
Concept explainers
(a)
The mass M in terms of m, g , and
(a)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The mass M in terms of m, g , and
Explanation of Solution
The system is in equilibrium, so force on either sides of the pulley must be the same.
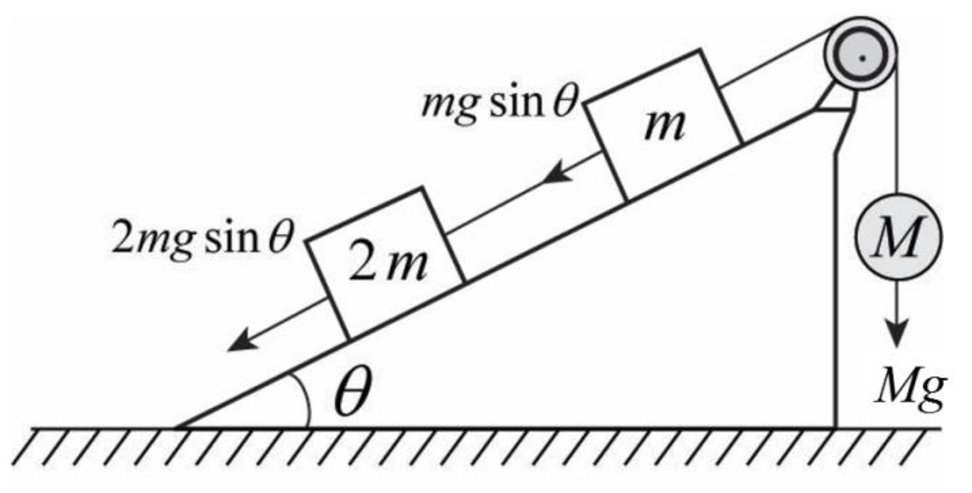
Write the expression for the equilibrium.
Here,
Conclusion:
Simplify the above equation.
Therefore, the mass M in terms of m, g, and
(b)
The tension
(b)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The tension
Explanation of Solution
Below figure shows the forces and tension acting on the string.
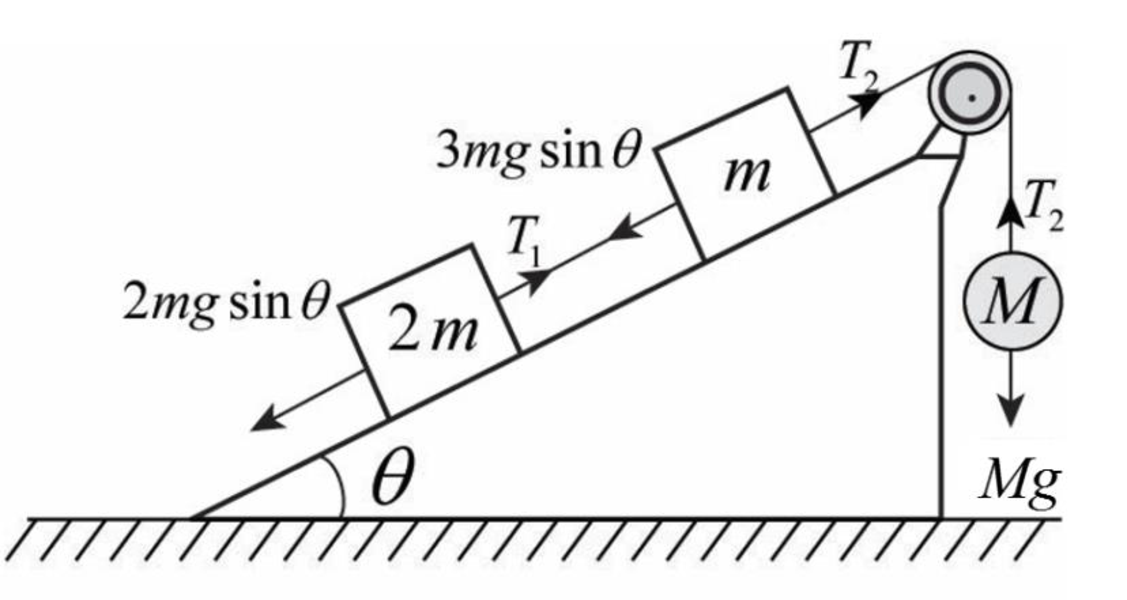
From the figure,
From the figure,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension
(c)
The acceleration of each object
(c)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The acceleration of each object is
Explanation of Solution
Below figure shows the forces and tension acting on the string.
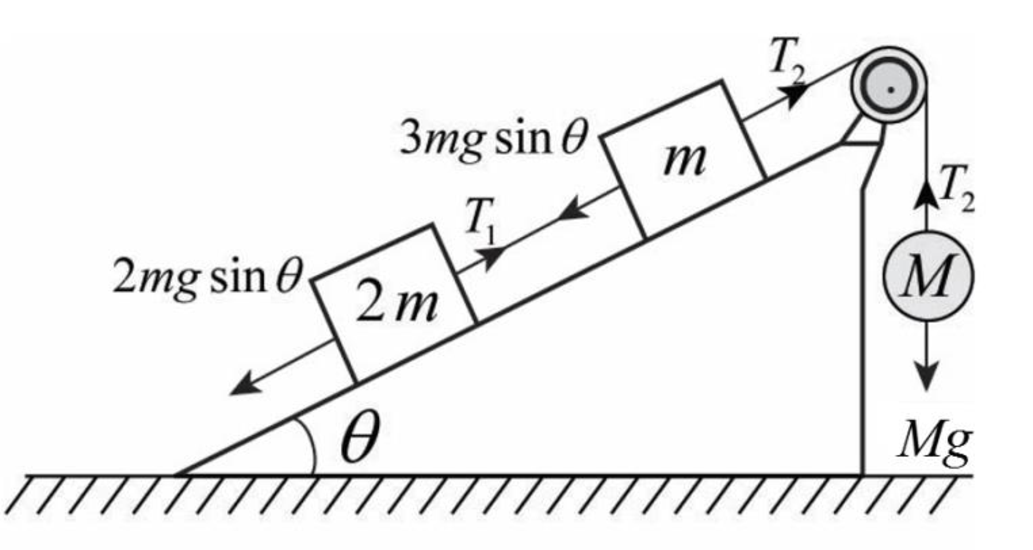
Use Newton’s second law to write the expression for tension
Use Newton’s second law to write the expression for tension
Substitute
Use Newton’s second law to write the expression for tension
Conclusion:
Substitute equation (I) and (II) in (III) and simplify.
