
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.46SP
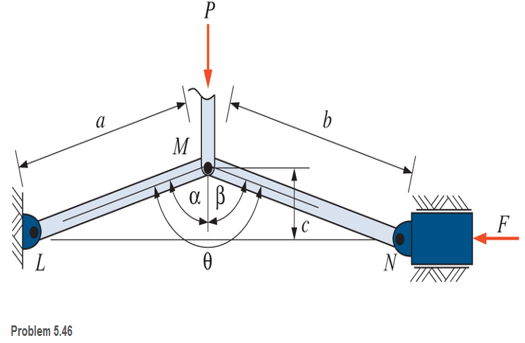
A toggle joint is a
P = 10 lb, a = 2 ft, b = 5 ft, and
c = 1 ft, as shown. Find force F. Neglect friction and the weights of the members.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:21
Students have asked these similar questions
1. The cylinder of weight, W (see the table of values), shown below is being hoisted up with the force
F against the vertical wall. If u, = 0.57
W
W = 500 kn
a. Determine the reaction force (resultant of normal force and frictional force) against the
vertical wall.
b. Calculate the force, F, needed to set the cylindrical roller in motion.
30 in.
40 in.
A
F
25 in.
45 in.
35 in.
Show Transcribed Text
60°
A thin U-shaped member is kept in equilibrium in the vertical plane by up to three fingers and the cord (gravity acts
downward). The weight of the member is uniformly distributed with 0.1 lb/in. So the total weight is 17.5 lb. Neglect the
thickness of the member and any friction between the fingers and the member. Assume the finger force at G is zero.
Determine the cord force and the other finger forces.
As shown, a roller of weight W and diameter R is pushed to the left over a tile of thickness 6. Consider
the forces acting on the roller when it is in a momentary state of mechanical equilibrium as it rolls over
the sharp corner of the tile.
Ө
1
P
a Sketch a free body diagram of the roller at this instant of momentary equilibrium
b Sketch the closed force vector triangle representing the equilibrium condition of this problem. Note
that the vectors drawn in the figure below are not necessarily to scale.
c Express each interior angle of the closed force triangle in terms of a and and clearly label each
force vector in the diagram and each interior angle of the force triangle.
d Establish a relation between a, 6, and r.
e Invoke static equilibrium and apply the law of sines to derive an expression for the force P expressed
in terms of W, r, 6, and 0.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 5 - through 5.7 Calculate the forces in all members of...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, DH, and HI for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, BE, and FE for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, CH, and CG in...
Ch. 5 - For the Howe roof truss shown, determine the...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members DE, CE, and BC in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in members BC, BG, and FG for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, BD, BE, and CB...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected A-frame supports a load, as shown....Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - A bracket is pin connected at points A, B, and D...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected frame is loaded, as shown....Ch. 5 - The cylinder shown has a mass of 500 kg. Determine...Ch. 5 - A simple frame is pin connected at points A, B,...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - through 5.31 Calculate the forces in all members...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38, Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38 , Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected crane framework is loaded and...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at pins A, B, and D in...Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - The wall bracket shown is pin-connected at points...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - The A-frame shown is pin-connected at A,B,C, and...Ch. 5 - The tongs shown are used to grip an object. For an...Ch. 5 - A toggle joint is a mechanism by which a...Ch. 5 - In the toggle joint of Problem 5.46 , assume that...Ch. 5 -
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
41. The largest hailstone is the United States was 44.5 centimeters [cm] in circumference in Coffeyville, Kansa...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
Determine the force in each of the cables AB and AC as a function of . If the maximum tension allowed in each c...
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Another term for an enlargement is a diffuser. A diffuser is used to convert kinetic energy (v2/2g) to pressure...
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
1.1 What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? A molecule and a crystal?
Manufacturing Engineering & Technology
In each case, the beam is subjected to the loadings shown. Draw the free-body diagram of the beam, and sketch t...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure shows a steel bar being processed by a rolling mill. Given that P=80kN and r =0.016, determine the force F required to advance the bar at a constant speed.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a three-pin arch. Determine the horizontal component of the pin reaction at A caused by the applied force P.arrow_forwardThe block of weight W is pulled by the force P inclined at the angle to the horizontal. Find the smallest force P and the corresponding angle that would cause impending sliding of the block. The angle of static friction between the block and the ground is s.arrow_forward
- Find the force P required to (a) push; and (b) pull the 80-lb homogeneous roller over the 3-in. curb.arrow_forwardDraw the FBD of the entire frame, assuming that friction and the weights of the members are negligible. How many unknowns appear on this FBD?arrow_forwardIn Sample Problem 5.4, determine the tension TAC using the equation MDB=0.arrow_forward
- In Sample Problem 5.5, compute the tension TAD using one scalar equilibrium equation.arrow_forwardThe bar ABC is supported by three identical, ideal springs. Note that the springs are always vertical because the collars to which they are attached are free to slide on the horizontal rail. Find the angle at equilibrium if W = kL. Neglect the weight of the bar.arrow_forwardThe coeffient of static friction between the uniform bar AB of weight W and the ground is 0.45. Find the smallest angle and the corresponding force P that would initiate simultaneous tipping and sliding of the bar.arrow_forward
- Compute the tension TAE in Sample Problem 5.7 using one scalar equilibrium equation.arrow_forwardDetermine the tension TB in Sample Problem 5.6 using one scalar equilibrium equation.arrow_forwardThe 180-lb homogeneous bar is supported by a ball-and-socket joint at A and two cables attached to B. Determine the forces in the cables.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY