
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305401969
Author: SERWAY, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 93AP
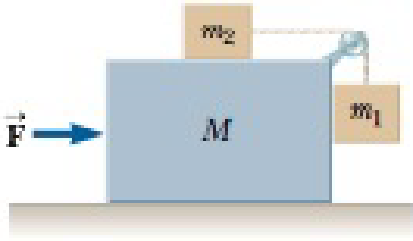
What horizontal force must be applied to a large block of mass M shown in Figure P5.49 so that the tan blocks remain stationary relative to M? Assume all surfaces and the pulley are frictionless. Notice that the force exerted by the string accelerates m2.
Figure P5.49 Problems 49 and 53
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
23.
What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 X 103 V/m and 7.5 X 10-3 T. respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off?
10.
A light bulb emits 25.00 W of power as visible light. What are the average electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 2.0 m?
9.
Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .15 seconds.
Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
Ch. 5.2 - Which of the following statements is correct? (a)...Ch. 5.4 - An object experiences no acceleration. Which of...Ch. 5.4 - You push an object, initially at rest, across a...Ch. 5.5 - Suppose you are talking by interplanetary...Ch. 5.6 - (i) If a fly collides with the windshield of a...Ch. 5.8 - You press your physics textbook flat against a...Ch. 5.8 - Prob. 5.7QQCh. 5 - The driver of a speeding empty truck slams on the...Ch. 5 - In Figure OQ5.2, a locomotive has broken through...Ch. 5 - Prob. 3OQ
Ch. 5 - Prob. 4OQCh. 5 - Prob. 5OQCh. 5 - The manager of a department store is pushing...Ch. 5 - Two objects are connected by a string that passes...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8OQCh. 5 - A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a...Ch. 5 - A large crate of mass m is place on the flatbed of...Ch. 5 - If an object is in equilibrium, which of the...Ch. 5 - A crate remains stationary after it has been...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m moves with acceleration a down...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1CQCh. 5 - Your hands are wet, and the restroom towel...Ch. 5 - In the motion picture It Happened One Night...Ch. 5 - If a car is traveling due westward with a constant...Ch. 5 - A passenger sitting in the rear of a bus claims...Ch. 5 - A child tosses a ball straight up. She says that...Ch. 5 - A person holds a ball in her hand. (a) Identify...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8CQCh. 5 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5 - Twenty people participate in a tug-of-war. The two...Ch. 5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 5 - Prob. 12CQCh. 5 - A weightlifter stands on a bathroom scale. He...Ch. 5 - Prob. 14CQCh. 5 - Suppose you are driving a classic car. Why should...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16CQCh. 5 - Describe two examples in which the force of...Ch. 5 - The mayor of a city reprimands some city employees...Ch. 5 - Give reasons for the answers to each of the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 20CQCh. 5 - Identify actionreaction pairs in the following...Ch. 5 - Prob. 22CQCh. 5 - Prob. 23CQCh. 5 - A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align...Ch. 5 - If a man weighs 900 N on the Earth, what would he...Ch. 5 - A 3.00-kg object undergoes an acceleration given...Ch. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - The average speed of a nitrogen molecule in air is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 7PCh. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - Review. The gravitational force exerted on a...Ch. 5 - Review. The gravitational force exerted on a...Ch. 5 - Review. An electron of mass 9. 11 1031 kg has an...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12PCh. 5 - One or more external forces, large enough to be...Ch. 5 - A brick of mass M has been placed on a rubber...Ch. 5 - Two forces, F1=(6.00i4.00j)N and...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5 - Prob. 17PCh. 5 - Prob. 18PCh. 5 - Prob. 19PCh. 5 - You stand on the seat of a chair and then hop off....Ch. 5 - Prob. 21PCh. 5 - Review. Three forces acting on an object are given...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Review. Figure P5.15 shows a worker poling a boata...Ch. 5 - An iron bolt of mass 65.0 g hangs from a string...Ch. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - The systems shown in Figure P5.28 are in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 29PCh. 5 - A block slides down a frictionless plane having an...Ch. 5 - The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0...Ch. 5 - A 3.00-kg object is moving in a plane, with its x...Ch. 5 - A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in...Ch. 5 - A bag of cement whose weight is Fg hangs in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - Prob. 36PCh. 5 - An object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have...Ch. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - An object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 41PCh. 5 - Two objects are connected by a light string that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43PCh. 5 - Prob. 44PCh. 5 - In the system shown in Figure P5.23, a horizontal...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m1 hangs from a string that...Ch. 5 - A block is given an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s...Ch. 5 - A car is stuck in the mud. A tow truck pulls on...Ch. 5 - Prob. 49PCh. 5 - Prob. 50PCh. 5 - In Example 5.8, we investigated the apparent...Ch. 5 - Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such...Ch. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - Prob. 54PCh. 5 - A 25.0-kg block is initially at rest on a...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impassible? Your...Ch. 5 - Prob. 57PCh. 5 - Before 1960m people believed that the maximum...Ch. 5 - Prob. 59PCh. 5 - A woman at an airport is towing her 20.0-kg...Ch. 5 - Review. A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the...Ch. 5 - The person in Figure P5.30 weighs 170 lb. As seen...Ch. 5 - A 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light,...Ch. 5 - Three objects are connected on a table as shown in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 65PCh. 5 - A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 67PCh. 5 - Prob. 68PCh. 5 - Prob. 69PCh. 5 - A 5.00-kg block is placed on top of a 10.0-kg...Ch. 5 - Prob. 71PCh. 5 - A black aluminum glider floats on a film of air...Ch. 5 - Prob. 73APCh. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A book...Ch. 5 - Prob. 75APCh. 5 - A 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 77APCh. 5 - Prob. 78APCh. 5 - Two blocks of masses m1 and m2, are placed on a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 80APCh. 5 - An inventive child named Nick wants to reach an...Ch. 5 - Prob. 82APCh. 5 - Prob. 83APCh. 5 - An aluminum block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 85APCh. 5 - Prob. 86APCh. 5 - Prob. 87APCh. 5 - Prob. 88APCh. 5 - A crate of weight Fg is pushed by a force P on a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 90APCh. 5 - A flat cushion of mass m is released from rest at...Ch. 5 - In Figure P5.46, the pulleys and pulleys the cord...Ch. 5 - What horizontal force must be applied to a large...Ch. 5 - Prob. 94APCh. 5 - A car accelerates down a hill (Fig. P5.95), going...Ch. 5 - Prob. 96CPCh. 5 - Prob. 97CPCh. 5 - Initially, the system of objects shown in Figure...Ch. 5 - A block of mass 2.20 kg is accelerated across a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 100CPCh. 5 - Prob. 101CPCh. 5 - In Figure P5.55, the incline has mass M and is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 103CPCh. 5 - Prob. 104CP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Rub your hands together vigorously. What happens? Discuss the energy transfers and transformations that take...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
The active ingredient in Tylenol and a host of other over-the-counter pain relievers is acetaminophen (C8H9NO2)...
Chemistry: Atoms First
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
11. In the early 1800s, French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggested that the best explanation for the rel...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the movie Fast X, a 10100 kg round bomb is set rolling in Rome. The bomb gets up to 17.6 m/s. To try to stop the bomb, the protagonist Dom swings the counterweight of a crane, which has a mass of 354000 kg into the bomb at 3.61 m/s in the opposite direction. Directly after the collision the crane counterweight continues in the same direction it was going at 2.13 m/s. What is the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the bomb right after the collision?arrow_forwardDon't use aiarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scalearrow_forwardUltimate Byleth and Little Mac fight. Little Mac, who is a boxer, dashes forward at 26.6 m/s, fist first. Byleth moves in the opposite direction at 3.79 m/s, where they collide with Little Mac’s fist. After the punch Byleth flies backwards at 11.1 m/s. How fast, and in what direction, is Little Mac now moving? Little Mac has a mass of 48.5 kg and Byleth has a mass of 72.0 kg.arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch with scale as wellarrow_forward
- Make sure to draw a sketch with scale pleasearrow_forwardKirby jumps towards his enemy/ally, Meta Knight, at 2.06 m/s while Meta Knight glides in the opposite direction (toward Kirby) at 5.06 m/s. Kirby then begins to inhale, swallowing Meta Knight. What is Kirby/Meta Knight’s velocity immediately after being swallowed? Please put the magnitude of the velocity and then mark direction using dropdown menu. Kirby has a mass of 0.283 kg and Meta Knight has a mass of 0.538 kg.arrow_forwardNo Aiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY