
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The tank with the highest total pressure needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
According to the
When at two different conditions gases are placed, then to determine the changed variable combined gas law is used. Below is the formula of combined gas law:
Here
- P1 and P2 are the pressure of gases
- V1 and V2 and volume of gases
- n1 and n2 number of moles
- T1 and T2 are the temperature of gases
Moles are known as the ratio of mass and molar mass. Below is the formula:
Here, MM is molar mass and m is the mass.
The kinetic model of gases is accounted for ideal gas behavior. The formula of average translational energy of gas is as below:
Here,
Et = average translational energy of gas
T = temperature in Kelvin
R = Universal gas constant
NA =
Effusion is known as the leakage of gas molecules from high to low pressure region via a pinhole. For any two gas molecules the formula to determine the time needed for effusion is as below:
Here u1 and u2 is the rate of effusion for gas1 and gas 2. MM1 and MM2 is the molar mass for gas1 and gas 2.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
Tank Y
Explanation of Solution
The given tanks are as follows:
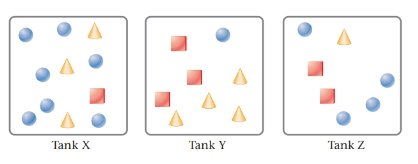
Here, circles represent
The highest total pressure is in the tank Y. Because, tank Y has the maximum amount of gases mixture.
(b)
Interpretation:
The tank containing highest SO2 pressure needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
According to the ideal
When at two different conditions gases are placed, then to determine the changed variable combined gas law is used. Below is the formula of combined gas law:
Here
- P1 and P2 are the pressure of gases
- V1 and V2 and volume of gases
- n1 and n2 number of moles
- T1 and T2 are the temperature of gases
Moles are known as the ratio of mass and molar mass. Below is the formula:
Here, MM is molar mass and m is the mass.
The kinetic model of gases is accounted for ideal gas behavior. The formula of average translational energy of gas is as below:
Here,
Et = average translational energy of gas
T = temperature in Kelvin
R = Universal gas constant
NA = Avogadro number
Effusion is known as the leakage of gas molecules from high to low pressure region via a pinhole. For any two gas molecules the formula to determine the time needed for effusion is as below:
Here, u1 and u2 is the rate of effusion for gas1 and gas 2. MM1 and MM2 is the molar mass for gas1 and gas 2.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
Tank Y
Explanation of Solution
The given tanks are as follows:
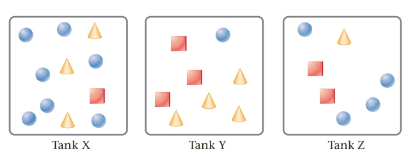
Here, circles represent
Tank Y contains highest partial pressure of SO2 . This is because, Tank Y has the maximum moles of SO2 due to which it will have the maximum partial pressure.
(c)
Interpretation:
The tank with same mass of all the three gases needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
According to the ideal gas law volume i.e. V, pressure i.e. P, number of moles i.e. m, temperature i.e. t and universal gas constant i.e. R are interrelated as below:
When at two different conditions gases are placed, then to determine the changed variable combined gas law is used. Below is the formula of combined gas law:
Here
- P1 and P2 are the pressure of gases
- V1 and V2 and volume of gases
- n1 and n2 number of moles
- T1 and T2 are the temperature of gases
Moles are known as the ratio of mass and molar mass. Below is the formula:
Here, MM is molar mass and m is the mass.
The kinetic model of gases is accounted for ideal gas behavior. The formula of average translational energy of gas is as below:
Here,
Et = average translational energy of gas
T = temperature in Kelvin
R = Universal gas constant
NA = Avogadro number
Effusion is known as the leakage of gas molecules from high to low pressure region via a pinhole. For any two gas molecules the formula to determine the time needed for effusion is as below:
Here, u1 and u2 is the rate of effusion for gas1 and gas 2. MM1 and MM2 is the molar mass for gas1 and gas 2.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
Tank Z
Explanation of Solution
The given tanks are as follows:
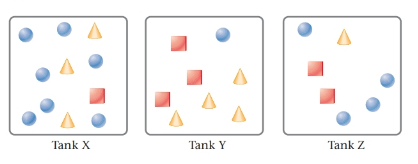
Here, circles represent
Tank Z contain the mass of all three gases same.
(d)
Interpretation:
The tank with the heaviest content needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
According to the ideal gas law volume i.e. V, pressure i.e. P, number of moles i.e. m, temperature i.e. t and universal gas constant i.e. R are interrelated as below:
When at two different conditions gases are placed, then to determine the changed variable combined gas law is used. Below is the formula of combined gas law:
Here
- P1 and P2 are the pressure of gases
- V1 and V2 and volume of gases
- n1 and n2 number of moles
- T1 and T2 are the temperature of gases
Moles are known as the ratio of mass and molar mass. Below is the formula:
Here, MM is molar mass and m is the mass.
The kinetic model of gases is accounted for ideal gas behavior. The formula of average translational energy of gas is as below:
Here,
Et = average translational energy of gas
T = temperature in Kelvin
R = Universal gas constant
NA = Avogadro number
Effusion is known as the leakage of gas molecules from high to low pressure region via a pinhole. For any two gas molecules the formula to determine the time needed for effusion is as below:
Here u1 and u2 is the rate of effusion for gas1 and gas 2. MM1 and MM2 is the molar mass for gas1 and gas 2.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
Tank Y
Explanation of Solution
The given tanks are as follows:
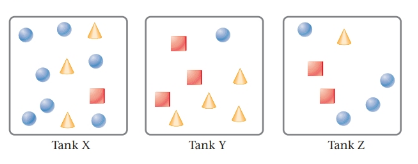
Here, circles represent
Tank Y contains the heaviest content. This is due to the number of moles of SO2 is highest in tank Y.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- Draw the two possible products produced in this E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the major products of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, wehre applicable. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Drawing Arrows THE Problem 33 of 35 N. C:0 Na + Submit Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the major producrs of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the sereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers where appllicable.arrow_forward
- 5) Oxaloacetic Acid is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of citric acid. Synthesize oxaloacetic acid using a mixed Claisen Condensation reaction with two different esters and a sodium ethoxide base. Give your answer as a scheme Hint 1: Your final acid product is producing using a decarboxylation reaction. Hint 2: Look up the structure of oxalic acid. HO all OH oxaloacetic acidarrow_forward20. The Brusselator. This hypothetical system was first proposed by a group work- ing in Brussels [see Prigogine and Lefever (1968)] in connection with spatially nonuniform chemical patterns. Because certain steps involve trimolecular reac tions, it is not a model of any real chemical system but rather a prototype that has been studied extensively. The reaction steps are A-X. B+X-Y+D. 2X+ Y-3X, X-E. 305 It is assumed that concentrations of A, B, D, and E are kept artificially con stant so that only X and Y vary with time. (a) Show that if all rate constants are chosen appropriately, the equations de scribing a Brusselator are: dt A-(B+ 1)x + x²y, dy =Bx-x²y. diarrow_forwardProblem 3. Provide a mechanism for the following transformation: H₂SO A Me. Me Me Me Mearrow_forward
- You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: xi 1. ☑ 2. H₂O хе i Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. There is no reagent that will make this synthesis work without complications. : ☐ S ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





