
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780132273244
Author: Doug Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 66GP
A crane’s trolley at point P in Fig. 4-53 moves for a few seconds to the right with constant acceleration, and the 870-kg load hangs at a 5.0° angle to the vertical as shown. What is the acceleration of the trolley and load?
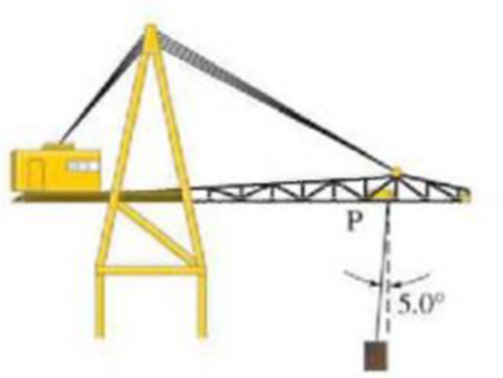
FIGURE 4-53 Problem 66.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A 85 turn, 10.0 cm diameter coil rotates at an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s in a 1.35 T field, starting with the normal of the plane of the coil perpendicular to the field. Assume that the positive max emf is reached first.
(a) What (in V) is the peak emf?
7.17
V
(b) At what time (in s) is the peak emf first reached?
0.196
S
(c) At what time (in s) is the emf first at its most negative?
0.589
x s
(d) What is the period (in s) of the AC voltage output?
0.785
S
A bobsled starts at the top of a track as human runners sprint from rest and then jump into the sled. Assume they reach 40 km/h from rest after covering a distance of 50 m over flat ice. a. How much work do they do on themselves and the sled which they are pushing given the fact that there are two men of combined mass 185 kg and the sled with a mass of 200 kg? (If you haven't seen bobsledding, watch youtube to understand better what's going on.) b. After this start, the team races down the track and descends vertically by 200 m. At the finish line the sled crosses with a speed of 55 m/s. How much energy was lost to drag and friction along the way down after the men were in the sled?
For what type of force is it not possible to define a potential energy expression?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
Ch. 4.4 - Suppose you watch a cup slide on the (smooth)...Ch. 4.5 - Return to the first Chapter-Opening Question, page...Ch. 4.5 - A massive truck collides head-on with a small...Ch. 4.5 - If you push on a heavy desk, does it always push...Ch. 4.7 - A 10.0-kg box is dragged on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - Why does a child in a wagon seem to fall backward...Ch. 4 - A box rests on the (frictionless) bed of a truck....Ch. 4 - If the acceleration of an object is zero, are no...Ch. 4 - If an object is moving, is it possible for the net...Ch. 4 - Only one force acts on an object. Can the object...
Ch. 4 - When a golf ball is dropped to the pavement, it...Ch. 4 - If you walk along a log floating on a lake, why...Ch. 4 - Why might your foot hurt if you kick a heavy desk...Ch. 4 - When you are running and want to slop quickly, you...Ch. 4 - (a) Why do you push down harder on the pedals of a...Ch. 4 - A father and his young daughter are ice skating....Ch. 4 - Suppose that you are standing on a cardboard...Ch. 4 - A stone hangs by a fine thread from the ceiling,...Ch. 4 - The force of gravity on a 2-kg rock is twice as...Ch. 4 - Would a spring scale carried to the Moon give...Ch. 4 - You pull a box with a constant force across a...Ch. 4 - When an object falls freely under the influence of...Ch. 4 - Compare the effort (or force) needed to lift a...Ch. 4 - Which of the following objects weighs about 1 N:...Ch. 4 - According to Newtons third law. each team in a tug...Ch. 4 - When you stand still on the ground, how large a...Ch. 4 - Whiplash sometimes results from an automobile...Ch. 4 - Mary exerts an upward force of 40N to hold a bag...Ch. 4 - A bear sling, Fig. 430, in used in some national...Ch. 4 - (I) What force is needed to accelerate a child on...Ch. 4 - (1) A net force of 265N accelerates a bike and...Ch. 4 - (I) What is the weight of a 68-kg astronaut (a) on...Ch. 4 - (I) How much tension must a rope withstand if it...Ch. 4 - (II) Superman must stop a 120-km/h train in 150 m...Ch. 4 - (II) What average force is required to stop a...Ch. 4 - (II) Estimate the average force exerted by a...Ch. 4 - (II) A 0.140-kg baseball traveling 35.0 m/s...Ch. 4 - (II) A fisherman yanks a fish vertically out of...Ch. 4 - (II) A 20.0-kg box rests on a table. (a) What is...Ch. 4 - (II) What average force is needed to accelerate a...Ch. 4 - (II) How much tension must a cable withstand if it...Ch. 4 - (II) A 14.0-kg bucket is lowered vertically by a...Ch. 4 - (II) A particular race car can cover a...Ch. 4 - (II) A 75-kg petty thief wants to escape from a...Ch. 4 - (II) An elevator (mass 4850 kg) is to he designed...Ch. 4 - (II) Can cars stop on a dime? Calculate the...Ch. 4 - (II) A person stands on a bathroom scale in a...Ch. 4 - (II) High-speed elevators function under two...Ch. 4 - (II) Using focused laser light, optical tweezers...Ch. 4 - (II) A rocket with a mass of 2.75 106 kg exerts a...Ch. 4 - (II) (a) What is the acceleration of two falling...Ch. 4 - (II) An exceptional standing jump would raise a...Ch. 4 - (II) The cable supporting a 2125-kg elevator has a...Ch. 4 - (III) The 100-m dash can be run by the best...Ch. 4 - (III) A person jumps from the roof of a house...Ch. 4 - (I) A box weighing 77.0 N rests on atable. A rope...Ch. 4 - (I) Draw the free-body diagram for a basketball...Ch. 4 - (I) Sketch the tree body diagram of a baseball (a)...Ch. 4 - (I) A 650-N force acts in a northwesterly...Ch. 4 - (II) Christian is making a Tyrolean traverse as...Ch. 4 - (II) A window washer pulls herself upward using...Ch. 4 - (II) One 3.2-kg paint bucket is hanging by a...Ch. 4 - (II) The cords accelerating the buckets in Problem...Ch. 4 - (II) Two snowcats in Antarctica are towing a...Ch. 4 - (II) A train locomotive is pulling two cars of the...Ch. 4 - (II) The two forces F1 and F2 shown in Fig. 4-40a...Ch. 4 - (II) At the instant a race began, a 65-kg sprinter...Ch. 4 - (II) A mass m is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 40PCh. 4 - (II) Uphill escape ramps are sometimes provided to...Ch. 4 - (II) A child on a sled reaches the bottom of a...Ch. 4 - (II) A skateboarder, with an initial speed of...Ch. 4 - (II) As shown in Fig. 4-41, five balls (masses...Ch. 4 - (II) A 27-kg chandelier hangs from a ceiling on a...Ch. 4 - (II) Three blocks on a frictionless horizontal...Ch. 4 - (II) Redo Example 413 but (a) set up the equations...Ch. 4 - (II) The block shown in Fig. 4-43 has mass m = 7.0...Ch. 4 - (II) A block is given an initial speed of 4.5 m/s...Ch. 4 - (II) An object is hanging by a string from your...Ch. 4 - (II) Figure 4-45 shows a block (mass mA) on a...Ch. 4 - (II) (a) If mA = 13.0 kg and mB = 5.0 kg in Fig....Ch. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the acceleration of...Ch. 4 - (III) Suppose the pulley in Fig. 446 is suspended...Ch. 4 - (III) A small block of mass m rests on the sloping...Ch. 4 - (III) The double Atwood machine shown in Fig. 4-48...Ch. 4 - (III) Suppose two boxes on a frictionless table...Ch. 4 - (III) The two masses shown in Fig, 450 are each...Ch. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the magnitude of the...Ch. 4 - (III) A particle of mass m, initially at rest at x...Ch. 4 - (III) A heavy steel cable of length and mass M...Ch. 4 - A person has a reasonable chance of surviving an...Ch. 4 - A 2.0-kg purse is dropped 58 m from the top of the...Ch. 4 - Toms hang glider supports his weight using the six...Ch. 4 - A wet bar of soap (m = 150 g) slides freely down a...Ch. 4 - A cranes trolley at point P in Fig. 4-53 moves for...Ch. 4 - A block (mass mA) lying on a fixed frictionless...Ch. 4 - (a) In Fig. 454, if mA = mB = 1.00 kg and 33.0,...Ch. 4 - The masses mA and mB slide on the smooth...Ch. 4 - A 75.0-kg person stands on a scale in an elevator....Ch. 4 - A city planner is working on the redesign of a...Ch. 4 - If a bicyclist of mass 65 kg (including the...Ch. 4 - A bicyclist can coast down a 5.0 hill at a...Ch. 4 - Francesca dangles her watch from a thin piece of...Ch. 4 - (a) What minimum force F is needed to lift the...Ch. 4 - In the design of a supermarket, there are to be...Ch. 4 - A jet aircraft is accelerating at 3.8m/s2 as it...Ch. 4 - A 7650-kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.80...Ch. 4 - A super high-speed 14-car Italian train has a mass...Ch. 4 - A fisherman in a boat is using a 10-lb test...Ch. 4 - An elevator in a tall building is allowed to reach...Ch. 4 - Two rock climbers, Bill and Karen, use safety...Ch. 4 - Three mountain climbers who are roped together in...Ch. 4 - A doomsday asteroid with a mass of 1.0 1010kg is...Ch. 4 - A 450-kg piano is being unloaded from a truck by...Ch. 4 - Consider the system shown in Fig. 462 with mA =...Ch. 4 - A 1.5-kg block rests on top of a 7.5-kg block...Ch. 4 - You are driving home in your 750-kg car at 15 m/s....Ch. 4 - (II) A large crate of mass 1500 kg starts sliding...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Identify me theme or themes exemplified by (a) the sharp quills of a porcupine (b) the development of a multice...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
33. Consider the reaction:
The tabulated data were collected for the concentration of C4H8 as a function...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
12. Which of the following experiments could test the hypothesis that bacteria cause ulcers in humans? (Assume ...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
9. The forces in FIGURE EX6.9 act on a 2.0 kg object. What are the values of ax and ay, the x- and y-componen...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. What do we conclude if a planet has fe...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Microphylls are found in which plant group? (A) lycophytes (B) liverworts (C) ferns (D) hornworts
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 10. Imagine you have a system in which you have 54 grams of ice. You can melt this ice and then vaporize it all at 0 C. The melting and vaporization are done reversibly into a balloon held at a pressure of 0.250 bar. Here are some facts about water you may wish to know. The density of liquid water at 0 C is 1 g/cm³. The density of ice at 0 C is 0.917 g/cm³. The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid water is 2.496 kJ/gram and the enthalpy of fusion of solid water is 333.55 J/gram.arrow_forwardConsider 1 mole of supercooled water at -10°C. Calculate the entropy change of the water when the supercooled water freezes at -10°C and 1 atm. Useful data: Cp (ice) = 38 J mol-1 K-1 Cp (water) 75J mol −1 K -1 Afus H (0°C) 6026 J mol −1 Assume Cp (ice) and Cp (water) to be independent of temperature.arrow_forwardThe molar enthalpy of vaporization of benzene at its normal boiling point (80.09°C) is 30.72 kJ/mol. Assuming that AvapH and AvapS stay constant at their values at 80.09°C, calculate the value of AvapG at 75.0°C, 80.09°C, and 85.0°C. Hint: Remember that the liquid and vapor phases will be in equilibrium at the normal boiling point.arrow_forward
- 3. The entropy of an ideal gas is S = Nkg In V. Entropy is a state function rather than a path function, and in this problem, you will show an example of the entropy change for an ideal gas being the same when you go between the same two states by two different pathways. A. Express ASV = S2 (V2) - S₁(V1), the change in entropy upon changing the volume from V₁to V2, at fixed particle number N and energy, U. B. Express ASN = S₂(N₂) - S₁ (N₁), the change in entropy upon changing the particle number from N₁ to N2, at fixed volume V and energy U. C. Write an expression for the entropy change, AS, for a two-step process (V₁, N₁) → (V2, N₁) → (V2, N₂) in which the volume changes first at fixed particle number, then the particle number changes at fixed volume. Again, assume energy is constant.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forward6. We used the constant volume heat capacity, Cv, when we talked about thermodynamic cycles. It acts as a proportionality constant between energy and temperature: dU = C₁dT. You can also define a heat capacity for constant pressure processes, Cp. You can think of enthalpy playing a similar role to energy, but for constant pressure processes δαρ C = (37) - Sup Ср ат P = ат Starting from the definition of enthalpy, H = U + PV, find the relationship between Cy and Cp for an ideal gas.arrow_forward
- Pure membranes of dipalmitoyl lecithin phospholipids are models of biological membranes. They melt = 41°C. Reversible melting experiments indicate that at Tm AHm=37.7 kJ mol-1. Calculate: A. The entropy of melting, ASm- B. The Gibbs free energy of melting, AGm- C. Does the membrane become more or less ordered upon melting? D. There are 32 rotatable CH2 CH2 bonds in each molecule that can rotate more freely if the membrane melts. What is the increase in multiplicity on melting a mole of bonds?arrow_forward5. Heat capacity often has a temperature dependence for real molecules, particularly if you go over a large temperature range. The heat capacity for liquid n-butane can be fit to the equation Cp(T) = a + bT where a = 100 J K₁₁ mol¹ and b = 0.1067 J K² mol¹ from its freezing point (T = 140 K) to its boiling point (T₁ = 270 K). A. Compute AH for heating butane from 170 K to 270 K. B. Compute AS for the same temperature range.arrow_forward4. How much energy must be transferred as heat to cause the quasi-static isothermal expansion of one mole of an ideal gas at 300 K from PA = 1 bar to PB = 0.5 bar? A. What is VA? B. What is VB? C. What is AU for the process? D. What is AH for the process? E. What is AS for the process?arrow_forward
- 1. The diagram shows the tube used in the Thomson experiment. a. State the KE of the electrons. b. Draw the path of the electron beam in the gravitational field of the earth. C. If the electric field directed upwards, deduce the direction of the magnetic field so it would be possible to balance the forces. electron gun 1KVarrow_forwardas a hiker in glacier national park, you need to keep the bears from getting at your food supply. You find a campground that is near an outcropping of ice. Part of the outcropping forms a feta=51.5* slopeup that leads to a verticle cliff. You decide that this is an idea place to hang your food supply out of bear reach. You put all of your food into a burlap sack, tie a rope to the sack, and then tie a bag full of rocks to the other end of the rope to act as an anchor. You currently have 18.5 kg of food left for the rest of your trip, so you put 18.5 kg of rocks in the anchor bag to balance it out. what happens when you lower the food bag over the edge and let go of the anchor bag? Determine the acceleration magnitude a of the two-bag system when you let go of the anchor bag?arrow_forward2. A thin Nichrome wire is used in an experiment to test Ohm's law using a power supply ranging from 0 to 12 V in steps of 2 V. Why isn't the graph of I vs V linear? 1. Nichrome wire does obey Ohm's law. Explain how that can that be true given the results abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY