
Concept explainers
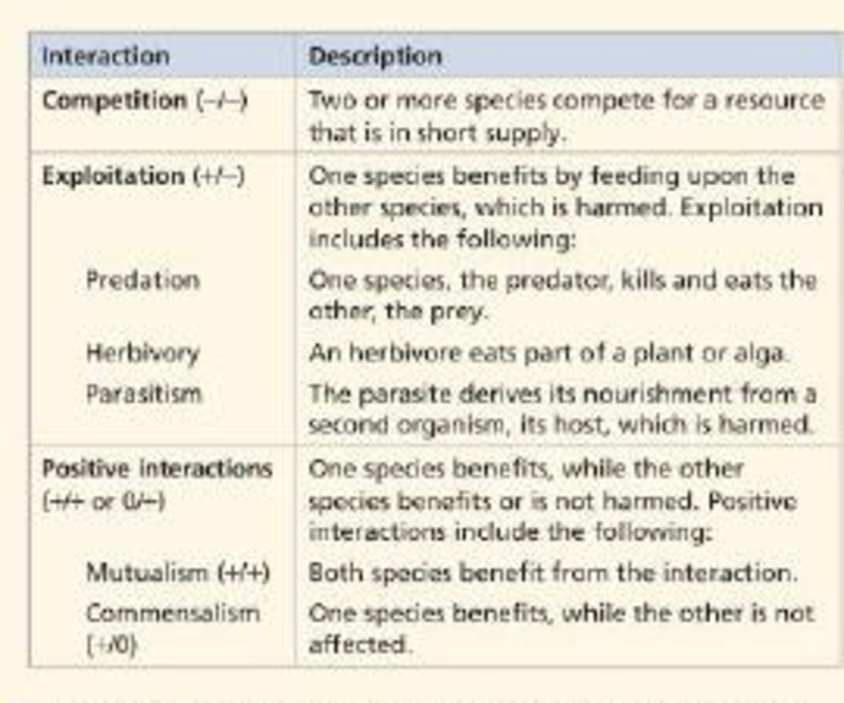
Interspecific interactions affect the survival and reproduction of the species that engage in them. As shown in the table, these interactions can he grouped into three broad categories: competition, exploitation, and positive interactions.
Competitive exclusion states that two species competing for the same
For each interaction listed in the table, give an example of a pair of species that exhibit the interaction.
To provide: Examples of species involved in different types of interspecific interactions.
Concept introduction: Interspecific interactions refer to the relationship that exists between members of different species of a biological community. It includes commensalism, parasitism, herbivory, predation, competition, and others. These interactions can have either positive or negative impact on the survival of species engaged in the interaction.
Given data: Refer to the table in the concept 54.1 “ Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved”, in the textbook.
Explanation of Solution
The interspecific interactions can be classified into three categories, namely, positive interactions, competition and exploitation.
The positive interaction is a type of interaction in which one species are benefitted and the other may or may not get benefits but is never harmed.
The competition is a type of engagement where both the species are affected (harmed) as they share a common resource (short in supply).
In exploitation, one species get benefit while the other is affected negatively (harmed).
The positive interactions include mutualism and commensalism. On the contrary, exploitation involves predation, parasitism and herbivory.
Interactions along with its examples are tabulated as follows:
| Type of interactions | Examples |
| Competition | Lynx and foxes of Alaska (compete for snowshoe hares) |
| Exploitation | |
| Predation | Lion (predator) and antelope (prey) |
| Herbivory | Rice grasshopper (herbivore) and rice plant (act as food) |
| Parasitism | Plasmodium(parasite) and human (host) |
| Positive interactions | |
| Mutualism | Acacia and ant (both benefit each other) |
| Commensalism | Cattle egrets (get a benefit)and African buffalo (not harmed) |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 54 Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





