
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.49P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The differences for stability of two given carbocations that is
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: The carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
The general carbocation stability order is as follows,
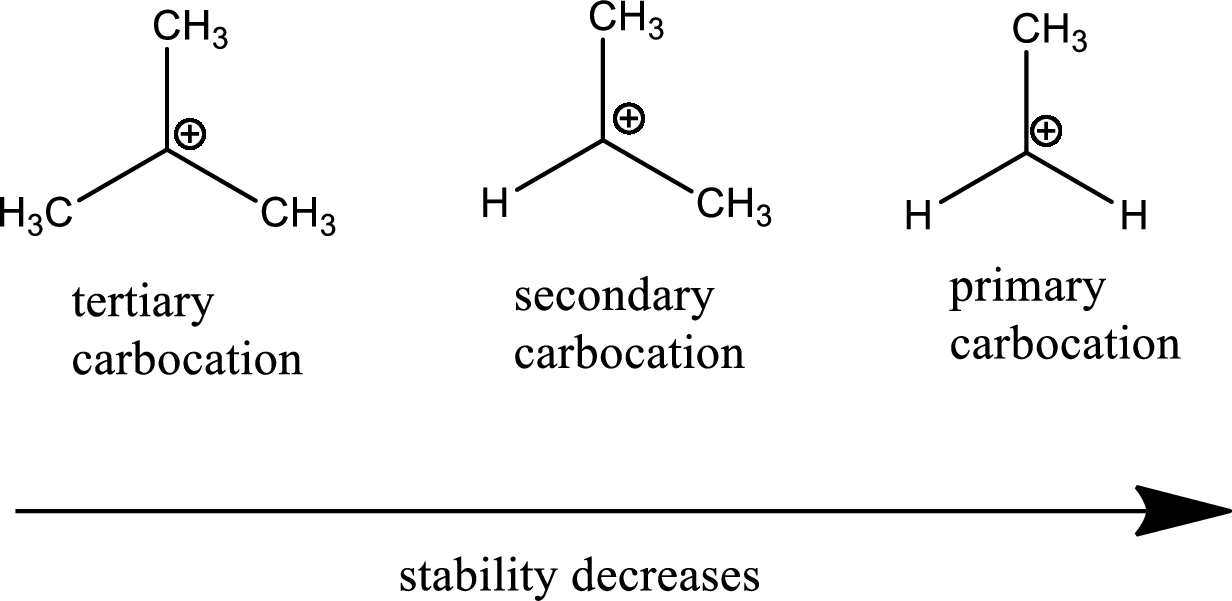
Resonance stabilization: Due to the delocalization of electrons within the molecule the overall energy becomes lower and makes that molecule more stable.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Identifying the stereochemistry of natural
Write the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below.
Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is.
molecule
H
O-C-CH2
H3N.
HN
N
H
C=O
common name
(not the IUPAC
name)
NH3
☐
H3N
H
☐
CH2
X
>
Draw the structure of alanine at pH 1.2.
Click and drag to start drawing a
structure.
Understanding the general acid-base properties of amino acids
O Proteins
Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or
neutral?
molecule
The solution is...
010
H3N-CH-C-OH
CH
HO
CH3
O acidic
O basic
neutral
O (unknown)
H3N
HO
0
O acidic
O basic
neutral
○ (unknown)
H3N-CH-C-O
CH2
CH3-CH-CH3
O acidic
O basic
Oneutral
○ (unknown)
O=
X
H2N-CH-C-O
CH3
CH
CH3
acidic
O basic
O neutral
○ (unknown)
?
000
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 6.2 - Using the BDE values from Appendix 3, calculate...Ch. 6.3 - Name and draw a structural formula for the product...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.3PCh. 6.3 - Propose a mechanism for the addition of HI to...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.5PCh. 6.3 - Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed...Ch. 6.3 - The acid-catalyzed hydration of...Ch. 6.3 - Complete these reactions. (a) (b)Ch. 6.3 - Draw the structure of the chlorohydrin formed by...Ch. 6.4 - Draw structural formulas for the alkene that gives...
Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 6.11PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 6.12PCh. 6.5 - What alkene with the molecular formula C6H12, when...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.15PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.16PCh. 6 - Predict the organic product(s) of the reaction of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.18PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.20PCh. 6 - Draw a structural formula for an alkene with the...Ch. 6 - Account for the fact that addition of HCl to...Ch. 6 - Account for the fact that treating propenoic acid...Ch. 6 - Draw a structural formula for the alkene with the...Ch. 6 - Draw the alternative chair conformations for the...Ch. 6 - Draw a structural formula for the cycloalkene with...Ch. 6 - Reaction of this bicycloalkene with bromine in...Ch. 6 - Terpin, prepared commercially by the...Ch. 6 - Propose a mechanism for this reaction and account...Ch. 6 - Treating 2-methylpropene with methanol in the...Ch. 6 - When 2-pentene is treated with Cl2 in methanol,...Ch. 6 - Treating cyclohexene with HBr in the presence of...Ch. 6 - Propose a mechanism for this reaction. 1-Pentane...Ch. 6 - Treating 4-penten-1-ol with bromine in water forms...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.35PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.36PCh. 6 - Reaction of -pinene with borane followed by...Ch. 6 - Write structural formulas for the major organic...Ch. 6 - Draw the structural formula of the alkene that...Ch. 6 - Consider the following reaction. (a) Draw a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.42PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.43PCh. 6 - Show how to convert ethylene to these compounds....Ch. 6 - Show how to convert cyclopentene into these...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.46PCh. 6 - Describe the stereochemistry of the bromohydrin...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.49PCh. 6 - Treating 1,3-butadiene with 1 mole of HBr gives a...Ch. 6 - In this chapter, we studied the mechanism of the...Ch. 6 - As we have seen in this chapter, carbon-carbon...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.53PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.54P
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule 0=0 H3N-CH-C-o HO CH2 OH The solution is... O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H₂N acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) + H3N O OH O acidic O basic O neutral O (unknown) H2N-CH-C-O CH3 O acidic O basic neutral ○ (unknown) X ? olo HEarrow_forwardRecognizing ampli Draw an a amino acid with a methyl (-CH3) side chain. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Carrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name × HO OH ☐ OH CI CI O CI OH OHarrow_forward
- く Check the box under each a amino acid. If there are no a amino acids at all, check the "none of them" box under the table. Note for advanced students: don't assume every amino acid shown must be found in nature. COO H3N-C-H CH2 HO CH3 NH3 O CH3-CH CH2 OH Onone of them Explanation Check + H3N O 0. O OH + NH3 CH2 CH3-CH H2N C-COOH H O HIC + C=O H3N-C-O CH3- - CH CH2 OH Х 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forwardtheres 2 productsarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forward
- Differentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forwardAn aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
