
(a)
Interpretation:
The number and kind of stereoisomers formed when given molecule is treated in presence of
Concept Introduction:
Geometric isomers: Two atoms with the same side location of the double bond are called cis isomers and two atoms with opposite side locations of the double bond are called Trans isomers.
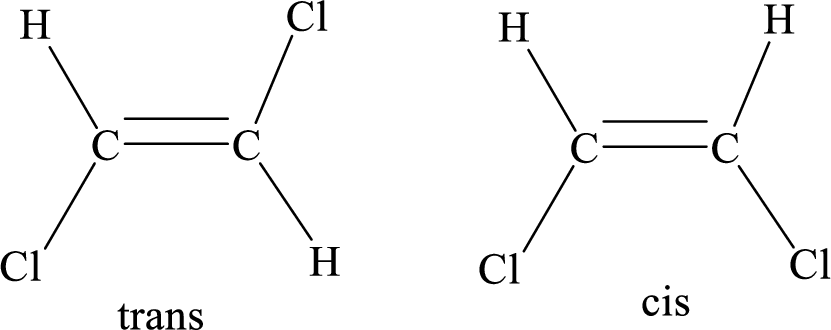
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number and kind of stereoisomers formed when given molecule is treated in presence of
Concept Introduction:
Geometric isomers: Two atoms with the same side location of the double bond are called cis isomers and two atoms with opposite side locations of the double bond are called Trans isomers.
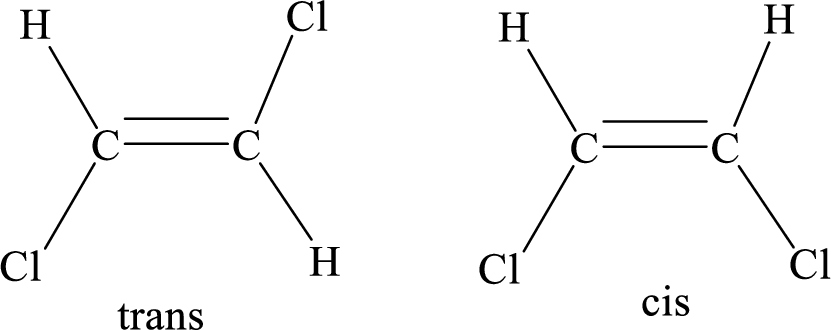
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number and kind of stereoisomers formed when given molecule is treated in presence of
Concept Introduction:
Geometric isomers: Two atoms with the same side location of the double bond are called cis isomers and two atoms with opposite side locations of the double bond are called Trans isomers.
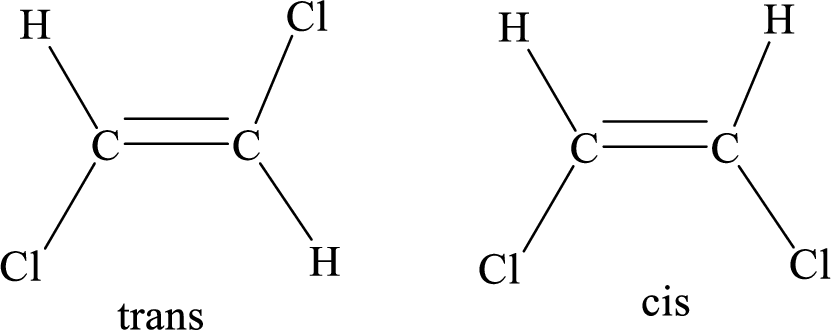
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number and kind of stereoisomers formed when given molecule is treated in presence of
Concept Introduction:
Geometric isomers: Two atoms with the same side location of the double bond are called cis isomers and two atoms with opposite side locations of the double bond are called Trans isomers.
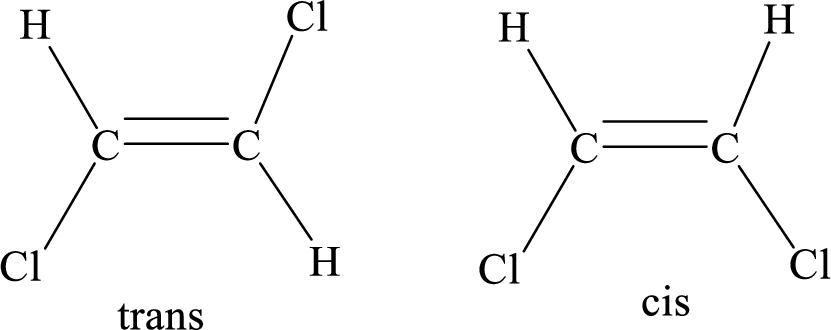
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Can you explain how I get these here and show the steps plz?arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for this compound Hydrocarbon Condensed Formulas Hint C2H5 CH2CH3 expand that in all the formula Part A: (CH3)2CHCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part B: CH2=C(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part C: (CH3)2C=CHC(C2H5)=CH2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part D: CH3C=CCH(C2H5)2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part E: (CH3)3CC=CCH2CH=C(CH3)2arrow_forwardSelect/ Match the correct letter from the image below for the IUPAC names given below: A B C D 3 E F G H K L Part 1. 4-methylheptane For example.mmmm Answer Letter H _for part 1 Part 2. 2,4-dimethylhexane Part 3. 2,3-dimethylpentane Part 4. 2,2-dimethylhexane Part 5. 2-ethyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylcyclopentane Part 6. 3-ethyl-2-methylpentanearrow_forward
- Can u show the process as to how to get these?arrow_forwardSketch the expected 'H NMR spectra for the following compound. Label all of the H's in the structure and the corresponding signal for the spectra you sketch. Make sure you include the integration value and the splitting pattern for each signal Indicate how many signals you would expect in the 13C NMRarrow_forwardUse IUPAC naming rules to name the following hydrocarbon compounds: CH2-CH3 | a) CH-CH-CH2-CH-CH-CH3 b) | CH2 CH3 | CH3 CH3 \ / C=C H 1 H CH2-CH3 c) d) CH=C-CH3 e) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 f) CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 g) CH3-CH2-C = C-CH2-CH3 h)arrow_forward
- Q5 Name the following : a. b. C. d. e.arrow_forward25. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 1 equivalent of each of the starting materials was used. H₂C CH3 CH3 H3C H3C H3C. CH2 + H3C. heat CH3 CH H.C. CH3 H.C H.C CH3 CH CH3 CH3 A B C Earrow_forwardFind chemical structures based on the below information. a) Chemical formula C6H8O Compound is aromatic plus has two 1H NMR peaks that integrated for 3 each that are singlets (it could have more peaks in the 1H NMR b) Chemical Formula: C6H100 Compounds is conjugated 'H NMR has a signal that integrates for 6 and is a doublet IR spectra has a signal at 1730 cm-1arrow_forward
- Jaslev Propose a synthesis of the following starting from benzene and any other reagents and chemicals. No mechanisms are required. Indicate the condition for each step plus the major product for each step. More than two steps are required. Step 1 Step 2 مہد Brarrow_forwardPart C: The line formula for another branched alkane is shown below. i. In the IUPAC system what is the root or base name of this compound? ii. How many alkyl substituents are attached to the longest chain? iii. Give the IUPAC name for this compound.arrow_forwardPart D: Draw the Structural Formula for 4-ethyl-2-methylhexane Part E. Draw the Structural Formula for 1-chloro-3,3-diethylpentane (Chloro = Cl)arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

