
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 36P
For each of the distributions of the electric potential V shown in Fig. P4.36, sketch the corresponding distribution of E (in all cases, the vertical axis is in volts and the horizontal axis is in meters).
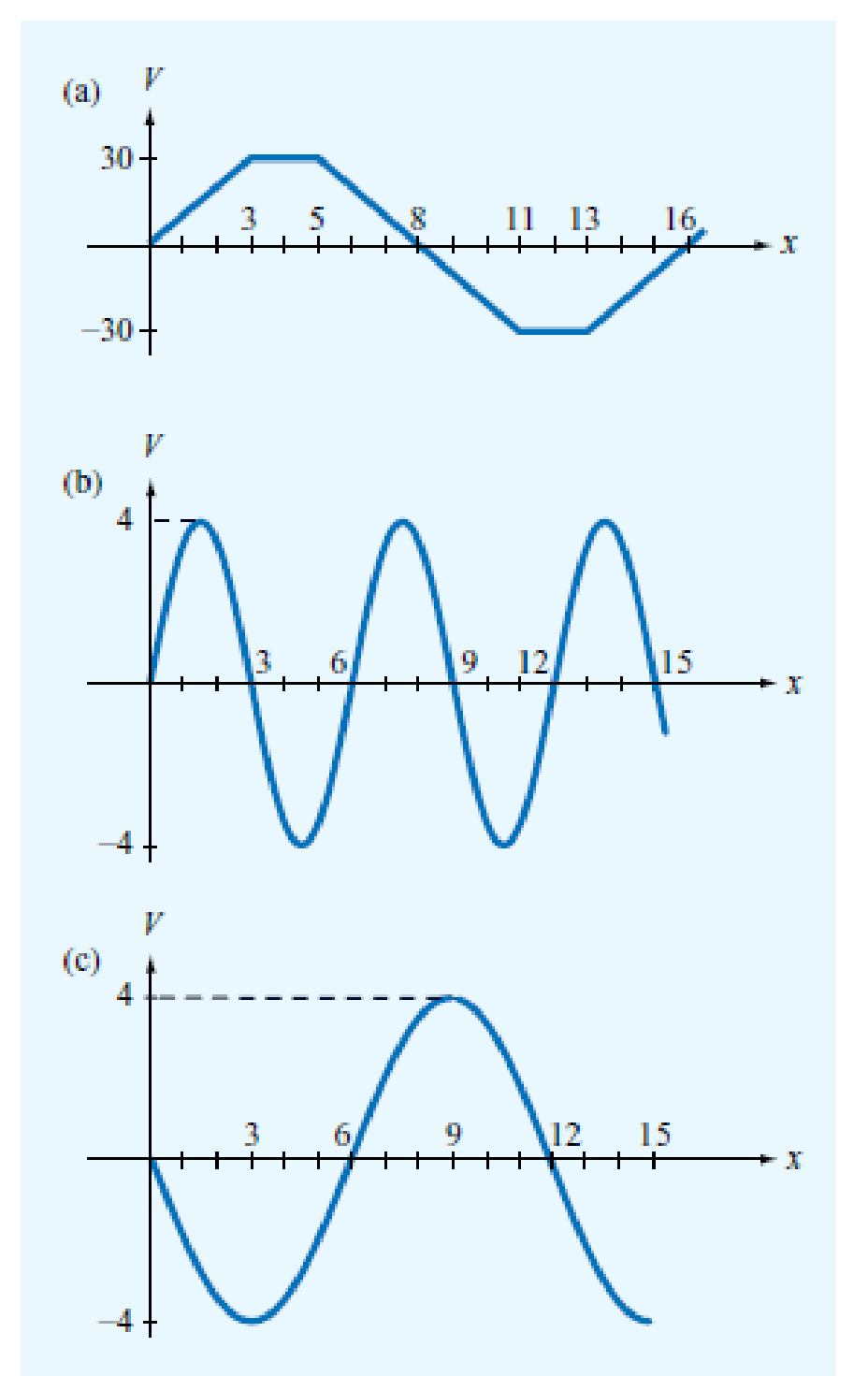
Figure P4.36 Electric potential distributions of Problem 4.36.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
For the circuit shown, let V₁ = 26, R1-30, R₂-40, R3-50, R4-20, R5-100, R6-10, and find:
RA
R5
R3
V
(+)
R₁
R₂
R6
www
• The voltage v
(V)
• The power delivered by the power source Vs: Power=
{Hint: you can use voltage divider (VD) or any other method.}
(W)
In the circuit shown, let R₁-7, R₂-12, R3-24, R4-2, V₁ =17, V2 -68, and V3-51, to calculate the power
delivered (or absorbed) by the circuit inside the box, as follows:
{NOTE: On Multiple Choice Questions, like this problem, you have only one attempt }
1. The current I is equal to (choose the closed values in amperes)
-0.791
0
-0.756
3.022
0.756
(A)
-3.022
0.791
2. The power delivered (or absorbed) (choose the closest value in watts) (W)
373.345
0
-373.345
-52.234
52.234
65.079
O-24.833
R₁
V₂
R3
R₂
www
V3
V₁
www
R4
Determine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the
differentiation property of the Fourier Transform.
x(t)
Figure (1)
-2
-1
1
2
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 4.2 - What happens to Maxwells equations under static...Ch. 4.2 - How is the current density J related to the volume...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 3CQCh. 4.2 - A square plate residing in the xy plane is...Ch. 4.2 - A thick spherical shell centered at the origin...Ch. 4.3 - When characterizing the electrical permittivity of...Ch. 4.3 - If the electric field is zero at a given point in...Ch. 4.3 - State the principle of linear superposition as it...Ch. 4.3 - Four charges of 10 C each are located in free...Ch. 4.3 - Two identical charges are located on the x axis at...
Ch. 4.3 - In a hydrogen atom the electron and proton are...Ch. 4.3 - An infinite sheet with uniform surface charge...Ch. 4.4 - Explain Gausss law. Under what circumstances is it...Ch. 4.4 - How should one choose a Gaussian surface?Ch. 4.4 - Two infinite lines, each carrying a uniform charge...Ch. 4.4 - A thin spherical shell of radius a carries a...Ch. 4.4 - A spherical volume of radius a contains a uniform...Ch. 4.5 - What is a conservative field?Ch. 4.5 - Why is the electric potential at a point in space...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 4.5 - Why is it usually easier to compute V for a given...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 13CQCh. 4.5 - Determine the electric potential at the origin due...Ch. 4.5 - A spherical shell of radius a has a uniform...Ch. 4.6 - What are the electromagnetic constitutive...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 15CQCh. 4.6 - What is the conductivity of a perfect dielectric?Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 17CQCh. 4.6 - Prob. 18CQCh. 4.6 - Determine the density of free electrons in...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 13ECh. 4.6 - A 50 m long copper wire has a circular cross...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 15ECh. 4.7 - What is a polar material? A nonpolar material?Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 20CQCh. 4.7 - What happens when dielectric breakdown occurs?Ch. 4.7 - Find E1 in Fig. 4-19 if E2=x2y3+z3(v/m),1=20,2=80,...Ch. 4.7 - Repeat Exercise 4.16 for a boundary with surface...Ch. 4.8 - What are the boundary conditions for the electric...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 23CQCh. 4.9 - How is the capacitance of a two-conductor...Ch. 4.9 - What are fringing fields and when may they be...Ch. 4.10 - To bring a charge q from infinity to a given point...Ch. 4.10 - Prob. 27CQCh. 4.10 - The radii of the inner and outer conductors of a...Ch. 4.11 - What is the fundamental premise of the image...Ch. 4.11 - Given a charge distribution, what are the various...Ch. 4.11 - Use the result of Example 4-13 to find the surface...Ch. 4 - A cube 2 m on a side is located in the first...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2PCh. 4 - Find the total charge contained in a round-top...Ch. 4 - If the line charge density is given by l = 24y2...Ch. 4 - Find the total charge on a circular disk defined...Ch. 4 - If J = 4xz (A/m2), find the current I flowing...Ch. 4 - Prob. 7PCh. 4 - An electron beam shaped like a circular cylinder...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9PCh. 4 - A line of charge of uniform density occupies a...Ch. 4 - A square with sides of 2 m has a charge of 40 C at...Ch. 4 - Three point charges, each with q = 3 nC, are...Ch. 4 - Charge q1 = 6 C is located at (1 cm, 1 cm, 0) and...Ch. 4 - A line of charge with uniform density = 8 (C/m)...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - A line of charge with uniform density l extends...Ch. 4 - Repeat Example 4-5 for liie circular disk of...Ch. 4 - Multiple charges at different locations are said...Ch. 4 - Three infinite lines of charge, all parallel to...Ch. 4 - Prob. 20PCh. 4 - A horizontal strip lying in the xy plane is of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4 - Charge Q1 is uniformly distributed over a thin...Ch. 4 - The electric flux density inside a dielectric...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26PCh. 4 - An infinitely long cylindrical shell extending...Ch. 4 - If the charge density increases linearly with...Ch. 4 - A spherical shell with outer radius b surrounds a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 30PCh. 4 - Prob. 31PCh. 4 - A circular ring of charge of radius a lies in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 33PCh. 4 - Find the electric potential V at a location a...Ch. 4 - For the electric dipole shown in Fig. 4-13, d = 1...Ch. 4 - For each of the distributions of the electric...Ch. 4 - Two infinite lines of charge, both parallel to the...Ch. 4 - Given the electric field E=R18R2(V/m) find the...Ch. 4 - An infinitely long line of charge with uniform...Ch. 4 - The xy plane contains a uniform sheet of charge...Ch. 4 - A cylindrical bar of silicon has a radius of 4 mm...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem 4.41 for a bar of germanium with e...Ch. 4 - A 100 m long conductor of uniform cross-section...Ch. 4 - Prob. 44PCh. 4 - Apply the result of Problem 4.44 to find the...Ch. 4 - A 2 103 mm thick square sheet of aluminum has 5 cm...Ch. 4 - A cylinder-shaped carbon resistor is 8 cm in...Ch. 4 - With reference to Fig. 4-19, find E1 if...Ch. 4 - An infinitely long cylinder of radius a is...Ch. 4 - If E=R150(V/m) at the surface of a 5-cm conducting...