All the objects are connected to a single string and hence they have same acceleration.
Therefore, the acceleration of each object is
(d)
The tension
(d)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The tension
Explanation of Solution
Rewrite (I).
Rewrite (II).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the tension
(e)
The maximum value of
(e)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The maximum value of
Explanation of Solution
Below figure shows the forces acting on the system (including frictional force).
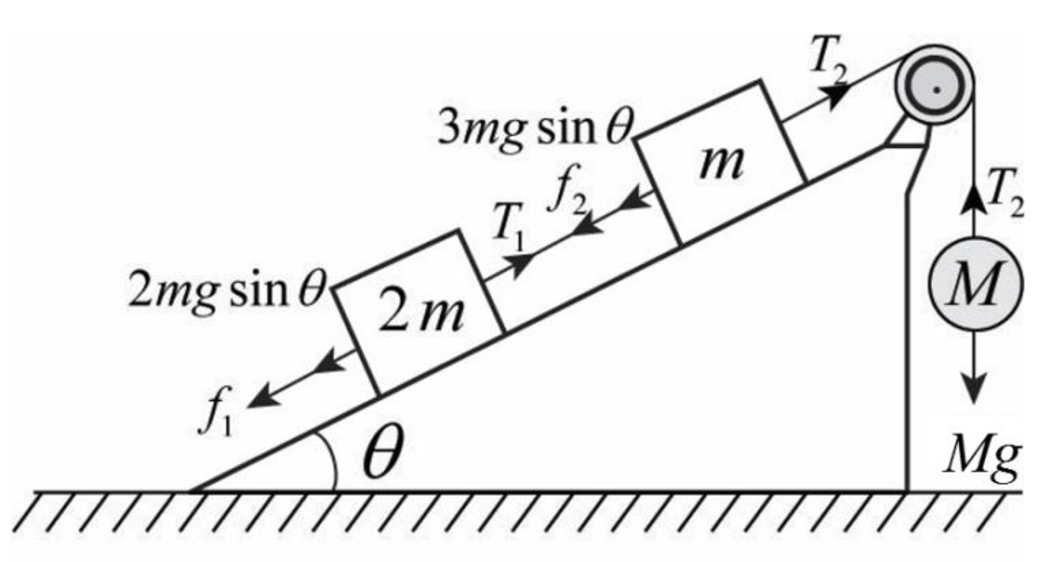
From the figure
Write the expression for friction force acting on
Here,
Write the expression for friction force acting on
Write the expression for tension
The system is in equilibrium,
Substitute 0 for
Similarly, Write the expression for tension
Substitute 0 for
Write the expression for
Substitute 0 for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Equate (V) and (VII).
Therefore, the maximum value of
(f)
The minimum value of
(f)
Answer to Problem 88AP
The minimum value of
Explanation of Solution
For minimum value of
Below figure shows the forces acting on the system (including frictional force).
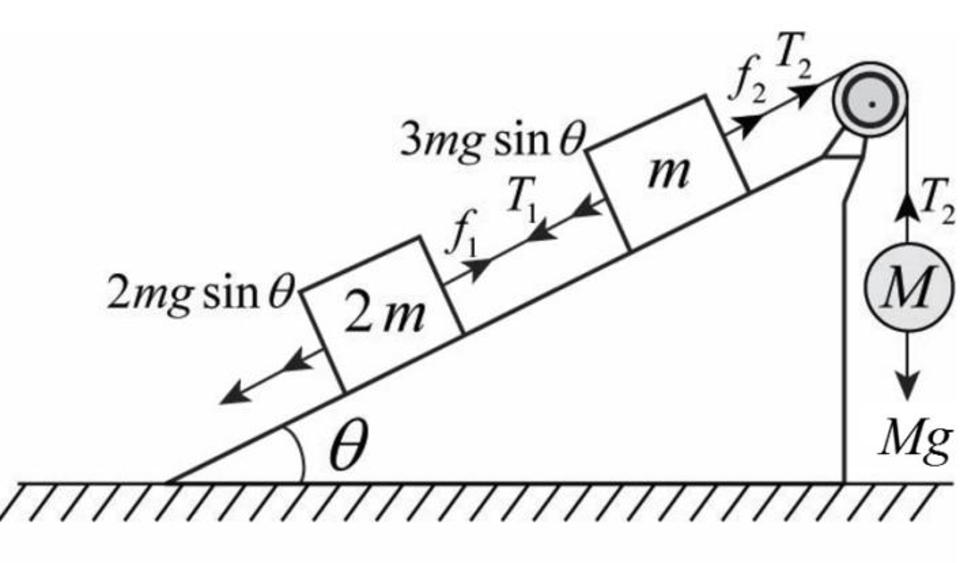
Therefore,
Conclusion:
Equate both the above expression for
Therefore, the minimum value of
(g)
Comparison the values of
(g)
Answer to Problem 88AP
Comparison the values of
Explanation of Solution
Compare (IX) and (VIII).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the Comparison of the values of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





