
Concept explainers
(a)
(a)
Answer to Problem 42E
Probability,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Two − way table represents the
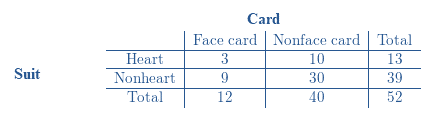
Calculations:
Complement rule:
We know that
H: getting a heart
F: getting a face card
Look at the bottom left corner of the table,
There are total 52 cards in a standard deck.
Thus,
The number of possible outcomes is 52.
Note that
13 of the 52 cards are Heart.
Thus,
The number of favorable outcomes is 13.
If we divide the number of favorable outcomes by the number of possible outcome, we get the probability.
Apply the complement rule:
Thus,
Probability for getting non − hearts is 0.75.
(b)
Probability for getting non − hearts and face card.
(b)
Answer to Problem 42E
Probability,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Two − way table represents the sample space for this chance process:
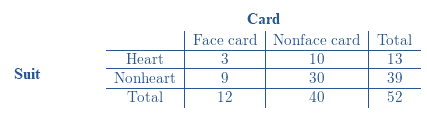
Calculations:
We know that
H: getting a heart
F: getting a face card
Hc: getting a non - heart
Look at the bottom left corner of the table,
There are total 52 cards in a standard deck.
Thus,
The number of possible outcomes is 52.
Note that
9 of the 52 cards are Face cards and non − Heart.
Thus,
The number of favorable outcomes is 9.
If we divide the number of favorable outcomes by the number of possible outcome, we get the probability.
Thus,
Around 17.31% of all cards are non − Heart and Face cards and the probability is approx. 0.1731.
(c)
Probability for getting non − heart or face card.
(c)
Answer to Problem 42E
Probability,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Two − way table represents the sample space for this chance process:
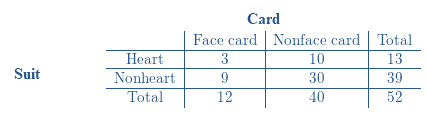
Calculations:
Complement rule:
General
For any two
From Part (a) and Part (b) results,
We have
Probability for getting non − Heart,
Probability for getting non − Heart and Face card,
Now,
Note that
12 of the 52 cards are Face cards.
Thus,
In this case, the number of favorable outcomes is 12 and number of possible outcomes in 52.
Apply general addition rule:
Thus,
Around 80.77% of all cards are non − Heart or Face cards and the probability is approx. 0.8077.
Chapter 5 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Precalculus
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Hi, I need to make sure I have drafted a thorough analysis, so please answer the following questions. Based on the data in the attached image, develop a regression model to forecast the average sales of football magazines for each of the seven home games in the upcoming season (Year 10). That is, you should construct a single regression model and use it to estimate the average demand for the seven home games in Year 10. In addition to the variables provided, you may create new variables based on these variables or based on observations of your analysis. Be sure to provide a thorough analysis of your final model (residual diagnostics) and provide assessments of its accuracy. What insights are available based on your regression model?arrow_forwardI want to make sure that I included all possible variables and observations. There is a considerable amount of data in the images below, but not all of it may be useful for your purposes. Are there variables contained in the file that you would exclude from a forecast model to determine football magazine sales in Year 10? If so, why? Are there particular observations of football magazine sales from previous years that you would exclude from your forecasting model? If so, why?arrow_forwardStat questionsarrow_forward
- 1) and let Xt is stochastic process with WSS and Rxlt t+t) 1) E (X5) = \ 1 2 Show that E (X5 = X 3 = 2 (= = =) Since X is WSSEL 2 3) find E(X5+ X3)² 4) sind E(X5+X2) J=1 ***arrow_forwardProve that 1) | RxX (T) | << = (R₁ " + R$) 2) find Laplalse trans. of Normal dis: 3) Prove thy t /Rx (z) | < | Rx (0)\ 4) show that evary algebra is algebra or not.arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Month Number (Thousands)Dec 1991 65.60Jan 1992 71.60Feb 1992 78.80Mar 1992 111.60Apr 1992 107.60May 1992 115.20Jun 1992 117.80Jul 1992 106.20Aug 1992 109.90Sep 1992 106.00Oct 1992 111.80Nov 1992 84.50Dec 1992 78.60Jan 1993 70.50Feb 1993 74.60Mar 1993 95.50Apr 1993 117.80May 1993 120.90Jun 1993 128.50Jul 1993 115.30Aug 1993 121.80Sep 1993 118.50Oct 1993 123.30Nov 1993 102.30Dec 1993 98.70Jan 1994 76.20Feb 1994 83.50Mar 1994 134.30Apr 1994 137.60May 1994 148.80Jun 1994 136.40Jul 1994 127.80Aug 1994 139.80Sep 1994 130.10Oct 1994 130.60Nov 1994 113.40Dec 1994 98.50Jan 1995 84.50Feb 1995 81.60Mar 1995 103.80Apr 1995 116.90May 1995 130.50Jun 1995 123.40Jul 1995 129.10Aug 1995…arrow_forward
- For each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Year Month Units1 Nov 42,1611 Dec 44,1862 Jan 42,2272 Feb 45,4222 Mar 54,0752 Apr 50,9262 May 53,5722 Jun 54,9202 Jul 54,4492 Aug 56,0792 Sep 52,1772 Oct 50,0872 Nov 48,5132 Dec 49,2783 Jan 48,1343 Feb 54,8873 Mar 61,0643 Apr 53,3503 May 59,4673 Jun 59,3703 Jul 55,0883 Aug 59,3493 Sep 54,4723 Oct 53,164arrow_forwardHigh Cholesterol: A group of eight individuals with high cholesterol levels were given a new drug that was designed to lower cholesterol levels. Cholesterol levels, in milligrams per deciliter, were measured before and after treatment for each individual, with the following results: Individual Before 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 237 282 278 297 243 228 298 269 After 200 208 178 212 174 201 189 185 Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 (a) Construct a 99.9% confidence interval for the mean reduction in cholesterol level. Let a represent the cholesterol level before treatment minus the cholesterol level after. Use tables to find the critical value and round the answers to at least one decimal place.arrow_forwardI worked out the answers for most of this, and provided the answers in the tables that follow. But for the total cost table, I need help working out the values for 10%, 11%, and 12%. A pharmaceutical company produces the drug NasaMist from four chemicals. Today, the company must produce 1000 pounds of the drug. The three active ingredients in NasaMist are A, B, and C. By weight, at least 8% of NasaMist must consist of A, at least 4% of B, and at least 2% of C. The cost per pound of each chemical and the amount of each active ingredient in one pound of each chemical are given in the data at the bottom. It is necessary that at least 100 pounds of chemical 2 and at least 450 pounds of chemical 3 be used. a. Determine the cheapest way of producing today’s batch of NasaMist. If needed, round your answers to one decimal digit. Production plan Weight (lbs) Chemical 1 257.1 Chemical 2 100 Chemical 3 450 Chemical 4 192.9 b. Use SolverTable to see how much the percentage of…arrow_forward
- At the beginning of year 1, you have $10,000. Investments A and B are available; their cash flows per dollars invested are shown in the table below. Assume that any money not invested in A or B earns interest at an annual rate of 2%. a. What is the maximized amount of cash on hand at the beginning of year 4.$ ___________ A B Time 0 -$1.00 $0.00 Time 1 $0.20 -$1.00 Time 2 $1.50 $0.00 Time 3 $0.00 $1.90arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Year Month Rate (%)2009 Mar 8.72009 Apr 9.02009 May 9.42009 Jun 9.52009 Jul 9.52009 Aug 9.62009 Sep 9.82009 Oct 10.02009 Nov 9.92009 Dec 9.92010 Jan 9.82010 Feb 9.82010 Mar 9.92010 Apr 9.92010 May 9.62010 Jun 9.42010 Jul 9.52010 Aug 9.52010 Sep 9.52010 Oct 9.52010 Nov 9.82010 Dec 9.32011 Jan 9.12011 Feb 9.02011 Mar 8.92011 Apr 9.02011 May 9.02011 Jun 9.12011 Jul 9.02011 Aug 9.02011 Sep 9.02011 Oct 8.92011 Nov 8.62011 Dec 8.52012 Jan 8.32012 Feb 8.32012 Mar 8.22012 Apr 8.12012 May 8.22012 Jun 8.22012 Jul 8.22012 Aug 8.12012 Sep 7.82012 Oct…arrow_forwardFor each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Date IBM9/7/2010 $125.959/8/2010 $126.089/9/2010 $126.369/10/2010 $127.999/13/2010 $129.619/14/2010 $128.859/15/2010 $129.439/16/2010 $129.679/17/2010 $130.199/20/2010 $131.79 a. Construct a line chart of the closing stock prices data. Choose the correct chart below.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





