
Concept explainers
5-114 Carbon dioxide gas, saturated with water vapor, can be produced by the addition of aqueous acid to calcium carbonate based on the following balanced net ionic equation:
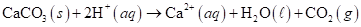
(a) How many moles of wet CO (g), collected at 60.°C and 774 torr total pressure, are produced by the complete reaction of 10.0 g of CaCO3 with excess acid?
(b) What volume does this wet CO2 occupy?
(c) What volume would the CO2 occupy at 774 torr if a desiccant (a chemical drying agent) were added to remove the water? The vapor pressure of water at 60.°C is 149.4 mm Hg.
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of moles of wet
Concept Introduction:
Moles of wet
Answer to Problem 5.114P
The number of moles of carbon dioxide produced is
Explanation of Solution
The weight of calcium carbonate is
The temperature is
The pressure is
The molecular weight of calcium carbonate is calculated below:
The number of moles in
The balanced chemical equation is below:
From the above equation,
Therefore, the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced is
(b)
Interpretation:
The volume of wet
Concept Introduction:
To determine the volume of wet
The relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature, under two sets of conditions, is given by following equation.
Answer to Problem 5.114P
The value of carbon dioxide produced is
Explanation of Solution
The weight of calcium carbonate is
The temperature is.
The pressure is
The molecular weight of calcium carbonate is calculated below:
The number of moles in
The balanced chemical equation is below:
From the above equation:
Therefore, the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced is
We know that at STP, 1 mole of any gas occupies
Therefore,
Therefore, the volume of
At STP, the value of
Now, convert the pressure from
We know that,
Therefore, the pressure is calculated below:
Now, convert temperature from
We know that,
Therefore,
The relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature, under two sets of conditions, is given by following equation:
Upon rearranging, we get,
By substituting the values of
Hence the value of carbon dioxide produced is
(c)
Interpretation:
The volume of wet
Concept Introduction:
To determine the volume of wet
The relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature, under two sets of conditions, is given by following equation.
Answer to Problem 5.114P
Explanation of Solution
The weight of calcium carbonate is
The temperature is
The pressure is
The vapor pressure of water at
The molecular weight of calcium carbonate is calculated below:
The number of moles in
The balanced chemical equation is below:
From the above equation:
Therefore, the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced is
We know that at STP, 1 mole of any gas occupies
Therefore,
Therefore, the volume of
At STP, the value of
The pressure is
Now, convert the pressure from
We know that,
Therefore, the pressure is calculated below,
The vapor pressure of water at
Therefore, the pressure is calculated below,
Now, convert temperature from°C to K.
We know that,
Therefore,
The relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature, under two sets of conditions, is given by following equation,
Upon rearranging, we get,
By substituting the values of
Hence the value of carbon dioxide produced is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Name the below disaccharide. Circle any hemiacetals. Identify the numbering of glycosidic linkage, and identify it as a or ẞ. OH HO HO OH HO HO HO OHarrow_forwardWhat are the monomers used to make the following polymers? F. а. b. с. d. Вецер хочому なarrow_forward1. Propose a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I'm looking for curved mechanistic arrows and appropriate formal charges on intermediates. OMe MeO OMe Me2N NMe2 OTBS OH xylenes OMe 'OTBSarrow_forward
- What is the polymer made from the following monomers? What type of polymerization is used for each? а. ОН H2N но b. ن -NH2 d. H₂N NH2 довarrow_forwardCondensation polymers are produced when monomers containing two different functional groups link together with the loss of a small molecule such as H2O. The difunctional monomer H2N(CH2)6COOH forms a condensation polymer. Draw the carbon-skeleton structure of the dimer that forms from this monomer.arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the monomer?arrow_forward
- → BINDERIYA GANBO... BINDERIYA GANBO. AP Biology Notes Gamino acid chart - G... 36:22 司 10 ☐ Mark for Review Q 1 Hide 80 8 2 =HA O=A¯ = H₂O Acid HIO HBrO HCIO Question 10 of 35 ^ Σ DELL □ 3 % Λ & 6 7 * ∞ 8 do 5 $ 4 # m 3 ° ( 9 Highlights & Notes AXC Sign out Carrow_forwardWhich representation(s) show polymer structures that are likely to result in rigid, hard materials and those that are likely to result in flexible, stretchable, soft materials?arrow_forward3. Enter the molecular weight of the product obtained from the Williamson Ether Synthesis? OH OH & OH excess CH3l Ag₂Oarrow_forward
- Please answer 1, 2 and 3 on the endarrow_forwardIn the box below, specify which of the given compounds are very soluble in polar aprotic solvents. You may select more than one compound. Choose one or more: NaCl NH4Cl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CN CH3CH2OH hexan-2-one NaOH CH3SCH3arrow_forwardOn the following structure, select all of the atoms that could ACCEPT a hydrogen bond. Ignore possible complications of aromaticity. When selecting be sure to click on the center of the atom.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning




