
Concept explainers
Consider the 30-Ω resistor in Fig. 4.134. First compute the Thevenin equivalent circuit as seen by the 30-Ω resistor. Compute the value of R that results in Thevenin equivalent resistance equal to the 30-Ω resistance and then calculate power delivered to the 30-Ω resistor. Now let R = 0 Ω, 110 Ω, and ∞, calculate the power delivered to the 30-Ω resistor in each case. What can you say about the value of R that will result in the maximum power that can be delivered to the 30-Ω resistor?
Figure 4.134
Find the Thevenin equivalent seen by the
Calculate the power delivered to the
Answer to Problem 68P
The Thevenin voltage is
The power delivered to the
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 4.134 in the textbook.
The current source is
The voltage source is
The Thevenin resistance
Calculation:
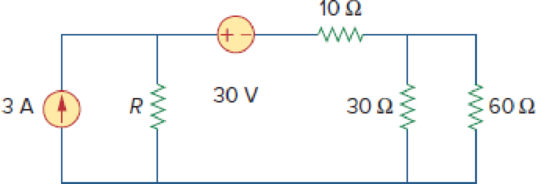
In the given circuit, find the Thevenin voltage by removing the 30 ohms resistor and the modified circuit is shown in Figure 1.
The modified circuit is shown in Figure 1.
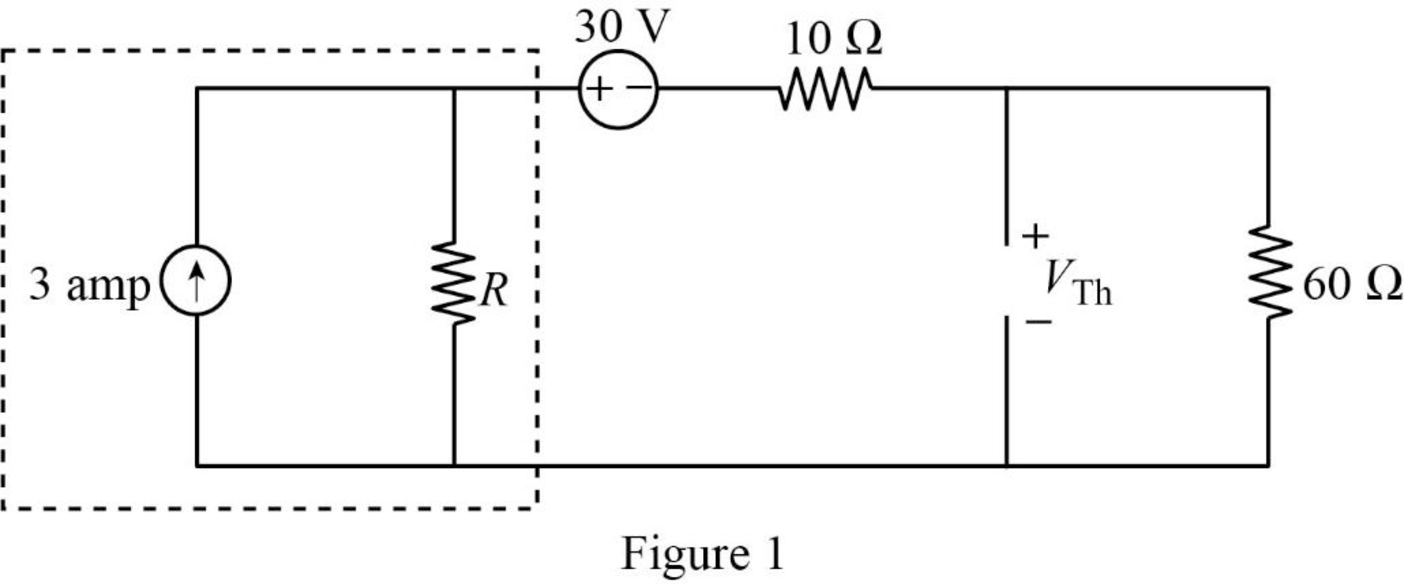
In Figure 1, the current source with parallel resistance is converted into voltage source with series resistance using source transformation. The voltage V is calculated by using ohms law as follows,
The source transformation is shown in Figure 2.
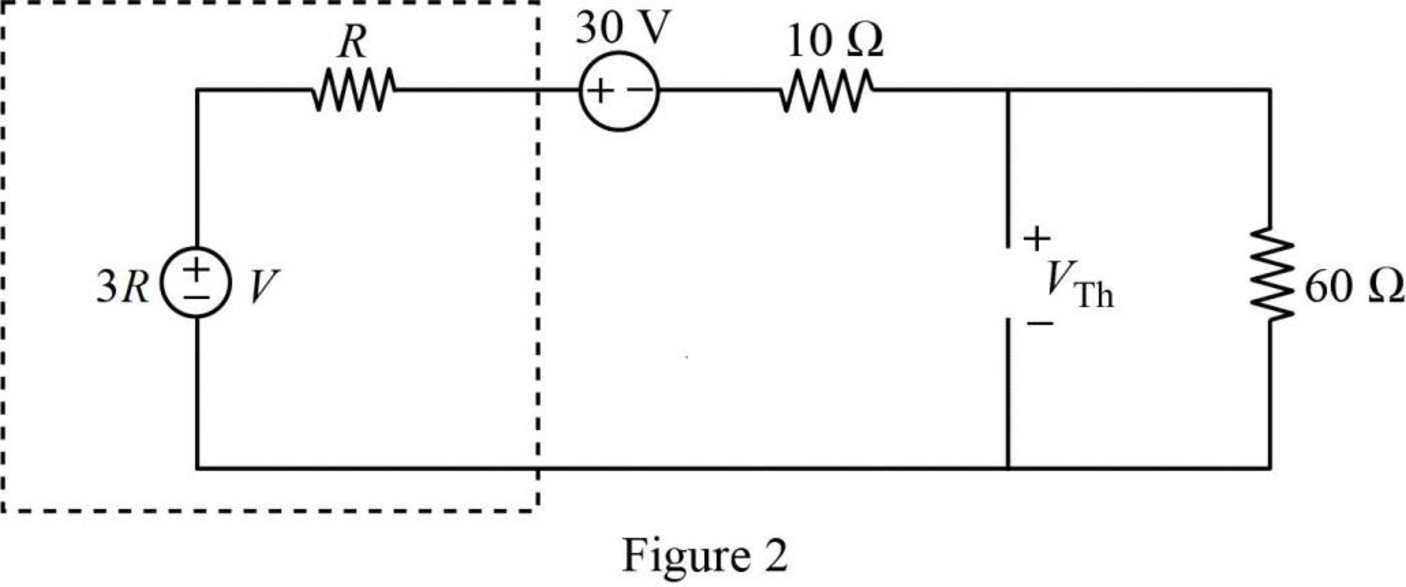
In Figure 2, the Thevenin voltage is,
Refer to Figure 4.134 in the textbook.
In the given circuit, find the Thevenin resistance by turning off the
The modified circuit is shown in Figure 3.
