom of the tank?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. In the following problems check to see if the set S is a vector subspace of the corresponding R. If it is not, explain why not. If it is, then find a basis and the dimension. (a) S = (b) S = {[],+,"} X1 x12x2 = x3 CR³ {[1], 4+4 = 1} CR³ X2arrow_forwardAAA Show laplace transform on 1; (+) to L (y(+)) : SY(s) = x (0) Y(s) = £ [lx (+)] = 5 x(+) · est de 2 -St L [ y (^) ] = So KG) et de D 2 D D AA Y(A) → Y(s) Ŷ (+) → s Y(s) -yarrow_forward1) In each of the following scenarios, based on the plane of impact (shown with an (n, t)) and the motion of mass 1, draw the direction of motion of mass 2 after the impact. Note that in all scenarios, mass 2 is initially at rest. What can you say about the nature of the motion of mass 2 regardless of the scenario? m1 15 <+ m2 2) y "L χ m1 m2 m1 בז m2 Farrow_forward
- 8. In the following check to see if the set S is a vector subspace of the corresponding Rn. If it is not, explain why not. If it is, then find a basis and the dimension. X1 (a) S = X2 {[2], n ≤ n } c X1 X2 CR² X1 (b) S X2 = X3 X4 x1 + x2 x3 = 0arrow_forward2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities V₁ and V₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 ↑ บา m2 ñ Вarrow_forwardThe fallowing question is from a reeds book on applied heat i am studying. Although the answer is provided, im struggling to understand the whole answer and the formulas and the steps theyre using. Also where some ov the values such as Hg and Hf come from in part i for example. Please explain step per step in detail thanks In an NH, refrigerator, the ammonia leaves the evaporatorand enters the cornpressor as dry saturated vapour at 2.68 bar,it leaves the compressor and enters the condenser at 8.57 bar with50" of superheat. it is condensed at constant pressure and leavesthe condenser as saturated liquid. If the rate of flow of the refrigerantthrough the circuit is 0.45 kglmin calculate (i) the compressorpower, (ii) the heat rejected to the condenser cooling water in kJ/s,an (iii) the refrigerating effect in kJ/s. From tables page 12, NH,:2.68 bar, hg= 1430.58.57 bar, hf = 275.1 h supht 50" = 1597.2Mass flow of refrigerant--- - - 0.0075 kgls 60Enthalpy gain per kg of refrigerant in…arrow_forward
- state the formulas for calculating work done by gasarrow_forwardExercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi, Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi. Determine the principal stresses. The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be kpsi. kpsi. The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [ The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [ The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [ kpsi. kpsi. kpsi. kpsi.arrow_forward
- Repeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load. (I want to understand this problem)arrow_forwardProb 2. The material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE. 50 mm B 200 mm 15 mm 30 mm D ΕΙ 50 mm x A 150 mm Farrow_forwardProb 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license