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.51 shows three planar dielectric slabs...Ch. 4 - Determine the force of attraction in a...Ch. 4 - Dielectric breakdown occurs in a material whenever...Ch. 4 - An electron with charge Qe = 1.61019 C and mass me...Ch. 4 - In a dielectric medium with r = 4, the electric...Ch. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - Prob. 57PCh. 4 - Prob. 58PCh. 4 - Prob. 59PCh. 4 - Prob. 60PCh. 4 - Prob. 61PCh. 4 - Conducting wires above a conducting plane carry...Ch. 4 - Prob. 63P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a enahnced-type NMOS transistor with V₁=+1V and kn'(w/L)= 2 mA/V2, find the minimum VDs required to operate in the saturation region when VGS=+2 V. What is the corresponding value of ID?arrow_forward. Using Properties to find the Z-Transform including the region of convergence for x(n) = n (2)" cos(0.2π(n − 2))u(n − 1) - -arrow_forwardJ VDD M₁ In the circuit of figure shown below, determine the region of operation of M₁as Vigoes from VDD.to zero. (You may want to draw a plot or just explain by the range, remember the transistor is a PMOS) Assume VDD = 2.5 V and | VTH | = 0.4V. 5 + 1 Varrow_forward
- We wish to design the circuit of the figure shown below for a drain current of 1 mA (l=1mA). If W/L = 18/0.18, compute R1 and R2 such that the input impedance is at least 20 k. R₁ VDD = 1.8 V 500 Ω M₁ R₂arrow_forwardIn the figure shown below, what is the minimum allowable value of VDD if M₁ must not enter the triode region? Assume λ=0 (use ideal current formula that is not dependent on VDs) 1 V + RD VDD = 1.8 V T M 500 Ω 1 W 10 L = 0.18arrow_forwardCalculate the total charge stored in the channel of an NMOS device if Cox=10fF/um², w=10 µm, L=0.1 μm, and VGS-VTH=1 V. Assume VDs=0. (means there is no movement of electrons, all of them are piled up in the channel, we want to calculate the magnitude of electron charge |Q|)arrow_forward
- The first photo is question 1arrow_forwarda) Write down the order of the transfer function in each of the following cases. Assume that there are no terms in the numerator that will cancel terms in the denominator. 10 H(s) H(s) = s+1 5 (s+3)(s—. 4) 4s1 5 H(s) = H(s) - 83 +1 s27s 6 H(s) H(s) = s(s²+4s) 2s27s+1 84583882 +3s+2 H(s) 83 +8 s+1 = H(s) s34s26s+5 s52s4383 + 4s2 +5s +6arrow_forwardQuestion 5 ( A system is found to have zeros of -3 and poles of 4, and -2. The system also has a gain of 4. Write out the corresponding transfer function. Question 6. A system has a transfer function of What is the gain, K, of the system? Question 7 ( A system has a transfer function of H(s) - 4 8+5 H(s): = 4 8 +5 A step input of size 3 is applied to the system at time zero (Since we're dealing with transfer functions, x(0) is also zero at time zero). a) [10] What is the response ✗(s) of the system? b) [10] Derive the time dependent solution, x(t), of this responsearrow_forward
- Note: You might want to do the last question first because the last question asks you to write some python code to calculate the zeros and poles. You could use that code here to help you (except the first problem which you should be able to do by inspection alone) Find the poles and zeros for each of the following transfer functions 1. S+3 H(s) = 8 5 2. H(s): = s238 +1 s2 +48 +3 3. s(s+4) H(s) s3+2s23s 4. 82-586 H(s) = - 8382-68 5. H(s): = s2 +48 +3 s45836s2 - 6arrow_forwardWrite python program to plot the zeros and poles if a user provides the coefficients for the numerator and denominator of the transfer function. Since the zeros and poles can be complex, this plot is essentially and argand diagram, where the x axis is the real component and the y axis the imaginary component of a given zero or pole. Create a method called plot-poles zeros(num, den) which takes two lists containing the coefficients. Here is an example and the resulting plot. num [1, 3, 7] # yields zeros at -1.5 +/- 2.17945j den = [1, 4, 5, 3] # yields poles at -2.46557, -0.7672143 +/- 0.7925519j plot_poles_zeros(num, den) Imaginary Page 2 Pole-Zero Plot 3 Zeros × Poles 2 1 -2 1 * Real When you write your code you are only allowed to use the packages numpy and matplotlib. Make sure you label the axes, provide a legend and give a title to your plot (See the example plot). Hint: numpy has a method called roots. When given a list of numbers corresponding to the coefficients of a polynomial,…arrow_forwarda) [10] Compute the zeros and poles for the following transfer function: $2 +5s+6 H(s): s2 +3s+2 b) [10] Factor both polynomials in the numerator and denominator. What does this tell you about one of the poles and zeros you found in a)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Electric Charge and Electric Fields; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VFbyDCG_j18;License: Standard Youtube License