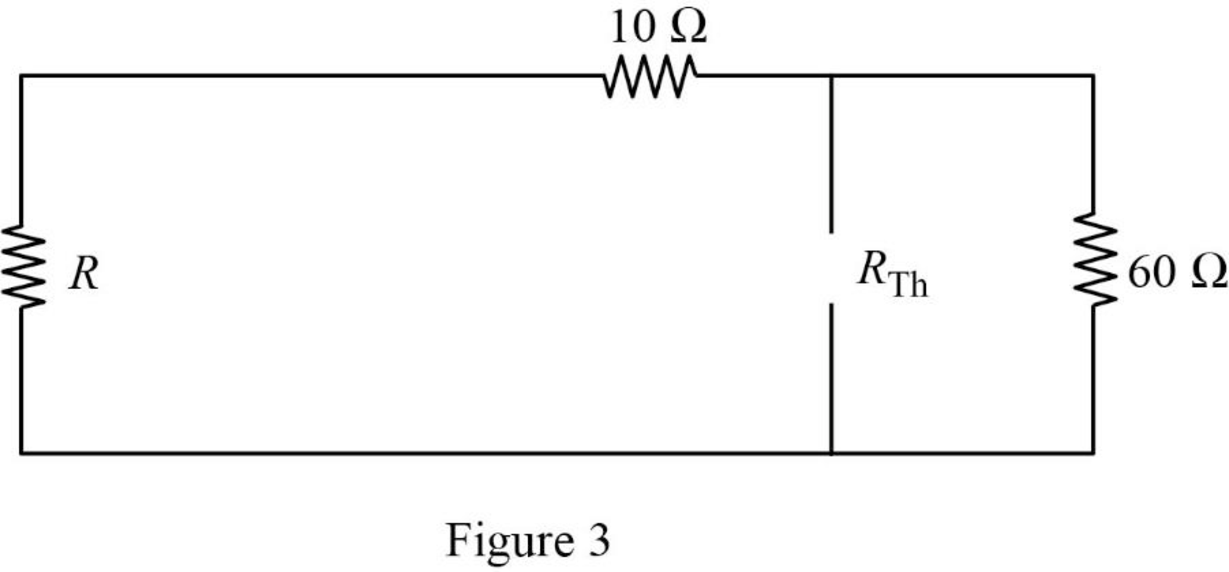
In Figure 3, the Thevenin resistance is,
Substitute
Substitute 50 for R in equation (1) to find the Thevenin voltage in volts.
Substitute 50 for R in equation (2) to find the Thevenin resistance in ohms.
The Thevenin equivalent connected to the 30 ohms resistor is shown in Figure 4.
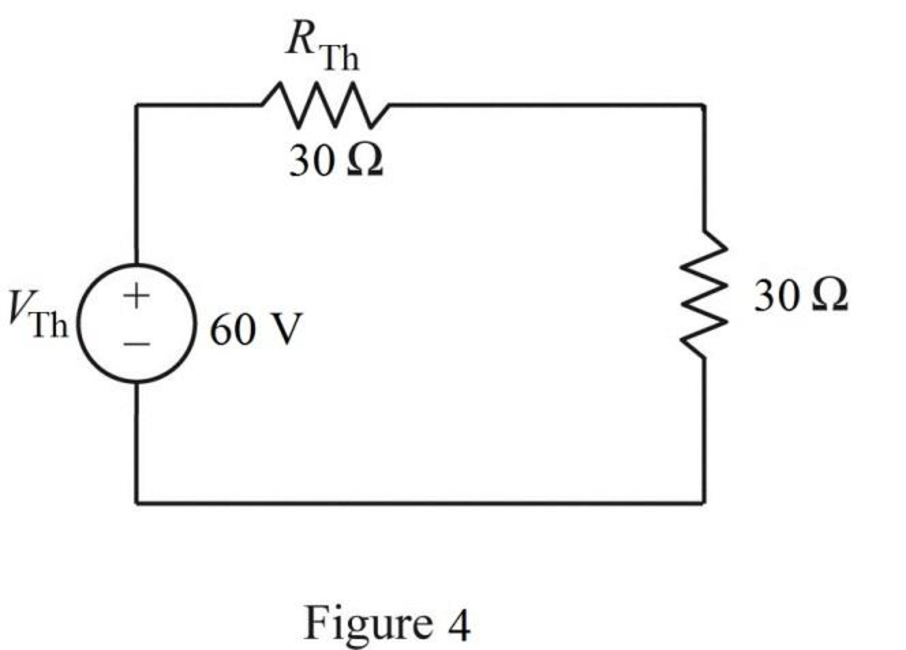
The power delivered to the 30 ohms resistor is,
Substitute 60 for
Consider the resistance
When
Substitute 0 for R in equation (2) to find the Thevenin resistance in ohms.
When
Substitute 0 for R in equation (1) to find the Thevenin voltage in volts.
When
Substitute
Consider the resistance
When
Substitute 110 for R in equation (2) to find the Thevenin resistance in ohms.
When
Substitute 110 for R in equation (1) to find the Thevenin voltage in volts.
When
Substitute
Consider the resistance
When
Simplify equation (2) as follows,
Substitute
When
Simplify equation (1) as follows,
Substitute
When
Substitute
Thus, when
Conclusion:
Thus, the Thevenin voltage is
The power delivered to the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- A plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Hi, σ¡ ). [ ει μη σ] Ex [ ει μη ση ] Ex tot E₁₂ (z) = E'₁e¹² -122 E(z) = Ee+ E₁₁₁² E₁x z=0 1. Specify the electric field reflection coefficient г and transmission coefficient T: E ΓΔ E E TA EL 2. Show that T=1+г. Can the transmitted electric field amplitude in region 2 be LARGER than the incident electric field amplitude? 3. Determine expressions for P₁AV'(z), PIAV'(z) and P2AV'(z) (note the sign for the reflected power direction should be (-z).arrow_forward2) In the ideal transformer circuit shown below find Vo and the complex power supplied by the source. 292 www b 1:4 16 Ω ww + + 240/0° V rms -12492arrow_forward3) In the ideal autotransformer circuit shown below find 11, 12 and lo. Find the average power delivered to the load. (hint: write KVL for both sides) 20/30° V(+ 2-1602 200 turns V₂ 10 + j40 Ω 80 turns V₁arrow_forward
- 1) Find Vo in the following circuit. Assume the mesh currents are clockwise. ΠΩ Ω ΖΩ ww 1Ω ww 24/0° (± 6 Ω j4 Ω 1Ω +arrow_forwardPlease show all stepsarrow_forward11-3) similar to Lathi & Ding, Prob. P.6.8-1 Consider the carrier modulator shown in the figure below, which transmits a binary carrier signal. The baseband generator uses polar NRZ signaling with rectangular pulses. The data rate is 8 Mbit/s. (a) If the modulator generates a binary PSK signal, what is the bandwidth of the modulated output? (b) If the modulator generates FSK with the difference fel - fco = 6 MHz (cf. Fig 6.32c), determine the modulated signal bandwidth. Binary data source Baseband signal generator Modulated output Modulator N-E---arrow_forward
- Choose the best answer for each: 1. What does SRAM use to store data? 。 a) Capacitors ob) Latches 。 c) Flip-flops od) Transistors 2. Which RAM type requires refreshing? o a) SRAM ob) DRAM 。 c) ROM od) Flash 3. What type of memory retains data only while power is on? a) ROM 。 b) EEPROM o c) DRAM od) Flash 4. How many addresses can a 15-bit address bus handle? o a) 32k • b) 64k o c) 16k od) lk 5. What operation occurs when data is copied out of memory without erasing? oa) Write ob) Read o c) Refresh o d) Load 6. DRAM cells store bits using: a) Flip-flops 。 b) Capacitors c) Diodes od) Resistors 7. The cache located inside the CPU is: 。 a) L2 cache o b) LI cache °c) ROM od) HDD 8. SDRAM is synchronized with: o a) Cache ob) Data Bus c) System Clock od) Hard Disk 9. The bus that carries commands is called: o a) Data Bus b) Control Bus o c) Address Bus o d) Logic Bus 10. What is the main use of SRAM? o Disk storage o Cache o Main memory o Registers 11. The smallest addressable unit in…arrow_forwardQ4: A cache memory is 128k × 16. How many bytes can it store?arrow_forwardSketch the output of the analogue computer shown below and find its closest describing function [suppose any variable to find the DF] +1 ew2 HI e2 1.0 +21 LO SJ eo SJ ew LO 1.0 +|e1| HI -1 ew1 ek(1 + e。) |e1| k = 1+|e1| Figure V-5 Feedback Limiter Behavior ROUNDED, DUE TO DIODE NONLINEARITY LIMIT VOLTAGE 409 DIODE CONDUCTS First, write the output transaction, then draw the output wave, and then find the Describing function. I need to solve the question step by step, with an explanation of each step.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





