
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.2.4P
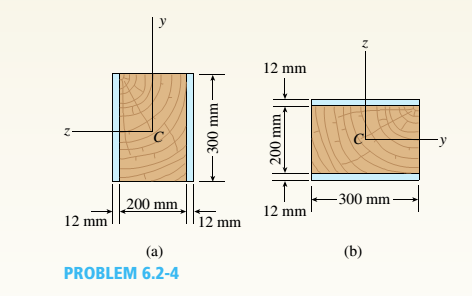
A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm x 300 mm is reinforced on its sides by steel plates 12 mm thick (see figure). The moduli of elasticity for the steel and wood are E±= 190 GPa and Ew= 11 GPa, respectively. Also, the corresponding allowable stresses are eS= 110 MPa and ew = 7.5 MPa,
(a)
Calculate the maximum permissible bending moment Mmaxwhen the beam is bent about the- axis.
- Repeat part (a) if the beam is now bent about its y axis.
Find the required thickness of the steel plates on the beam bent about the y axis so that Mmaxis the same for both beam orientations.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
I had a theoretical question about attitude determination. In the attached images, I gave two axis and angles. The coefficient of the axes are the same and the angles are the same. The only difference is the vector basis. Lets say there is a rotation going from n hat to b hat. Then, you introduce a intermediate rotation s hat. So, I want to know if the DCM produced from both axis and angles will be the same or not. Does the vector basis affect the numerical value of the DCM? The DCM formula only cares about the coefficient of the axis and the angle. So, they should be the same right?
3-15. A small fixed tube is shaped in the form of a vertical helix of radius a
and helix angle y, that is, the tube always makes an angle y with the horizontal.
A particle of mass m slides down the tube under the action of gravity. If there is
a coefficient of friction μ between the tube and the particle, what is the steady-state
speed of the particle? Let y
γ
30° and assume that µ < 1/√3.
The plate is moving at 0.6 mm/s when the force applied to the plate is 4mN. If the surface area of the plate in contact with the liquid is 0.5 m^2, deterimine the approximate viscosity of the liquid, assuming that the velocity distribution is linear.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3-9. Given that the force acting on a particle has the following components: Fx = −x + y, Fy = x − y + y², F₂ = 0. Solve for the potential energy V. -arrow_forward2.5 (B). A steel rod of cross-sectional area 600 mm² and a coaxial copper tube of cross-sectional area 1000 mm² are firmly attached at their ends to form a compound bar. Determine the stress in the steel and in the copper when the temperature of the bar is raised by 80°C and an axial tensile force of 60 kN is applied. For steel, E = 200 GN/m² with x = 11 x 10-6 per °C. E = 100 GN/m² with α = 16.5 × 10-6 For copper, per °C. [E.I.E.] [94.6, 3.3 MN/m².]arrow_forward3–16. A particle of mass m is embedded at a distance R from the center of a massless circular disk of radius R which can roll without slipping on the inside surface of a fixed circular cylinder of radius 3R. The disk is released with zero velocity from the position shown and rolls because of gravity, all motion taking place in the same vertical plane. Find: (a) the maximum velocity of the particle during the resulting motion; (b) the reaction force acting on the disk at the point of contact when it is at its lowest position. KAR 60° 3R M Fig. P3-16arrow_forward
- I have figured out the support reactions, Ay = 240 kN, Ax = 0 kN, Ma = 639.2 kN*m and the constant term for V(x) is 240. I am not figuring out the function of x part right. Show how to derive V(x) and M(x) for this distributed load.arrow_forward2.4 (A). A 75 mm diameter compound bar is constructed by shrinking a circular brass bush onto the outside of a 50 mm diameter solid steel rod. If the compound bar is then subjected to an axial compressive load of 160 kN determine the load carried by the steel rod and the brass bush and the compressive stress set up in each material. For steel, E 210 GN/m²; for brass, E = 100 GN/m². [I. Struct. E.] [100.3, 59.7 kN; 51.1, 24.3 MN/m².]arrow_forward1.7 (A). A bar ABCD consists of three sections: AB is 25 mm square and 50 mm long, BC is of 20 mm diameter and 40 mm long and CD is of 12 mm diameter and 50 mm long. Determine the stress set up in each section of the bar when it is subjected to an axial tensile load of 20 kN. What will be the total extension of the bar under this load? For the bar material, E = 210GN/m2. [32,63.7, 176.8 MN/mZ, 0.062mrn.l 10:41 مarrow_forward
- 2.2 (A). If the maximum stress allowed in the copper of the cable of problem 2.1 is 60 MN/m2, determine the maximum tension which C3.75 kN.1 10:41 مarrow_forward1.1 (A). A 25mm squarecross-section bar of length 300mm carries an axial compressive load of 50kN. Determine the stress set up ip the bar and its change of length when the load is applied. For the bar material E = 200 GN/m2. [80 MN/m2; 0.12mm.larrow_forward2.1 (A). A power transmission cable consists of ten copper wires each of 1.6 mm diameter surrounding three steel wires each of 3 mm diameter. Determine the combined E for the compound cable and hence determine the extension of a 30 m length of the cable when it is being laid with a tension of 2 kN. For steel, E200 GN/mZ; for copper, E = 100 GN/mZ. C151.3 GN/mZ; 9.6 mm.] 10:41 مarrow_forward
- question 662 thank youarrow_forward1.5 (A). A simple turnbuckle arrangement is constructed from a 40 mm outside diameter tube threaded internally at each end to take two rods of 25 mm outside diameter with threaded ends. What will be the nominal stresses set up in the tube and the rods, ignoring thread depth, when the turnbuckle cames an axial load of 30 kN? Assuming a sufficient strength of thread, what maximum load can be transmitted by the turnbuckle if the maximum stress is limited to 180 MN/mz? C39.2, 61.1 MN/m2, 88.4 kN.1arrow_forward1.3 (A). Define the terms shear stress and shear strain, illustrating your answer by means of a simple sketch. Two circular bars, one of brass and the other of steel, are to be loaded by a shear load of 30 kN. Determine the necessary diameter of the bars (a) in single shear, (b) in double shear, if the shear stress in the two materials must not exceed 50 MN/m2 and 100 MN/ mZ respectively. C27.6, 19.5, 19.5, 13.8mm.l 11arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License