
Concept explainers
Some of the most important organic compounds in biochemistry are the
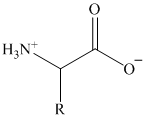
Write structural formulas for the following α-amino acids.
Alanine (R = methyl)
Valine (R = isopropyl)
Leucine (R = isobutyl)
Isoleucine (R = sec-butyl)
Serine (R =
Cysteine (R =
Aspartic acid (R =
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- Do the amino acid sequences: valine-asparagine and asparagine-valine represent the same compound? Explain.arrow_forwardWhat functional groups are found in all amino acids? How many different amino acids are found in naturally occurring proteins?arrow_forward22-62 Distinguish between intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding between backbone groups. Where in protein structures do you find one, and where do you find the other?arrow_forward
- During the hydrolysis of proteins, some amino acids, such as tryptophan, do not survive the reaction conditions. Other amino acids, such as asparagine and glutamine, are modified. Referring to Table 1-7 (p. 39), which shows the structures of the 20 common amino acids, write the structures of the two amino acids that are formed when asparagine and glutamine decompose in hot, concentrated HCl.arrow_forwardAspartame, an artificial sweetener used in Equal® and diet beverages, has the following structure. Identify the functional groups in Aspartame. II NH, O OH O 1= ester; I| = amide; III = amine O 1 = ester; I| = amine; III = amide O1= ether; I| = amide; III = amine O 1 = ether; I| = amine; III = amide O 1 = anhydride; Il = ketone; I|| = aminearrow_forwardAspartame is a non-calorie sweetener. Aspartame is not a sugar and is, instead, a dipeptide. Which amino acids is aspartame synthesized from? Based on the molecular structure shown below, identify possible AH, B, and Y structures making aspartame a sweetener.arrow_forward
- As we’ve discussed, a peptide bond is made when amino group of one amino acid combines with the carboxylic acid group of another amino acid (releasing a water molecule in the process). The C-N bond formed in this process is called a peptide bond. Peptide bonds have a few properties that might be unexpected. a) One property is that the molecular geometries around the C and N atom in the peptide bond are generally planar with bond angles of approximately 120 degrees. Provide an explanation for why the peptide bond would have this property, using Lewis structures, VSEPR theory and/or valence bond theory as appropriate.arrow_forward7. Identify the amino acids contained in each of the following tripeptides. a. он он H3N-CH2-C-N-CH-C-N-CH2-COO CH-CH3 ČH3 b. O H он 2/2 H,Ñ-CH-C-Ñ-CH-C-Ñ–CH–COO CH2 CH2 CH2 OH CH-CH3 CH2 CH3 ČOO ... ...arrow_forwardCarbohydrates or sugars can be represented into two forms Fischer projections (open chain) or Haworth projections (ring structures). Let us identify the functional group present in carbohydrates Fischer projections of D-allose and D-fructose. H,C H-C-OH C=0 H-C-OH HO-C H-C-OH H-C-OH H C+OH H-C-OH HyC, HO. HO D-allose D-fructose a.) The functional group present in D-allose is b.) The functional group present in D-fructose is c.) The functional group common for D-allose and D-fructose isarrow_forward
- How many atoms of each element are in a molecule of the amino acid lysine C6H14N3O2 ?arrow_forwardPalmitoleic acid, a fatty acid with various pharmaceutical applications, is mainly obtained from macadamia nuts. The condensed structural formula for a triacylglycerol containing three palmitoleic acid units is provided below. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding this triacylglycerol? O || CH,−O−C–(CH,)–CH=CH—(CH2)5–CH3 O || CH−O−C−(CH2)–CH=CH–(CH,)5–CH3 O CH,−O−C−(CH,)–CH=CH–(CH,)5–CH, O Its name is glyceryl tripalmitate or tripalmitin. O It is most likely to be liquid at room temperature. O It is an oil (not a fat). O It contains 3 molecules of the same unsaturated fatty acid.arrow_forwardProteins are formed when the group of one amino acid forms a peptide bond with the group of a second amino acid. OR group; H-bond + O NH3*, R group + O -COO, NH3 -COO, R grouparrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





