
a.
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction: The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom which is unique for every element.
a.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
49
Explanation of Solution
For a neutral atom, the number of protons is always equal to the number of electrons. The number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom are fix for every element that is they are unique for every element and are said to be the atomic number of that element.
Since, the number of protons present in In is 49 so, the atomic number of In is 49.
b.
Interpretation:
The number of electrons in an atom of In should be determined.
Concept Introduction: The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom which is unique for every element.
b.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
49
Explanation of Solution
For a neutral atom, the number of protons is always equal to the number of electrons. The number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom are fix for every element that is they are unique for every element and are said to be the atomic number of that element.
Since, the number of protons present in In is 49 so, the number of electrons present in In is 49.
c.
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration and abbreviated electron configuration of In should be determined.
Concept Introduction: The protons and neutrons of an atom are present in the nucleus of an atom whereas the electrons are always moving around the nucleus of an atom that is they possess kinetic energy. The lowest possible energy level of an electron in an atom is its ground state.
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
c.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
The electronic configuration of In is:
The abbreviated electron configuration of In is:
Explanation of Solution
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the subshell. The specific region of space in which the movement of electrons is confined is said to be shells which are divided into subshells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these subshells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these subshells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, subshell is:
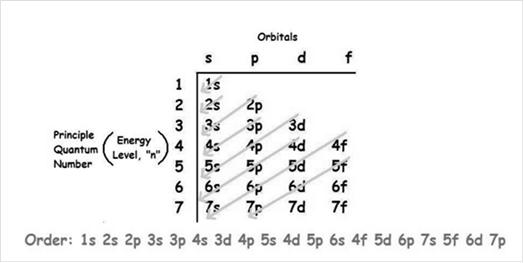
Since, the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom. So,
Number of electrons in In is 49. So, the electronic configuration of In is:
The abbreviated electron configuration of In is:
d.
Interpretation:
The group number and the Lewis symbol for In should be determined.
Concept Introduction: Structural
d.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
The group number for In is 3A (13)
Lewis symbol for In is:
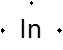
Explanation of Solution
Since, the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom. So,
Number of electrons in In is 49. So, the electronic configuration of In is:
From the electronic configuration, the number of valence electrons of In is 3. So, the Lewis dot structure will be:
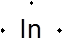
Since, the outer most orbital in which electron is present is p-orbital so, the group number will be:
Number of valence electron + 10
3 + 10 = 13
So, the group number for In is 3A (13).
e.
Interpretation:
The larger atom among indium and iodine should be determined.
Concept Introduction: The distance from the center of the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron is said to be the atomic radius of an atom.
e.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
Indium is the larger atom.
Explanation of Solution
The given atoms belong to the same period that is period 5. Within a period, the outer electrons are in the same valence shell thus on moving from left to right in a period the number of protons increases in the nucleus of the atom resulting in increase in the effective nuclear charge due to decrease in shielding due to which the last shell gets pulled closer, that is atomic size of the atom decreases.
Since,
f.
Interpretation:
The atom having largest ionization energy among indium and iodine should be determined.
Concept Introduction: The energy which is required to remove an electron from the gaseous state of an atom or ion is said to be the ionization energy.
f.
Answer to Problem 5.77FU
Iodine will have largest ionization energy.
Explanation of Solution
The given atoms belong to the same period that is period 5. Within a period, the outer electrons are in the same valence shell thus on moving from left to right in a period the number of protons increases in the nucleus of the atom resulting in increase in the effective nuclear charge due to decrease in shielding due to which the last shell gets pulled closer, that is atomic size of the atom decreases thus, making it harder to remove an electron from an atom so, on moving across the period, the ionization energy increases.
Since,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Basic Chemistry (5th Edition)
- 2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forward
- Instructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forwardC. NaOMe, Br Brarrow_forward
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





