
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The volume of the solution contains the given amount and strength of the solute have to determine.
Concept introduction:
The concentration of any solution is mean the amount of solute present in the specific volume of the solvent. Now the amount of solute present in the solution is expressed by different units like: gram, gram-equivalent, gram-mole or mole etc. The amount of solvent to prepare the solution can be expressed in terms of weight or volume. The different unit of expression the concentration of a solution are- percentage strength, normality, molarity, molality, formality, gram per litter, mole fraction, parts per million etc.
Molarity: In per litter (1000 mL or 1000 cc) volume of any solution the amount of solute present in gram-mole is called the molarity of the solution. It is expressed by ‘M’. Like- If in 1 L of H2SO4 solution 2 gm-mole of the pure H2SO4 is present then the strength of the solution will be 2M. It can be expressed as-
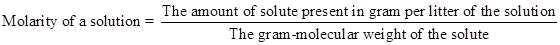
The equation can be rewritten as
(b)
Interpretation:
The volume of the solution contains the given amount and strength of the solute have to determine.
Concept introduction:
The concentration of any solution is mean the amount of solute present in the specific volume of the solvent. Now the amount of solute present in the solution is expressed by different units like: gram, gram-equivalent, gram-mole or mole etc. The amount of solvent to prepare the solution can be expressed in terms of weight or volume. The different unit of expression the concentration of a solution are- percentage strength, normality, molarity, molality, formality, gram per litter, mole fraction, parts per million etc.
Molarity: In per litter (1000 mL or 1000 cc) volume of any solution the amount of solute present in gram-mole is called the molarity of the solution. It is expressed by ‘M’. Like- If in 1 L of H2SO4 solution 2 gm-mole of the pure H2SO4 is present then the strength of the solution will be 2M. It can be expressed as-
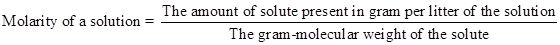 The equation can be rewritten as
The equation can be rewritten as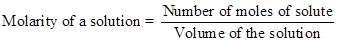
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY FOR CHANGING TIMES
- 2. 200 LOD For an unknown compound with a molecular ion of 101 m/z: a. Use the molecular ion to propose at least two molecular formulas. (show your work) b. What is the DU for each of your possible formulas? (show your work) C. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 4 2 (ppm) 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI-11arrow_forwardComplete the spectroscopy with structurearrow_forwardComplete the spectroscopy with structurearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





