
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168390
Author: Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 11E
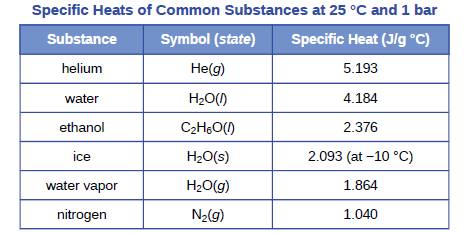
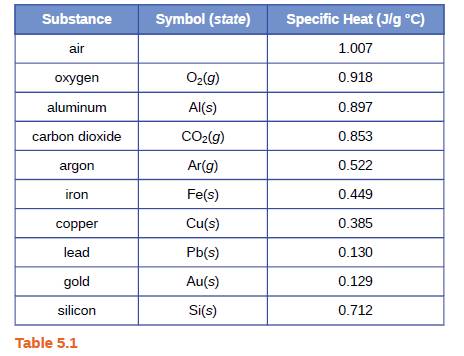
A piece of unknown solid substance weighs 437.2 g, and requires 8460 J to increase its temperature from 19.3 °C to 68.9 °C.
(a) What is the specific heat of the substance?
(b) If it is one of the substances found in Table 5.1, what is its likely identity?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
11. Complete the following esterification reaction with names of all the reactants and products under.
Hint: Remove the water and end up with ester
R-C-OH + ROH
R-C-OR + H₂O
A carboxylic acid
An alcohol
An ester
Water
BYJU'S
H-C-C
O-H
Нин
C-C-C-H
HAAA
H O-C-C-C-H
AAA
Ethanoic acid
Propanol
Water Propyl ethanoate
By com
CH3COOH + CH3CH2CH2CH₂CH₂OH →
Practice for alcohols aldehydes and ketones:
12. Draw the structures from the following names mixed of alcohol/aldehyde and ketone:
a. 4-methyl cyclohexanone
b. 3-methyl-2-pentenal
c. 2,3-dimethylcyclohexanone
d. 1,3propanediol or Propane 1,3 diol
13. Write systematic names for the following compounds identify
functional group:
a.
b. (CH3)2CH-C
OH
c) CH(CH₂)--
OH
-,-,
may you please show all steps! i am having a hard time understanding and applying in this format, thank you!
10. Complete the substitution reaction of 2 pentanol with these reagents.
Reagents & Reaction Conditions use practice sheet. Please write only
major products, minor product like water, other gases are not
required.
Hint: In substitution of alcohol, we generally substitute OH group
with Halogens like cl, Br, F using some reagent containing
halogens. Ensure to add halogens to the same carbon number
where you are removing OH from
Examples
Alcohols can be converted to Alkyl Halides with HX acids
HBr
H₂O
HCI
+ H₂O
HI
+
H₂O
CH,CH₂OH + SOCI₂
CH,CH₂OH + PCI₁₂
A
BBYJU'S
CH CHCI + SO₂+ HCI
CH₂CH CIP(OH), + HCI
CH,CH₂OH + PCI CHCHCI + POCI + HCI
CH,CH₂OH + PBr, CH,CH,Br + P(OH), + HBr
1. Reaction with HBr with 2 Pentanol
2.Reaction with HI with 2 pentanol
© Byjus.com
3.Reaction with HCI+ZnCl,, with 2 pentanol (Zncl2 is catalyst no role)
4.Reaction with SOCI,, with 2 Pentanol
5.Reaction with PBr; or PCl, with 2 pentanol
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Ch. 5 - A burning match and a bonfire may have the same...Ch. 5 - Prepare a table identifying several energy...Ch. 5 - Explain the difference between heat capacity and...Ch. 5 - Calculate the heat capacity, in joules and in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the heat capacity, in joules and in...Ch. 5 - How much heat, in joules and in calories, must be...Ch. 5 - How much heat, in joules and in calories, is...Ch. 5 - How much would the temperature of 275 g of water...Ch. 5 - If 14.5 kJ of heat were added to 485 g of liquid...Ch. 5 - A piece of unknown substance weighs 44.7 g and...
Ch. 5 - A piece of unknown solid substance weighs 437.2 g,...Ch. 5 - An aluminum kettle weighs 1.05 kg. (a) What is the...Ch. 5 - Most people find waterbeds uncomfortable unless...Ch. 5 - A 500-mL bottle of water at room temperature and a...Ch. 5 - Would the amount of heat measured for the reaction...Ch. 5 - Would the amount of heat absorbed by the...Ch. 5 - Would the amount of heat absorbed by the...Ch. 5 - How many milliliters of water at 23 C with a...Ch. 5 - How much will the temperature of a cup (180 g) of...Ch. 5 - A 45-g aluminum spoon (specific heat 0.88 J/g C)...Ch. 5 - The temperature of the cooling water as it leaves...Ch. 5 - A 70.0-g piece of metal at 80.0 °C is placed in...Ch. 5 - If a reaction produces 1.506 kJ of heat, which is...Ch. 5 - A 0.500-g sample of KCl is added to 50.0 g of...Ch. 5 - Dissolving 3.0 g of CaCl2(s) in 150.0 g of water...Ch. 5 - When 50.0 g of 0.200 M NaCl(aq) at 24.1 C is added...Ch. 5 - The addition of 3.15 g of Ba(OH)28H2O to a...Ch. 5 - The reaction of 50 mL of acid and 50 mL of base...Ch. 5 - If the 3.21 g of NH4NO3 in Example 5.6 were...Ch. 5 - When 1.0 g of fructose, C6H12O6(s), a sugar...Ch. 5 - When a 0.740-g sample of trinitrotoluene (TNT),...Ch. 5 - One method of generating electricity is by burning...Ch. 5 - The amount of fat recommended for someone with a...Ch. 5 - A teaspoon of the carbohydrate sucrose (common...Ch. 5 - What is the maximum mass of carbohydrate in a 6-oz...Ch. 5 - A pint of premium ice cream can contain 1100...Ch. 5 - A serving of a breakfast cereal contains 3 g of...Ch. 5 - Which is the least expensive source of energy in...Ch. 5 - Explain how the heat measured in Example 5.5...Ch. 5 - Using the data in the check your learning section...Ch. 5 - Calculate the enthalpy of solution ( H for the...Ch. 5 - Calculate H for the reaction described by the...Ch. 5 - Calculate the enthalpy of solution ( H for the...Ch. 5 - Although the gas used in an oxyacetylene torch...Ch. 5 - How much heat is produced by burning 4.00 moles of...Ch. 5 - How much heat is produced by combustion of 125 g...Ch. 5 - How many moles of isooctane must be burned to...Ch. 5 - What mass of carbon monoxide must be burned to...Ch. 5 - When 2.50 g of methane burns in oxygen, 125 kJ of...Ch. 5 - How much heat is produced when loo mL of 0.250 M...Ch. 5 - A sample of 0.562 g of carbon is burned in oxygen...Ch. 5 - Before the introduction of chlorofluorocarbons,...Ch. 5 - Homes may be heated by pumping hot water through...Ch. 5 - Which of the enthalpies of combustion in Table 5.2...Ch. 5 - Does the standard enthalpy of formation of H2O(g)...Ch. 5 - Joseph Priestly prepared oxygen in 1774 by heating...Ch. 5 - How many kilojoules of heat will be released when...Ch. 5 - How many kilojoules of heat will be released when...Ch. 5 - The following sequence of reactions occurs in the...Ch. 5 - Both graphite and diamond burn....Ch. 5 - From the molar heats of formation in Appendix G,...Ch. 5 - Which produces more heat?...Ch. 5 - Calculate H298 for the process...Ch. 5 - Calculate H298 for the process...Ch. 5 - Calculate H for the process Hg2Cl2(s)2Hg(l)+Cl2(g)...Ch. 5 - Calculate H298 for the process...Ch. 5 - Calculate the standard molar enthalpy of formation...Ch. 5 - Using the data in Appendix G, calculate the...Ch. 5 - Using the data in Appendix G, calculate the...Ch. 5 - The following reactions can be used to prepare...Ch. 5 - The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, has...Ch. 5 - Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of propane,...Ch. 5 - Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of butane,...Ch. 5 - Both propane and butane are used as gaseous fuels....Ch. 5 - The white pigment TiO2 is prepared by the reaction...Ch. 5 - Water gas, a mixture of H2 and CO, is an important...Ch. 5 - In the early days of automobiles, illumination at...Ch. 5 - From the data in Table 5.2, determine which of the...Ch. 5 - The enthalpy of combustion of hard coal averages...Ch. 5 - Ethanol, C2H5OH, is used as a fuel for motor...Ch. 5 - Among the substances that react with oxygen and...Ch. 5 - How much heat is produced when 1.25 g of chromium...Ch. 5 - Ethylene, C2H2, a byproduct from the fractional...Ch. 5 - The oxidation of the sugar glucose, C6H12O6, is...Ch. 5 - Propane, C3H8, is a hydrocarbon that is commonly...Ch. 5 - During a recent winter month in Sheboygan,...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
17. Anthropologists are interested in locating areas in Africa where fossils 4-8 million years old might be fou...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
4. What five specific threats to biodiversity are described in this chapter? Provide an example of each.
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
In your own words, briefly distinguish between relative dates and numerical dates.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS In Concept 20.2, you learned about genome-wide association studies. Explain how these studies...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Is 2-methyl-2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-methyl-2-propanol and also any oxidation products of 2- methyl-2- propanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 4. 2-Propanol is the IUPAC systematic name of this alcohol. It has a common name by which it is much better known (You'll see it in the grocery store or pharmacy). Give that common name 5. Aldehydes can be synthesized by the oxidation of. Please choose from below choices A. Primary alcohols B. Secondary alcohols C. Organic acids D. Inorganic acids 6. Tertiary alcohol Can undergo oxidation. yes or no. ? If yes then answer the product.arrow_forwardFinish the reactions hand written pleasearrow_forwardPart A Identify each alcohol as primary, secondary, or tertiary Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. CH₂ H₂C- -C-OH HO CH₂ Primary Он OH CH₂ OH CCH₂OH CH₂ сн Secondary Tertiary Reset Help CH,CH₂ (CH)CHCH,OH CH,CH,CH,CCH, CHOH CH₂ Different types of alcohol groups Alcohol and its reaction: 8. Combing two alcohol molecules below and completing the reaction with Product .( Hint Reaction called etherification as ether is formed and name the ether once you complete the reaction. Hint.: R-O-H+H-O-RR-O-R Do the reaction: CH₂OH + CH₂OH---→ + H-O-H 9. Write the reaction of formation of alcohol from alkene by adding water: Addition reaction also called hydration reaction as we are adding water which occur always in presence of acid Hint: Break the double bond and add H and OH if symmetrical then add anywhere if unsymmetrical then follow Markovnikov rule H should go to that double bone carbon which has more hydrogen CH2=CH2 + H₂O-→arrow_forward
- Complete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. dm Re Explanation Check ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forwardb) Use curved arrows to show the reaction of the radical with hydrogen bromide. Br: Br H .. Answer Bankarrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY