
(a)
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(a)
Answer to Problem 41P
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
Explanation of Solution
The slope of the speed versus time graph gives the magnitude of the acceleration. Consider positive slope of speed versus time graph as positive acceleration and negative slope of speed versus time graph gives negative acceleration. When the slope is zero the acceleration is zero.
According to Newton’s second law,
Here,
Rewrite the above equation in terms of
Write the expression to calculate the acceleration.
Here,
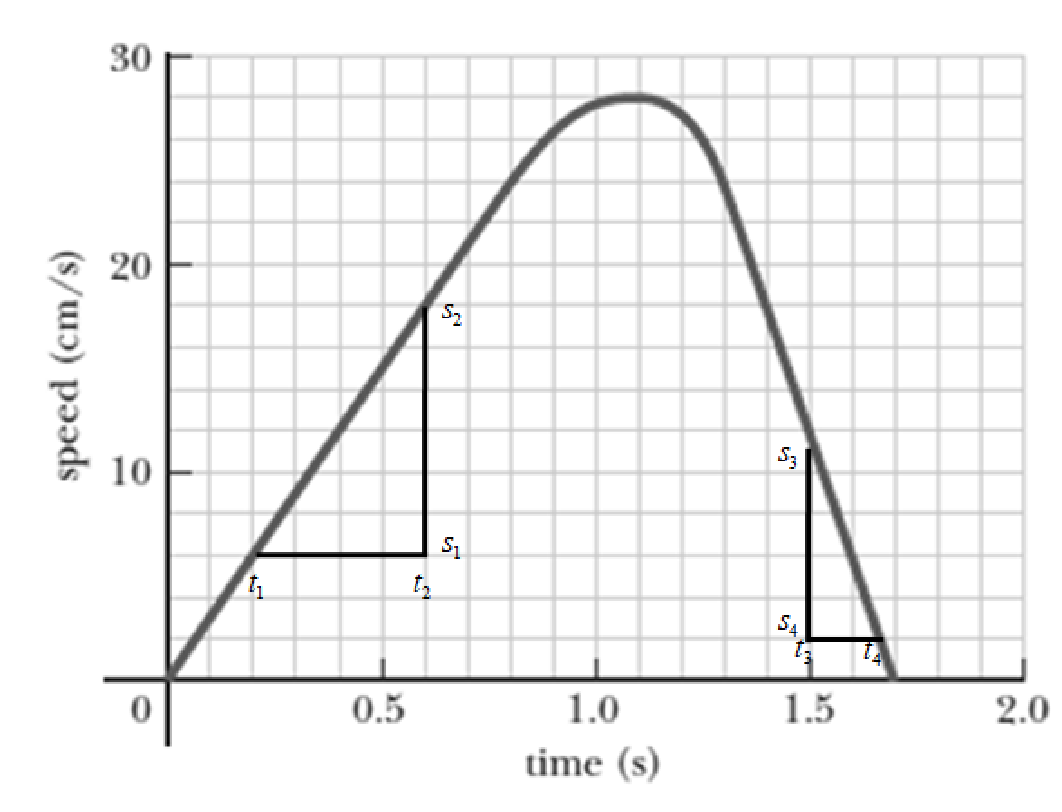
From the graph the slope at time
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(b)
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(b)
Answer to Problem 41P
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
Explanation of Solution
The slope of the speed versus time graph gives the magnitude of the acceleration. The slope of the graph at 0.5 s is same as that of 0 s. That is the graph is a straight line at these moment. If the graph is a straight line, the acceleration is same.
The mass of the person does not change and the acceleration is same as that at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(c)
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(c)
Answer to Problem 41P
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
Explanation of Solution
The graph below is the speed versus time graph
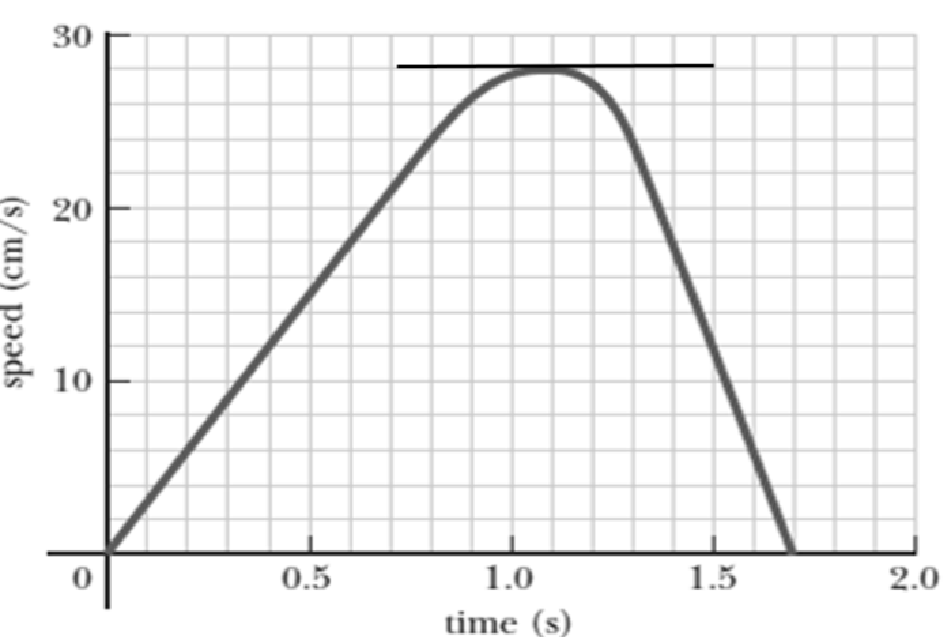
From the graph it is evident that at
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(d)
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
(d)
Answer to Problem 41P
The force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
Explanation of Solution
The graph below is the speed versus time graph.
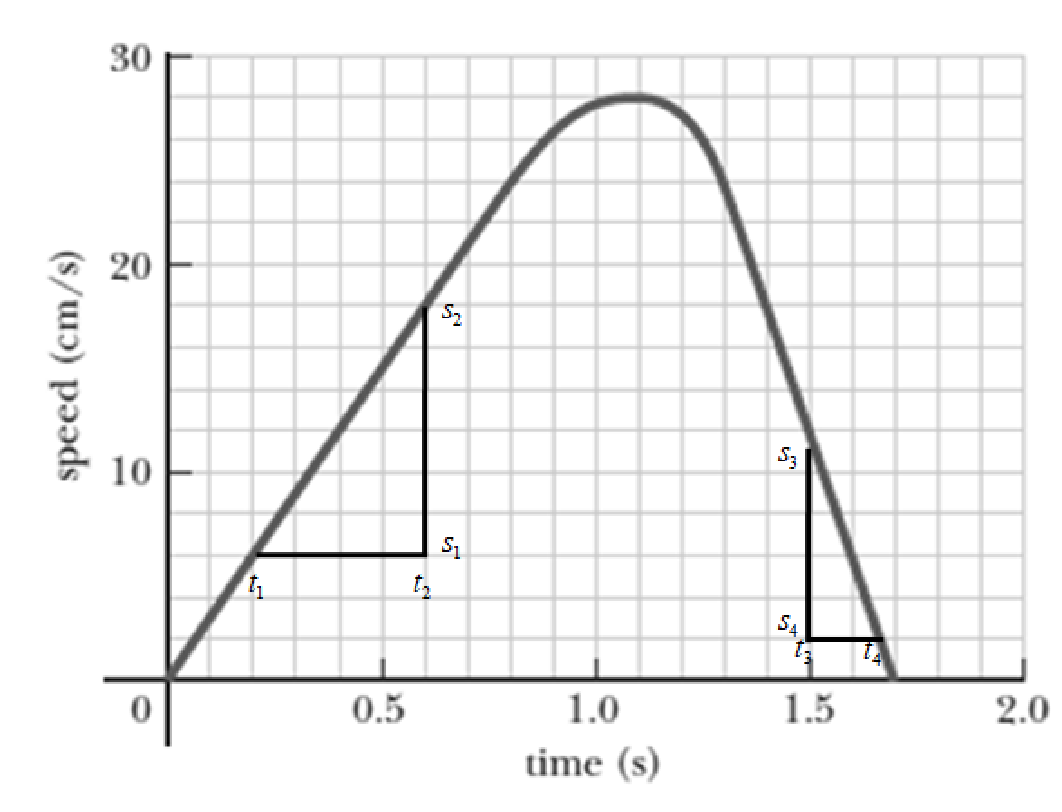
From the graph the slope at time
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the force exerted by the chin-up bar on the person’s body at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
- How can I remember this Formula: p = m × v where m is in kg and v in Meter per second in the best way?arrow_forwardHow can I remember the Formula for the impulsearrow_forwardA Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hollow, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius ra and a coaxial cylindrical wire (the anode) of radius г (see figure below) with a gas filling the space between the electrodes. Assume that the internal diameter of a Geiger-Mueller tube is 3.00 cm and that the wire along the axis has a diameter of 0.190 mm. The dielectric strength of the gas between the central wire and the cylinder is 1.15 × 106 V/m. Use the equation 2πrlE = 9in to calculate the maximum potential difference that can be applied between the wire and the cylinder before breakdown occurs in the gas. V Anode Cathodearrow_forward
- 3.77 is not the correct answer!arrow_forwardA I squar frame has sides that measure 2.45m when it is at rest. What is the area of the frame when it moves parellel to one of its diagonal with a m² speed of 0.86.c as indicated in the figure? >V.arrow_forwardAn astronent travels to a distant star with a speed of 0.44C relative to Earth. From the austronaut's point of view, the star is 420 ly from Earth. On the return trip, the astronent travels speed of 0.76c relative to Earth. What is the distance covered on the return trip, as measured by the astronant? your answer in light-years. with a Give ly.arrow_forward
- star by spaceship Sixus is about 9.00 ly from Earth. To preach the star in 15.04 (ship time), how fast must you travel? C.arrow_forwardIf light-bulb A is unscrewed, how will the brightness of bulbs B and C change, if at all? How does the current drawn by from the battery change?arrow_forwardCan someone help mearrow_forward
- Can someone help me with this thank youarrow_forward(a) For a spherical capacitor with inner radius a and outer radius b, we have the following for the capacitance. ab C = k₂(b- a) 0.0695 m 0.145 m (8.99 × 10º N · m²/c²)( [0.145 m- 0.0695 m × 10-11 F = PF IIarrow_forwardA pendulum bob A (0.5 kg) is given an initialspeed of vA = 4 m/s when the chord ishorizontal. It then hits a stationary block B (1kg) which then slides to a maximum distanced before it stops. Determine the value of d.The coefficient of static friction between theblock and the plane is μk = 0.2. The coefficientof restitution between A and B is e = 0.8.Ans: d=1.0034 marrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





