
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780132273244
Author: Doug Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 50P
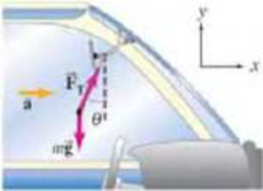
(II) An object is hanging by a string from your rearview mirror. While you are accelerating at a constant rate from rest to 28 m/s in 6.0 s, what angle θ does the string make with the vertical? See Fig. 4–44.
FIGURE 4–44
Problem 50.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Experimental Research Report Template
Title: Paper Airplane Flight. Materials: Paper, ruler, tape
Procedure: Fold paper into different airplane designs, such as dart, glider, or classic. Measure and record the distances each design flies when thrown with the same force. Discuss aerodynamics and the factors that affect flight distance.
Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.)
Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.)
Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.)
Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.)
Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the…
Title: Studying the Relationship Between Drop Height and Bouncing Height of a Ball: You can drop balls of different materials (e.g., rubber, plastic, ping pong) from various heights onto a flat surface and measure the height of their bounce using a ruler.
Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.)
Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.)
Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.)
Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.)
Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the lab: tables, charts, graphs, sketches, etc.)
Data Analysis: (Explain you…
A traveler at an airport takes an escalator up one floor as in the figure below. The moving staircase would itself carry him upward with vertical velocity component v between entry and exit points separated by height h. However, while the escalator is moving, the hurried traveler climbs the
steps of the escalator at a rate of n steps/s. Assume that the height of each step is hs.
(a) Determine the amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy by the traveler's leg muscles during his escalator ride given that his mass is m. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.)
energy =
(b) Determine the work the escalator motor does on this person. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.)
work =
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics for Science and Engineering With Modern Physics, VI - Student Study Guide
Ch. 4.4 - Suppose you watch a cup slide on the (smooth)...Ch. 4.5 - Return to the first Chapter-Opening Question, page...Ch. 4.5 - A massive truck collides head-on with a small...Ch. 4.5 - If you push on a heavy desk, does it always push...Ch. 4.7 - A 10.0-kg box is dragged on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - Why does a child in a wagon seem to fall backward...Ch. 4 - A box rests on the (frictionless) bed of a truck....Ch. 4 - If the acceleration of an object is zero, are no...Ch. 4 - If an object is moving, is it possible for the net...Ch. 4 - Only one force acts on an object. Can the object...
Ch. 4 - When a golf ball is dropped to the pavement, it...Ch. 4 - If you walk along a log floating on a lake, why...Ch. 4 - Why might your foot hurt if you kick a heavy desk...Ch. 4 - When you are running and want to slop quickly, you...Ch. 4 - (a) Why do you push down harder on the pedals of a...Ch. 4 - A father and his young daughter are ice skating....Ch. 4 - Suppose that you are standing on a cardboard...Ch. 4 - A stone hangs by a fine thread from the ceiling,...Ch. 4 - The force of gravity on a 2-kg rock is twice as...Ch. 4 - Would a spring scale carried to the Moon give...Ch. 4 - You pull a box with a constant force across a...Ch. 4 - When an object falls freely under the influence of...Ch. 4 - Compare the effort (or force) needed to lift a...Ch. 4 - Which of the following objects weighs about 1 N:...Ch. 4 - According to Newtons third law. each team in a tug...Ch. 4 - When you stand still on the ground, how large a...Ch. 4 - Whiplash sometimes results from an automobile...Ch. 4 - Mary exerts an upward force of 40N to hold a bag...Ch. 4 - A bear sling, Fig. 430, in used in some national...Ch. 4 - (I) What force is needed to accelerate a child on...Ch. 4 - (1) A net force of 265N accelerates a bike and...Ch. 4 - (I) What is the weight of a 68-kg astronaut (a) on...Ch. 4 - (I) How much tension must a rope withstand if it...Ch. 4 - (II) Superman must stop a 120-km/h train in 150 m...Ch. 4 - (II) What average force is required to stop a...Ch. 4 - (II) Estimate the average force exerted by a...Ch. 4 - (II) A 0.140-kg baseball traveling 35.0 m/s...Ch. 4 - (II) A fisherman yanks a fish vertically out of...Ch. 4 - (II) A 20.0-kg box rests on a table. (a) What is...Ch. 4 - (II) What average force is needed to accelerate a...Ch. 4 - (II) How much tension must a cable withstand if it...Ch. 4 - (II) A 14.0-kg bucket is lowered vertically by a...Ch. 4 - (II) A particular race car can cover a...Ch. 4 - (II) A 75-kg petty thief wants to escape from a...Ch. 4 - (II) An elevator (mass 4850 kg) is to he designed...Ch. 4 - (II) Can cars stop on a dime? Calculate the...Ch. 4 - (II) A person stands on a bathroom scale in a...Ch. 4 - (II) High-speed elevators function under two...Ch. 4 - (II) Using focused laser light, optical tweezers...Ch. 4 - (II) A rocket with a mass of 2.75 106 kg exerts a...Ch. 4 - (II) (a) What is the acceleration of two falling...Ch. 4 - (II) An exceptional standing jump would raise a...Ch. 4 - (II) The cable supporting a 2125-kg elevator has a...Ch. 4 - (III) The 100-m dash can be run by the best...Ch. 4 - (III) A person jumps from the roof of a house...Ch. 4 - (I) A box weighing 77.0 N rests on atable. A rope...Ch. 4 - (I) Draw the free-body diagram for a basketball...Ch. 4 - (I) Sketch the tree body diagram of a baseball (a)...Ch. 4 - (I) A 650-N force acts in a northwesterly...Ch. 4 - (II) Christian is making a Tyrolean traverse as...Ch. 4 - (II) A window washer pulls herself upward using...Ch. 4 - (II) One 3.2-kg paint bucket is hanging by a...Ch. 4 - (II) The cords accelerating the buckets in Problem...Ch. 4 - (II) Two snowcats in Antarctica are towing a...Ch. 4 - (II) A train locomotive is pulling two cars of the...Ch. 4 - (II) The two forces F1 and F2 shown in Fig. 4-40a...Ch. 4 - (II) At the instant a race began, a 65-kg sprinter...Ch. 4 - (II) A mass m is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 40PCh. 4 - (II) Uphill escape ramps are sometimes provided to...Ch. 4 - (II) A child on a sled reaches the bottom of a...Ch. 4 - (II) A skateboarder, with an initial speed of...Ch. 4 - (II) As shown in Fig. 4-41, five balls (masses...Ch. 4 - (II) A 27-kg chandelier hangs from a ceiling on a...Ch. 4 - (II) Three blocks on a frictionless horizontal...Ch. 4 - (II) Redo Example 413 but (a) set up the equations...Ch. 4 - (II) The block shown in Fig. 4-43 has mass m = 7.0...Ch. 4 - (II) A block is given an initial speed of 4.5 m/s...Ch. 4 - (II) An object is hanging by a string from your...Ch. 4 - (II) Figure 4-45 shows a block (mass mA) on a...Ch. 4 - (II) (a) If mA = 13.0 kg and mB = 5.0 kg in Fig....Ch. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the acceleration of...Ch. 4 - (III) Suppose the pulley in Fig. 446 is suspended...Ch. 4 - (III) A small block of mass m rests on the sloping...Ch. 4 - (III) The double Atwood machine shown in Fig. 4-48...Ch. 4 - (III) Suppose two boxes on a frictionless table...Ch. 4 - (III) The two masses shown in Fig, 450 are each...Ch. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the magnitude of the...Ch. 4 - (III) A particle of mass m, initially at rest at x...Ch. 4 - (III) A heavy steel cable of length and mass M...Ch. 4 - A person has a reasonable chance of surviving an...Ch. 4 - A 2.0-kg purse is dropped 58 m from the top of the...Ch. 4 - Toms hang glider supports his weight using the six...Ch. 4 - A wet bar of soap (m = 150 g) slides freely down a...Ch. 4 - A cranes trolley at point P in Fig. 4-53 moves for...Ch. 4 - A block (mass mA) lying on a fixed frictionless...Ch. 4 - (a) In Fig. 454, if mA = mB = 1.00 kg and 33.0,...Ch. 4 - The masses mA and mB slide on the smooth...Ch. 4 - A 75.0-kg person stands on a scale in an elevator....Ch. 4 - A city planner is working on the redesign of a...Ch. 4 - If a bicyclist of mass 65 kg (including the...Ch. 4 - A bicyclist can coast down a 5.0 hill at a...Ch. 4 - Francesca dangles her watch from a thin piece of...Ch. 4 - (a) What minimum force F is needed to lift the...Ch. 4 - In the design of a supermarket, there are to be...Ch. 4 - A jet aircraft is accelerating at 3.8m/s2 as it...Ch. 4 - A 7650-kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.80...Ch. 4 - A super high-speed 14-car Italian train has a mass...Ch. 4 - A fisherman in a boat is using a 10-lb test...Ch. 4 - An elevator in a tall building is allowed to reach...Ch. 4 - Two rock climbers, Bill and Karen, use safety...Ch. 4 - Three mountain climbers who are roped together in...Ch. 4 - A doomsday asteroid with a mass of 1.0 1010kg is...Ch. 4 - A 450-kg piano is being unloaded from a truck by...Ch. 4 - Consider the system shown in Fig. 462 with mA =...Ch. 4 - A 1.5-kg block rests on top of a 7.5-kg block...Ch. 4 - You are driving home in your 750-kg car at 15 m/s....Ch. 4 - (II) A large crate of mass 1500 kg starts sliding...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In the following diagram, the white spheres represent hydrogen atoms and the blue Sphere represent the nitrogen...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Police Captain Jeffers has suffered a myocardial infarction. a. Explain to his (nonmedically oriented) family w...
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
During exponential growth, a population always (A) has a constant per capita population growth rate. (B) quickl...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
16. Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a g...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
A Slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is part of the interior of the Sun? photosphere the corona sunspots radiation zonearrow_forwardMost craters on the surface of the Moon are believed to be caused by which of the following? faults asteroids volcanoes meteoroidsarrow_forwardAn object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes? y (m) C B (5.00, 5.00) A x (m) © (a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O ] (b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation? ○ The force of friction is a conservative force. ○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done by the applied force. ] (b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table. ] (c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. ] (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. ]arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.845 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.357 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 294 N on the crate. e (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude direction ---Select--- N (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. ] (c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. × J 37° Barrow_forward
- You are working for the Highway Department. In mountainous regions, highways sometimes include a runaway truck ramp, and you are asked to help with the design of such a ramp. A runaway truck ramp is often a lane of gravel adjacent to a long downhill section of roadway where trucks with failing brakes may need assistance to stop. Working with your supervisor, you develop a worst-case scenario: a truck with a mass of 6.00 × 104 kg enters a runaway truck lane traveling at 34.1 m/s. Assume that the maximum constant value for safe acceleration of the truck is -5.00 m/s². Any higher magnitude of acceleration increases the likelihood that semi-trailer rigs could jackknife. Your supervisor asks you to advise her on the required length (in m) of a runaway truck lane on a flat section of ground next to the roadway. marrow_forwardA large cruise ship of mass 6.20 × 107 kg has a speed of 10.2 m/s at some instant. (a) What is the ship's kinetic energy at this time? ] (b) How much work is required to stop it? (Give the work done on the ship. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) ] (c) What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 3.10 km? Narrow_forwardA 7.80 g bullet is initially moving at 660 m/s just before it penetrates a block of wood to a depth of 6.20 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average frictional force (in N) that is exerted on the bullet while it is moving through the block of wood? Use work and energy considerations to obtain your answer. N (b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, how much time (in s) elapses between the moment the bullet enters the block of wood and the moment it stops moving? Sarrow_forward
- Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to ①, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. ] 37° A © Barrow_forwardA skateboarder with his board can be modeled as a particle of mass 80.0 kg, located at his center of mass. As shown in the figure below, the skateboarder starts from rest in a crouching position at one lip of a half-pipe (point). On his descent, the skateboarder moves without friction so that his center of mass moves through one quarter of a circle of radius 6.20 m. i (a) Find his speed at the bottom of the half-pipe (point Ⓡ). m/s (b) Immediately after passing point Ⓑ, he stands up and raises his arms, lifting his center of mass and essentially "pumping" energy into the system. Next, the skateboarder glides upward with his center of mass moving in a quarter circle of radius 5.71 m, reaching point D. As he passes through point ①, the speed of the skateboarder is 5.37 m/s. How much chemical potential energy in the body of the skateboarder was converted to mechanical energy when he stood up at point Ⓑ? ] (c) How high above point ① does he rise? marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY