
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 20P
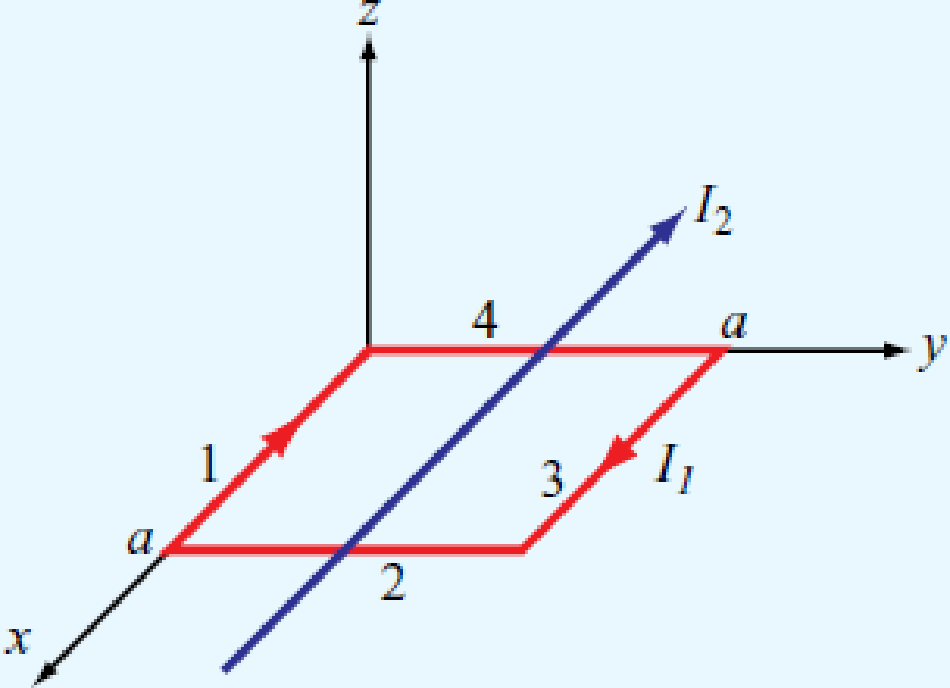
A square loop placed as shown in Fig. P5.20 has 2 m sides and carries a current I1 = 5A. If a straight, long conductor carrying a current I2 = 10A is introduced and placed just above the midpoints of two of the loop’s sides, determine the net force acting on the loop.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Open plc - ladder logic To control traffic, we have red lights to stop cars and green lights to initiate entry/exit.
If a car is in the lane, then the red lights turn ON. If no cars are in the lane, then the
green lights turn ON. Upon turning ON the main switch button, the main switch indicator
should turn ON and the system should start with green lights ON and red lights OFF?
3-4)
3.4-2 Signals g₁(t) = 104П(104) and g2(t) = 8(t) are applied at the inputs of the ideal low-pass
filters H₁(f)=(f/20,000) and H2(f) = П(f/10,000) (Fig. P3.4-2). The outputs y₁ (t) and
y2(t) of these filters are multiplied to obtain the signal y(t) = y1 (1)y2(t).
(a) Sketch G1(f) and G2(f).
(b) Sketch H₁(f) and H₂(f).
(c) Sketch Y₁ (f) and Y2(f).
(d) Find the bandwidths of y₁ (t), y2(t), and y(t).
8₁ (1)
H₁(f)
y, (t)
y(t) = y₁ (1) y2 (1)
82(1)
½⁄2 (1)
H₂(f)
solve the differential equation y'' -2y'-3y=x³e^5x cos(3x)
Don't use AI,I need it handwritten
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 5.1 - What are the major differences between the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 2CQCh. 5.1 - How is the direction of the magnetic moment of a...Ch. 5.1 - If one of two wires of equal length is formed into...Ch. 5.1 - An electron moving in the positive x direction...Ch. 5.1 - A proton moving with a speed of 2 106 m/s through...Ch. 5.1 - A charged particle with velocity u is moving in a...Ch. 5.1 - A horizontal wire with a mass per unit length of...Ch. 5.1 - A square coil of 100 turns and 0.5 m long sides is...Ch. 5.2 - Two infinitely long parallel wires carry currents...
Ch. 5.2 - Devise a right-hand rule for the direction of the...Ch. 5.2 - What is a magnetic dipole? Describe its magnetic...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 5.2 - A wire carrying a current of 4 A is formed into a...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 5.3 - What are the fundamental differences between...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5.3 - Compare the utility of applying the BiotSavart law...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 11CQCh. 5.3 - A current I flows in the inner conductor of a long...Ch. 5.3 - The metal niobium becomes a superconductor with...Ch. 5.5 - What are the three types of magnetic materials and...Ch. 5.5 - What causes magnetic hysteresis in ferromagnetic...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 14CQCh. 5.5 - The magnetic vector M is the vector sum of the...Ch. 5.6 - With reference to Fig. 5-24, determine the single...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 15CQCh. 5.7 - What is the difference between self-inductance and...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 17CQCh. 5.7 - Use Eq. (5.89) to obtain an expression for B at a...Ch. 5 - An electron with a speed of 8 106 m/s is...Ch. 5 - When a particle with charge q and mass m is...Ch. 5 - The circuit shown in Fig. P5.3 uses two identical...Ch. 5 - The rectangular loop shown in Fig. P5.4 consists...Ch. 5 - In a cylindrical coordinate system, a 2 m long...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6PCh. 5 - Prob. 7PCh. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - The loop shown in Fig. P5.9 consists of radial...Ch. 5 - An infinitely long, thin conducting sheet defined...Ch. 5 - An infinitely long wire carrying a 25 A current in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12PCh. 5 - Prob. 13PCh. 5 - Prob. 14PCh. 5 - A circular loop of radius a carrying current I1 is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5 - Prob. 17PCh. 5 - Prob. 18PCh. 5 - Three long, parallel wires are arranged as shown...Ch. 5 - A square loop placed as shown in Fig. P5.20 has 2...Ch. 5 - Prob. 21PCh. 5 - Prob. 22PCh. 5 - Repeat Problem 5.22 for a current density J=zJ0er.Ch. 5 - In a certain conducting region, the magnetic field...Ch. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 26PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - A uniform current density given by J=zj0 (A/m2)...Ch. 5 - A thin current element extending between z = L/2...Ch. 5 - In the model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr...Ch. 5 - Iron contains 8.5 1028 atoms/m3. At saturation,...Ch. 5 - The xy plane separates two magnetic media with...Ch. 5 - Given that a current sheet with surface current...Ch. 5 - In Fig. P5.34, the plane defined by x y = 1...Ch. 5 - The plane boundary defined by z = 0 separates air...Ch. 5 - Prob. 36PCh. 5 - Prob. 37PCh. 5 - A solenoid with a length of 20 cm and a radius of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - The rectangular loop shown in Fig. P5.40 is...Ch. 5 - Determine the mutual inductance between the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3-3) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 3.3-7. The signals in the figure below are modulated signals with carrier cos(5t). Find the Fourier transforms of these signals using the appropriate properties of the Fourier transform and text Table 3.1. The sketch the magnitude and phase spectra for figure parts (a) and (b). Hint: these functions can be expressed in the form g(t) cos(2лfot) (a) 1 1 2π www. σπ (b) (c) όπarrow_forward3-1) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 3.1-1. Use direct integration to find the Fourier transforms of the signals shown below. a) g₁(t) = II(t − 2) + 2 exp (−3|t|) b) g(t) = d(t+2)+3e¯u (t − 2)arrow_forward3-2) Lathi & Ding prob. 3.1-5. From the definition in eq. 3.1b, find the inverse Fourier transforms of the spectra in the figure below. G(f) COS лf 10 (a) G(f) 1 -B B (b)arrow_forward
- Construct a battery pack to deliver 360V and 450-mile range for a vehicle that consumes 200 Wh/mile, from prismatic cells with 25Ah and 3.6 V. Physical dimensions of the cell are 0.5 cm thickness, 20 cm width and 40 cm length. a) Report configuration of the battery pack. 10-points b) Resistance of each cell is 0.05 Ohm, calculate the total internal resistance of the battery pack. 10-points c) Calculate the voltage drop during discharge when the battery is discharged at 100A. 10-points d) Calculate the amount of anode and cathode to build a prismatic cell with 25Ah capacity. Assume the cell chemistry as: Si anode and [Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2] cathode. Atomic weight of elements: Li=7, Si = 28, Ni=58, Co=59, Mn=55, O=16, 10-points e) Calculate the theoretical specific energy (Wh/kg) and practical energy density (Wh/liter) of the battery pack. 10-points f) Calculate the thickness on anode and cathode coating assuming each electrode has 30%…arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardDesign a battery pack for an electric bike that consumes in average 10Wh/mile and drive 30 miles per charge. The battery state of charge window is 80%. Design the battery by using new commercial cylindrical cells with 20mm diameter and 80mm height. The battery is constructed based on graphite anode C6 and cathode Li(Ni0.8Co0.15Al0,05)O2 that provides 3.75V at the cell level and 10Ah capacity. Density of anode is 2.2 g/cm3 and density of cathode is 4.5 g/cm3. Report on the battery pack configuration if the required battery pack voltage is 75 volts. If the thickness of anode and cathode is limited to 130 microns (130 x 10-4 cm) calculate the total electrode surface area in each cell. Assume the porosity of electrodes are 30%. Calculate the weight of active materials (anode and cathode) in grams and the total current collector’s and electrolyte membrane areas in (cm2).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
03 - The Cartesian coordinate system; Author: Technion;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hOgKEplCx5E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY