
Concept explainers
(a)
(a)
Answer to Problem 43E
Probability that the person not aged 18 − 34 and does not own iPhone is approx. 0.5973.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Data summarized in two − way table:
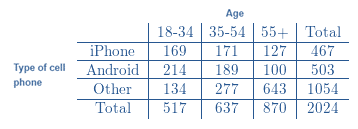
The table consists of data about 2024 adult cell − phone users.
Thus,
The number of possible outcomes is 2024.
Now,
The people not aged 18 − 34 and do not own iPhone are as follows:
Android users (other than aged 18 − 34):
189 adults aged 35 − 54 use Android.
100 adults aged 55+ use Android.
Other cell − phone users (other than aged 18 − 34):
277 adults aged 35 − 54 use other cell − phones.
643 adults aged 55+ use other cell − phones.
When we sum up all the above counts, it becomes 1209.
That means
1209 adults not aged 18 − 34 do not own an iPhone.
Thus,
The number of favorable outcomes is 1209.
If we divide number of favorable outcomes by number of possible outcomes, we get the probability.
Thus,
Probability for the person not aged 18 − 34 and does not own an iPhone is approx. 0.5973
(b)
Probability for the person aged 18 − 34 or owns an iPhone.
(b)
Answer to Problem 43E
Probability that the person aged 18 − 34 or owns an iPhone is approx. 0.4027.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Data summarized in two − way table:
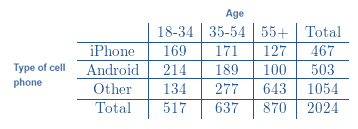
The table consists of data about 2024 adult cell − phone users.
Thus,
The number of possible outcomes is 2024.
Now,
For people aged 18 − 34 or own an iPhone:
Aged18 − 34:
517 of 2024 adults are aged 18 − 34.
iPhone users (other than aged 18 − 34):
171 adults aged 35 − 54 use iPhone.
127 adults aged 55+ use iPhone.
When we sum up all the above counts, it becomes 815.
That means
815 adults aged 18 − 34 or own an iPhone.
Thus,
The number of favorable outcomes is 815.
If we divide number of favorable outcomes by number of possible outcomes, we get the probability.
Thus,
Probability for the person aged 18 − 34 or owns an iPhone is approx. 0.4027.
Chapter 5 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
- Find the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forward
- Show all workarrow_forwardplease find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture belowarrow_forwardA marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





