
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 3P
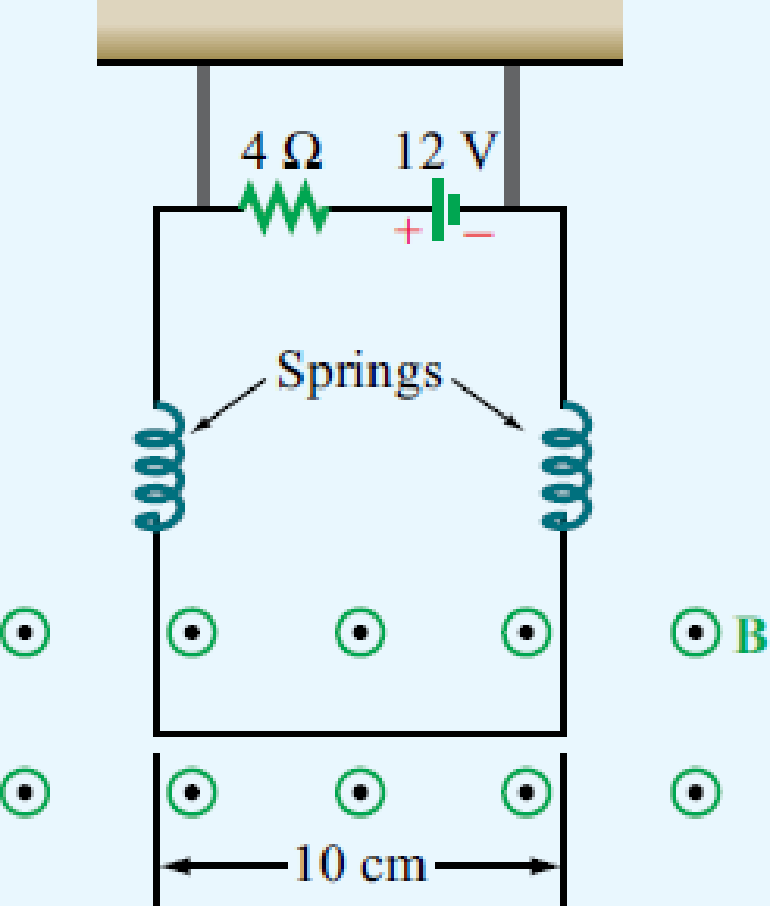
The circuit shown in Fig. P5.3 uses two identical springs to support a 10 cm long horizontal wire with a mass of 20 g. In the absence of a magnetic field, the weight of the wire causes the springs to stretch a distance of 0.2 cm each. When a uniform magnetic field is turned on in the region containing the horizontal wire, the springs are observed to stretch an additional 0.5 cm each. What is the intensity of the magnetic flux density B? The force equation for a spring is F = kd, where k is the spring constant and d is the distance it has been stretched.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How would you solve this question using nodal analysis?
For the circuit, calculate Vr. Calculate the threshold input voltage Vi that will change the output of the comparator from high to low. Show all calculations and explain your work.
I need expert solutions to this
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 5.1 - What are the major differences between the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 2CQCh. 5.1 - How is the direction of the magnetic moment of a...Ch. 5.1 - If one of two wires of equal length is formed into...Ch. 5.1 - An electron moving in the positive x direction...Ch. 5.1 - A proton moving with a speed of 2 106 m/s through...Ch. 5.1 - A charged particle with velocity u is moving in a...Ch. 5.1 - A horizontal wire with a mass per unit length of...Ch. 5.1 - A square coil of 100 turns and 0.5 m long sides is...Ch. 5.2 - Two infinitely long parallel wires carry currents...
Ch. 5.2 - Devise a right-hand rule for the direction of the...Ch. 5.2 - What is a magnetic dipole? Describe its magnetic...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 5.2 - A wire carrying a current of 4 A is formed into a...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 5.3 - What are the fundamental differences between...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5.3 - Compare the utility of applying the BiotSavart law...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 11CQCh. 5.3 - A current I flows in the inner conductor of a long...Ch. 5.3 - The metal niobium becomes a superconductor with...Ch. 5.5 - What are the three types of magnetic materials and...Ch. 5.5 - What causes magnetic hysteresis in ferromagnetic...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 14CQCh. 5.5 - The magnetic vector M is the vector sum of the...Ch. 5.6 - With reference to Fig. 5-24, determine the single...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 15CQCh. 5.7 - What is the difference between self-inductance and...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 17CQCh. 5.7 - Use Eq. (5.89) to obtain an expression for B at a...Ch. 5 - An electron with a speed of 8 106 m/s is...Ch. 5 - When a particle with charge q and mass m is...Ch. 5 - The circuit shown in Fig. P5.3 uses two identical...Ch. 5 - The rectangular loop shown in Fig. P5.4 consists...Ch. 5 - In a cylindrical coordinate system, a 2 m long...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6PCh. 5 - Prob. 7PCh. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - The loop shown in Fig. P5.9 consists of radial...Ch. 5 - An infinitely long, thin conducting sheet defined...Ch. 5 - An infinitely long wire carrying a 25 A current in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12PCh. 5 - Prob. 13PCh. 5 - Prob. 14PCh. 5 - A circular loop of radius a carrying current I1 is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5 - Prob. 17PCh. 5 - Prob. 18PCh. 5 - Three long, parallel wires are arranged as shown...Ch. 5 - A square loop placed as shown in Fig. P5.20 has 2...Ch. 5 - Prob. 21PCh. 5 - Prob. 22PCh. 5 - Repeat Problem 5.22 for a current density J=zJ0er.Ch. 5 - In a certain conducting region, the magnetic field...Ch. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 26PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - A uniform current density given by J=zj0 (A/m2)...Ch. 5 - A thin current element extending between z = L/2...Ch. 5 - In the model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr...Ch. 5 - Iron contains 8.5 1028 atoms/m3. At saturation,...Ch. 5 - The xy plane separates two magnetic media with...Ch. 5 - Given that a current sheet with surface current...Ch. 5 - In Fig. P5.34, the plane defined by x y = 1...Ch. 5 - The plane boundary defined by z = 0 separates air...Ch. 5 - Prob. 36PCh. 5 - Prob. 37PCh. 5 - A solenoid with a length of 20 cm and a radius of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - The rectangular loop shown in Fig. P5.40 is...Ch. 5 - Determine the mutual inductance between the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ARD1 Reset BTN OOOOOO RESET +5V Gnd Gnd Vin 10 PC0/ADCO A1 PC1/ADC1 A2 ANALOG IN PC2/ADC2 A3 PC3/ADC3 4 PC4/ADC4/SDA A5 PC5/ADC5/SCL ARDUINO UNO ON ATMEGA328P PU AREF 13 PB5/SCK 12 PB4/MISO 11 ~ PB3/MOSI/OC2A ~ PB2/OC1B 10 9 - PB1/OC1A PB0/ICP1/CLKO 8 PD7/AIN1 ~ PD7/AIN1 5 ~ PD5/T1/OC0B ~ PD3/INT1/OC2B 4 PD4/T0/XCK 3 2 PD2/INTO PD1/TXD 0 PDO/RXDarrow_forwardPls show neat and whole solutionarrow_forwardPls show neat and whole solutionarrow_forward
- Solve the homework in a realistic way in more than one way with paper and pen without artificial intelligencearrow_forwardA 460 V 25 HP 4 poles connected in Y wound rotor induction motor has the following parameters: R1 = 0.641 ohms, X1 = 1.106 ohms, R2 = 0.332 ohms, X2 = 0.464 ohms and Xm = 26.3 ohms. For this machine calculate the maximum torque, rotation and corresponding slip.arrow_forwardFor the following circuit. What is Vr. Additionally, what is the threshold input voltage VL that will change the output of the comparator from hight ot low.arrow_forward
- Corrections & Additions for Your Pneumatic Circuit Drawing Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding. Next Steps: Revise your diagram to include these missing elements. Ensure all components follow correct safety and operational requirements.arrow_forwardFor the following circuit, What is Vout as a function of R and Id assuming the op-amp is ideal. Additionally, If Id is 4000µA and the desired Vout is -1.6V what is the proper value for R?arrow_forwardCan you solve for the voltage through the 1k ohm resistor with the diode present. Additionally, can you find the voltage through the 1kohm resistor when the 5 V source is shorted. Then when the 5V is on and the 2V is shorted.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Electric Charge and Electric Fields; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VFbyDCG_j18;License: Standard Youtube License