
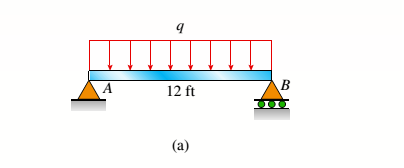
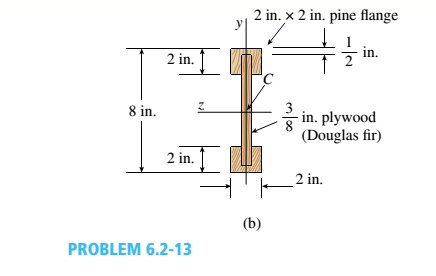
A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span supports a distributed load of intensity q = 90 lb/ft over its length (see figure part a). The beam is constructed with a web of Douglas-fir plywood and flanges of pine glued to the web, as shown in the figure part b. The plywood is 3/8 in. thick: the flanges are 2 in, × 2 in, (actual size). The modulus of elasticity for the plywood is 1,600,000 psi and for the pine is 1,200,000 psL
- Calculate the maximum bending stresses in the pine flanges and in the plywood web.
a.
The bending stress that is maximum in the plywood web and pine flanges
Answer to Problem 6.2.13P
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood
Bending Stress Maximum for pine
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure
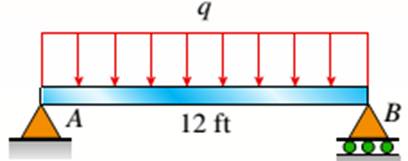
The I beam that is wooden has the span of 12 ft over its length supporting a distributed intensity load q=90lb/ft. The beam is made of Douglas fir plywood web and pine flanges with the plywood having a thickness of 3/8 in and that of flanges 2in.*2in. The elasticity modulus of the plywood is 1,600,000psi and for pine it is 1,200,000psi.
Concept Used:
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood,
Where,
Calculation:
Bending moment maximum is given as
Substituting the values we have,
Plywood moment of inertia is given as,
Pine moment of inertia is given as,
Bending Stress Maximum for plywood,
Bending Stress Maximum for pine,
Conclusion:
Thus, the bending stress that is maximum in the plywood web and pine flanges is given by equating the maximum bending movement
b.
The qmax with 1600psi maximum stress in flanges and for web being 1200psi.
Answer to Problem 6.2.13P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure:
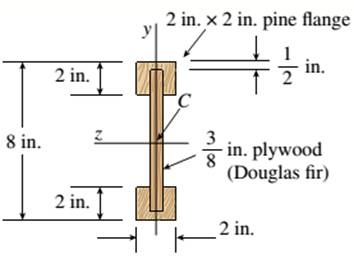
The I beam that is wooden has the span of 12 ft over its length supporting a distributed intensity load q=90lb/ft. The beam is made of Douglas fir plywood web and pine flanges with the plywood having a thickness of 3/8 in and that of flanges 2in.*2in. The elasticity modulus of the plywood is 1,600,000psi and for pine it is 1,200,000psi.
Concept Used:
Web maximum stress,
Where,
Calculation:
Maximum stress Maximum for Web,
Substituting the values we have,
Maximum stress Maximum for flange,
Substituting the values we have,
Bending moment that is maximum,
Maximum uniform load distributed is given as,
Conclusion:
Thus, the qmax with 1600psi maximum stress in flanges and for web being 1200psi is given by the equation of maximum load.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- what is an air preheater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forwardQf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC. a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D P = 4 kip Ma = 5 kip-ft w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft a = 3 ftarrow_forward
- From the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?arrow_forward(a) What kind of equation is it?(b) Is it linear or non-linear?(c) Is it a coupled system or uncoupled?arrow_forwardWhat kind of system is presented in Figure 2? Open loop or closed loop?arrow_forward
- What are the control hardware shown in the Figure?arrow_forwardQuestion 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forward
- If you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forwardProblem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
