
Concept explainers
Read Appendix B on naming bicyclic compounds. Then give IUPAC name for each of the following compounds.
a. 
b. 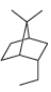
c. 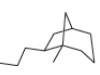
d. 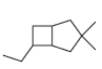
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The root name of bicyclic compounds depends upon the number of carbon atoms present in the rings. The naming of bicyclic compounds is done as,
(1) The total number of carbon atoms in the molecule is to be counted. It represents the root name.
(2) The number of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads is to be counted and placed in square brackets in descending order.
(3) The word bicyclo is placed at the beginning of the name.
The general name such compounds is represented as
Answer to Problem 4.75P
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given bicyclic compound is shown below.
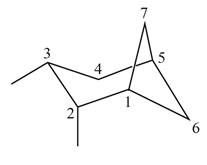
Figure 1
The given compound contains seven carbon atoms in the ring which are single bonded to each other. Therefore, the root name is heptane. In this case, there are
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The root name of bicyclic compounds depends upon the number of carbon atoms present in the rings. The naming of bicyclic compounds is done as,
(1) The total number of carbon atoms in the molecule is to be counted. It represents the root name.
(2) The number of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads is to be counted and placed in square brackets in descending order.
(3) The word bicyclo is placed at the beginning of the name.
The general name such compounds is represented as
Answer to Problem 4.75P
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given bicyclic compound is shown below.
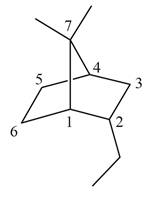
Figure 2
The given compound contains seven carbon atoms in the ring which are single bonded to each other. Therefore, the root name is heptane. In this case, there are
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The root name of bicyclic compounds depends upon the number of carbon atoms present in the rings. The naming of bicyclic compounds is done as,
(1) The total number of carbon atoms in the molecule is to be counted. It represents the root name.
(2) The number of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads is to be counted and placed in square brackets in descending order.
(3) The word bicyclo is placed at the beginning of the name.
The general name such compounds is represented as
Answer to Problem 4.75P
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given bicyclic compound is shown below.
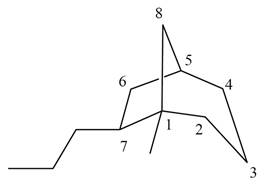
Figure 3
The given compound contains eight carbon atoms in the ring which are single bonded to each other. Therefore, the root name is octane. In this case, there are
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
(d)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The root name of bicyclic compounds depends upon the number of carbon atoms present in the rings. The naming of bicyclic compounds is done as,
(1) The total number of carbon atoms in the molecule is to be counted. It represents the root name.
(2) The number of carbon atoms between the bridgeheads is to be counted and placed in square brackets in descending order.
(3) The word bicyclo is placed at the beginning of the name.
The general name such compounds is represented as
Answer to Problem 4.75P
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given bicyclic compound is shown below.
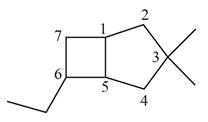
Figure 4
The given compound contains seven carbon atoms in the ring which are single bonded to each other. Therefore, the root name is heptane. In this case, there are
The IUPAC name for the given bicyclic compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning




