
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving the chloride ion
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chloride ion
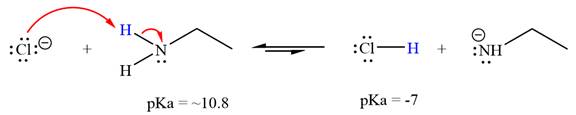
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is a not suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
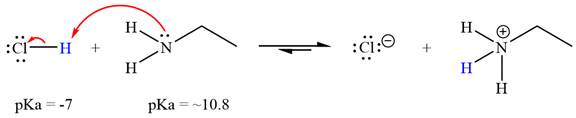
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
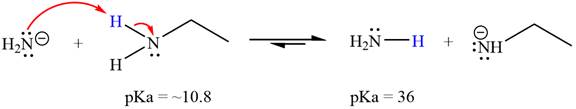
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine (
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
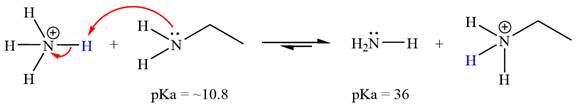
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanamine ( ) as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
Leveling effect refers to the effect of a solvent on the properties of acids and bases. For an acid-base reaction, the strength of the strong acid is limited or leveled by the basicity of the solvent. Similarly, the strength of the strong base is leveled by the acidity of the solvent. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.46P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamine is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of hydroxide ion
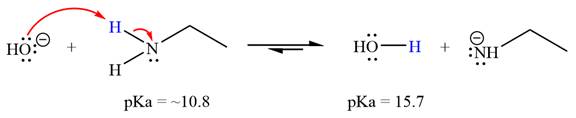
Ethanamine,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward

 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





