
(a)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
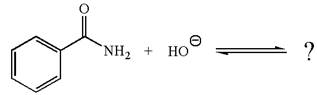
The ion

In the conjugate base formed, the negative charge on nitrogen is delocalized through the electron withdrawing resonance effect of carbonyl group. Thus, amide is a stronger acid than water, and hence, the equilibrium is favored to the product side.
The
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(b)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with the numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:
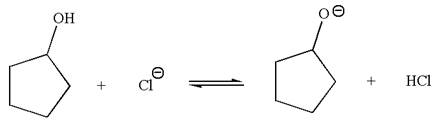
The equilibrium is favored to the reactant side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
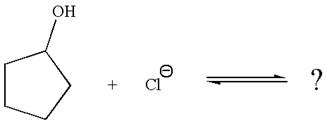
In the given reaction,
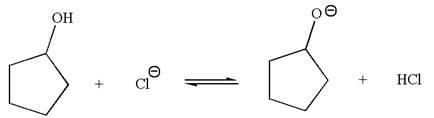
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of the stronger acid and
(c)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:
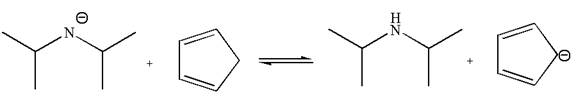
The equilibrium is favored to product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
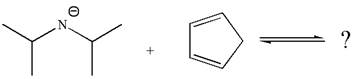
In the given reaction, cyclopentadiene acts as an acid and the negatively charge nitrogen abstracts a proton from diisopropylamine to give the following products:
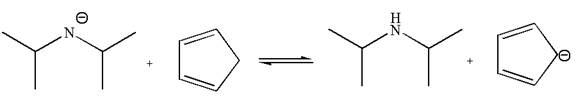
On the product side, the negative charge on carbon is a resonance stabilized by a conjugated double bond; such stabilization of the negative charge is not possible on the reactant side where the negative charge is on nitrogen bonded to two electron donating isopropyl groups. The acid is stronger when its conjugate base is stable, therefore, cyclopentadiene is a stronger acid than
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(d)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
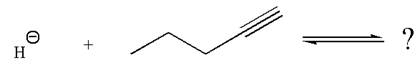
In the given reaction, the hydride ion abstracts the terminal proton of an

As the effective electronegativity of
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(e)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
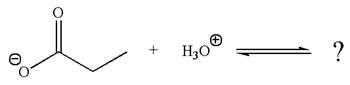
In the given reaction, the propanoate ion abstracts the proton of hydronium ion to give the following products:

According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(f)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side. Benzene is the weaker acid by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
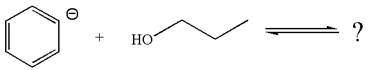
In the given reaction, the

As the oxygen atom is more electronegative than carbon, the negative charge on oxygen is more stable as compared to carbon. Thus, an anion on the right side, having negative charge on oxygen, is more stable than the anion on the left side where the negative charge is on carbon. Therefore, propanol is more acidic than benzene, and hence, the reaction is favored to the product side.
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and the
(g)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side. Benzene is the weaker acid by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
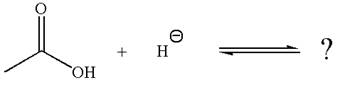
In the given reaction, the hydride ion abstracts the proton from carboxylic acid and gives the following products:

The conjugate base formed with a negative charge on the oxygen atom is better stabilized by the resonance effect. This makes the carboxylic acid the stronger acid, and the equilibrium is favored to the product side.
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forward
- As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forwardgive example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward
- 2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward(Methanesulfinyl)methane is reacted with NaH, and then with acetophenone. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward3-Oxo-butanenitrile and (E)-2-butenal are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

