
EBK BASIC CHEMISTRY
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220101472335
Author: Timberlake
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.117CQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The term energy level, a sublevel and an orbital should be explained.
Concept introduction:
The rules for the allowed quantum numbers combinations are as follows:
- All the three quantum numbers ( n, l and m ) describes the orbital of an atom and they are integers.
- The principal quantum number, n value cannot be zero. Thus, the values allowed for the principal quantum number are 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
- The value of angular quantum number, l can be between 0 to n-1. Thus, if value of n is equal to 3 the value of l can be 0, 1 or 2.
- The value of magnetic quantum number, m can be between − l to +l . Thus, if value of l is equal to 2, m can be wither -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2
Here, for s orbital value of
The relative energy of orbitals is represented as follows:
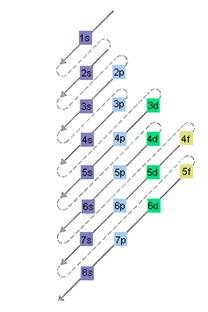
A s orbital can have maximum of 2 electrons, p orbital can have maximum of 6 electrons. Similarly, maximum electrons that a d and f orbital can have are 10 and 14 respectively.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Calculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbons
Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu
Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK BASIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 5.1 - What is meant by the wavelength of UV light?Ch. 5.1 - How are the wavelength and frequency of light...Ch. 5.1 - What is the difference between “white” light and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.4QAPCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.5QAPCh. 5.1 - AM radio waves have a frequency of 8105s-1 ....Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.7QAPCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.8QAPCh. 5.1 - Which ty pe of electromagnetic radiation, cell...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.10QAP
Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.11QAPCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.12QAPCh. 5.1 - Place the following types of electromagnetic...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.14QAPCh. 5.2 - What feature of an atomic spectrum indicates that...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.16QAPCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5.17QAPCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5.18QAPCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5.19QAPCh. 5.2 - Identify the photon in each pair with the greater...Ch. 5.3 - Describe the shape of each of the following...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.22QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.23QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.24QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.25QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.26QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.27QAPCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.28QAPCh. 5.4 - Compare the terms electron configuration and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.30QAPCh. 5.4 - 5.31 Draw the orbital diagram for each of the...Ch. 5.4 - 5.32 Draw the orbital diagram for each of the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.33QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.34QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.35QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.36QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.37QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.38QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.39QAPCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.40QAPCh. 5.5 - Use the sublevel blocks on the periodic table to...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.42QAPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.43QAPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.44QAPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.45QAPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.46QAPCh. 5.5 - Use the periodic table to give the symbol of the...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.48QAPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 5.49QAPCh. 5.5 - Use the periodic table to give the number of...Ch. 5.6 - What do the group numbers from 1A (1) to 8A (18)...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.52QAPCh. 5.6 - Write the group number using both A/B and 1 to 18...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.54QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.55QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.56QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.57QAPCh. 5.6 - Indicate the number of valence electrons in each...Ch. 5.6 - Write the group number and draw the Lewis symbol...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.60QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.61QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.62QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.63QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.64QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.65QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.66QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.67QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.68QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.69QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.70QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.71QAPCh. 5.6 - Fill in each of the following blanks using higher...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.73QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.74QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.75QAPCh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.76QAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.77FUCh. 5 - Prob. 5.78FUCh. 5 - Prob. 5.79UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.80UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.81UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.82UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.83UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.84UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.85UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.86UTCCh. 5 - Prob. 5.87AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.88AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.89AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.90AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.91AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.92AQAPCh. 5 - 5.93 a. What electron sublevel starts to fill...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.94AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.95AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.96AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.97AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.98AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.99AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.100AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.101AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.102AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.103AQAPCh. 5 - Why is the ionization energy of Br lower than that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.105AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.106AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.107AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.108AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.109AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.110AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.111AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.112AQAPCh. 5 - Prob. 5.113CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.114CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.115CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.116CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.117CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.118CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.119CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5.120CQ
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward
- III O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forward
- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. Br Br₂, light D Br Br Br Brarrow_forward
- Select all molecules which are chiral. Brarrow_forwardUse the reaction coordinate diagram to answer the below questions. Type your answers into the answer box for each question. (Watch your spelling) Energy A B C D Reaction coordinate E A) Is the reaction step going from D to F endothermic or exothermic? A F G B) Does point D represent a reactant, product, intermediate or transition state? A/ C) Which step (step 1 or step 2) is the rate determining step? Aarrow_forward1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY