
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 62P
Conducting wires above a conducting plane carry currents I1 and I2 in the directions shown in Fig. P4.62. Keeping in mind that the direction of a current is defined in terms of the movement of positive charges, what are the directions of the image currents corresponding to I1 and I2?
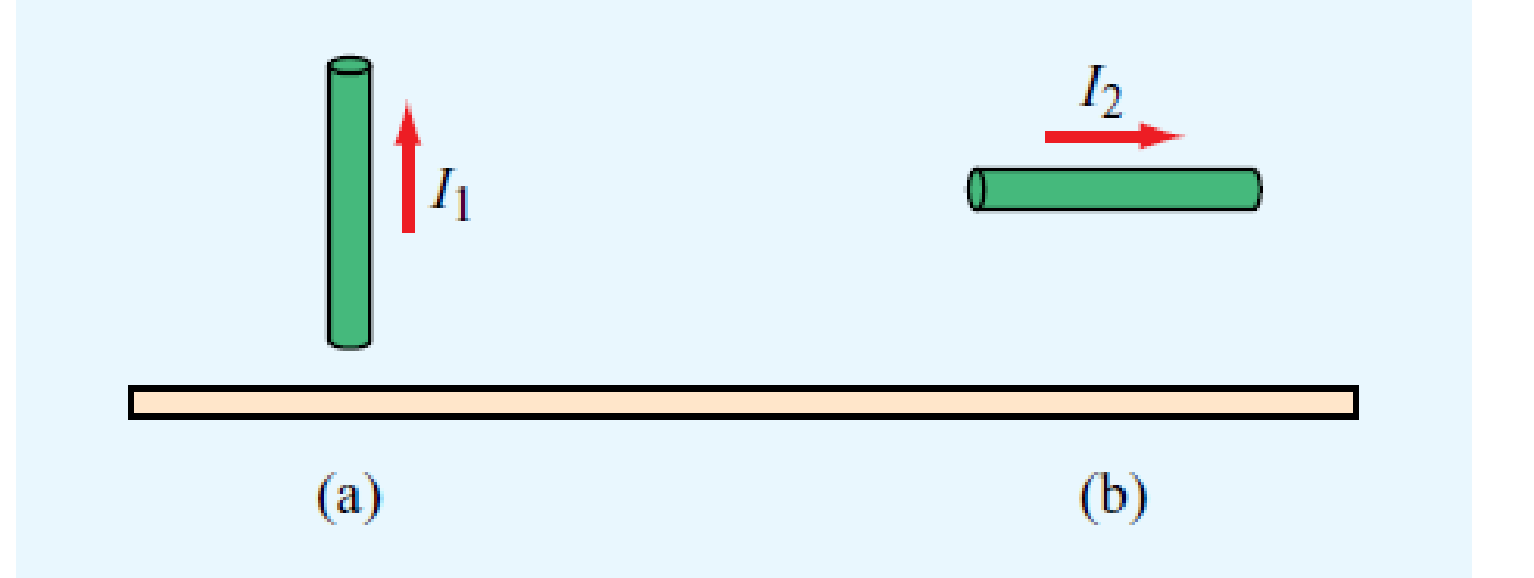
Figure P4.62 Currents above a conducting plane (Problem 4.62).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A dc compound motor having a rating of 10 kW,
1150 r/min, 230 V, 50 A, has the following losses at
full-load:
bearing friction loss
40 W
brush friction loss
==
50 W
windage loss
=
200 W
(1)
total mechanical losses
=
290 W
(2)
iron losses
=
420 W
(3)
copper loss in the shunt field
=
120 W
copper losses at full-load:
(4)
a. in the armature
b. in the series field
c. in the commutating winding
total copper loss in the
500 W
25 W
70 W
armature circuit at full-load
=
595 W
4 What determines the power rating of a ma-
chine?
-5 If we cover up the vents in a motor, its out-
put power must be reduced. Explain.
-6 If a motor operates in a cold environment,
may we load it above its rated power? Why?
An electric motor driving a skip hoist with-
draws 1.5 metric tons of minerals from a
trench 20 m deep every 30 seconds. If the
hoist has an overall efficiency of 94 percent,
calculate the power output of the motor in
horsepower and in kilowatts.
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 4.2 - What happens to Maxwells equations under static...Ch. 4.2 - How is the current density J related to the volume...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 3CQCh. 4.2 - A square plate residing in the xy plane is...Ch. 4.2 - A thick spherical shell centered at the origin...Ch. 4.3 - When characterizing the electrical permittivity of...Ch. 4.3 - If the electric field is zero at a given point in...Ch. 4.3 - State the principle of linear superposition as it...Ch. 4.3 - Four charges of 10 C each are located in free...Ch. 4.3 - Two identical charges are located on the x axis at...
Ch. 4.3 - In a hydrogen atom the electron and proton are...Ch. 4.3 - An infinite sheet with uniform surface charge...Ch. 4.4 - Explain Gausss law. Under what circumstances is it...Ch. 4.4 - How should one choose a Gaussian surface?Ch. 4.4 - Two infinite lines, each carrying a uniform charge...Ch. 4.4 - A thin spherical shell of radius a carries a...Ch. 4.4 - A spherical volume of radius a contains a uniform...Ch. 4.5 - What is a conservative field?Ch. 4.5 - Why is the electric potential at a point in space...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 4.5 - Why is it usually easier to compute V for a given...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 13CQCh. 4.5 - Determine the electric potential at the origin due...Ch. 4.5 - A spherical shell of radius a has a uniform...Ch. 4.6 - What are the electromagnetic constitutive...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 15CQCh. 4.6 - What is the conductivity of a perfect dielectric?Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 17CQCh. 4.6 - Prob. 18CQCh. 4.6 - Determine the density of free electrons in...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 13ECh. 4.6 - A 50 m long copper wire has a circular cross...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 15ECh. 4.7 - What is a polar material? A nonpolar material?Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 20CQCh. 4.7 - What happens when dielectric breakdown occurs?Ch. 4.7 - Find E1 in Fig. 4-19 if E2=x2y3+z3(v/m),1=20,2=80,...Ch. 4.7 - Repeat Exercise 4.16 for a boundary with surface...Ch. 4.8 - What are the boundary conditions for the electric...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 23CQCh. 4.9 - How is the capacitance of a two-conductor...Ch. 4.9 - What are fringing fields and when may they be...Ch. 4.10 - To bring a charge q from infinity to a given point...Ch. 4.10 - Prob. 27CQCh. 4.10 - The radii of the inner and outer conductors of a...Ch. 4.11 - What is the fundamental premise of the image...Ch. 4.11 - Given a charge distribution, what are the various...Ch. 4.11 - Use the result of Example 4-13 to find the surface...Ch. 4 - A cube 2 m on a side is located in the first...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2PCh. 4 - Find the total charge contained in a round-top...Ch. 4 - If the line charge density is given by l = 24y2...Ch. 4 - Find the total charge on a circular disk defined...Ch. 4 - If J = 4xz (A/m2), find the current I flowing...Ch. 4 - Prob. 7PCh. 4 - An electron beam shaped like a circular cylinder...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9PCh. 4 - A line of charge of uniform density occupies a...Ch. 4 - A square with sides of 2 m has a charge of 40 C at...Ch. 4 - Three point charges, each with q = 3 nC, are...Ch. 4 - Charge q1 = 6 C is located at (1 cm, 1 cm, 0) and...Ch. 4 - A line of charge with uniform density = 8 (C/m)...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - A line of charge with uniform density l extends...Ch. 4 - Repeat Example 4-5 for liie circular disk of...Ch. 4 - Multiple charges at different locations are said...Ch. 4 - Three infinite lines of charge, all parallel to...Ch. 4 - Prob. 20PCh. 4 - A horizontal strip lying in the xy plane is of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4 - Charge Q1 is uniformly distributed over a thin...Ch. 4 - The electric flux density inside a dielectric...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26PCh. 4 - An infinitely long cylindrical shell extending...Ch. 4 - If the charge density increases linearly with...Ch. 4 - A spherical shell with outer radius b surrounds a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 30PCh. 4 - Prob. 31PCh. 4 - A circular ring of charge of radius a lies in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 33PCh. 4 - Find the electric potential V at a location a...Ch. 4 - For the electric dipole shown in Fig. 4-13, d = 1...Ch. 4 - For each of the distributions of the electric...Ch. 4 - Two infinite lines of charge, both parallel to the...Ch. 4 - Given the electric field E=R18R2(V/m) find the...Ch. 4 - An infinitely long line of charge with uniform...Ch. 4 - The xy plane contains a uniform sheet of charge...Ch. 4 - A cylindrical bar of silicon has a radius of 4 mm...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem 4.41 for a bar of germanium with e...Ch. 4 - A 100 m long conductor of uniform cross-section...Ch. 4 - Prob. 44PCh. 4 - Apply the result of Problem 4.44 to find the...Ch. 4 - A 2 103 mm thick square sheet of aluminum has 5 cm...Ch. 4 - A cylinder-shaped carbon resistor is 8 cm in...Ch. 4 - With reference to Fig. 4-19, find E1 if...Ch. 4 - An infinitely long cylinder of radius a is...Ch. 4 - If E=R150(V/m) at the surface of a 5-cm conducting...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.51 shows three planar dielectric slabs...Ch. 4 - Determine the force of attraction in a...Ch. 4 - Dielectric breakdown occurs in a material whenever...Ch. 4 - An electron with charge Qe = 1.61019 C and mass me...Ch. 4 - In a dielectric medium with r = 4, the electric...Ch. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - Prob. 57PCh. 4 - Prob. 58PCh. 4 - Prob. 59PCh. 4 - Prob. 60PCh. 4 - Prob. 61PCh. 4 - Conducting wires above a conducting plane carry...Ch. 4 - Prob. 63P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The efficiency of a motor is always low when it operates at 10 percent of its nominal power rating. Explain.arrow_forwardA dc motor connected to a 240 V line pro- duces a mechanical output of 160 hp. Knowing that the losses are 12 kW, calculate the input power and the line current.arrow_forwardA 115 V dc generator delivers 120 A to a load. If the generator has an efficiency of 81 percent, calculate the mechanical power needed to drive it [hp].arrow_forward
- A machine having class B insulation attains a temperature of 208°C (by resistance) in a torrid ambient temperature of 180°C. a. What is the temperature rise? b. Is the machine running too hot and, if so, by how much?arrow_forward1 Name the losses in a dc motor. 2 What causes iron losses and how can they be reduced? -3 Explain why the temperature of a machine increases as the load increases.arrow_forward20. A tractor weighing 14 kN with a wheel base of 3m carries an 8 kN load on its rear wheel. Compute the maximum bending moment and shear when crossing a 4.5 span. Consider the load only at the wheels.arrow_forward
- A 110-V, three-phase, Y-connected, 8 pole, 48-slot, 6000-rpm, double-layer wound chronoun anı vonorotor boo 10 +1 urn or oilarrow_forward-7 Name some of the factors that contribute to the deterioration of organic insulators. -8 A motor is built with class H insulation. What maximum hot-spot temperature can it withstand?arrow_forwardCalculate the full-load current of a 250 hp, 230 V dc motor having an efficiency of 92 percent.arrow_forward
- Assignment #2 A 110-V, three-phase, Y-connected, 8 pole, 48-slot, 6000-rpm, double-layer wound, synchronous generator has 12 turns per coil. If one side of the coil is in slot 1, the other side is in slot 6. There are 4 parallel paths. When the generator delivers the rated load at a line voltage of 110 V, the voltage regulation is 5%. What is the flux per pole? Draw two consecutive phasegroups of one of the phase windings and connect them (a) in series and (b) in parallel showing the Start (S) and Finish (F) of both connections. (A separate drawing for each connection)arrow_forward3-4 Transmissiva Live of 120km has R= 0.2 ~2/15 X= 0.8 -2/km Y = 15H/6 5/km The line is supplies a load of 45 kV, SOMW, 0.8 lead p.f find sending voltage, Sending Current p.f. Sanding Voltage Regulation ⑨Voltage 5 Ⓒ charching coming! изу usy π cct लेarrow_forwardA (medium) single phase transmission line 100 km long has the following constants : Resistance/km = 0.25 Q; Susceptance/km = 14 × 10° siemen ; Reactance/km = 0.8 Receiving end line voltage = 66,000 V Assuming that the total capacitance of the line is localised at the receiving end alone, determine (i) the sending end current (ii) the sending end voltage (iii) regulation and (iv) supply power factor. The line is delivering 15,000 kW at 0.8 power factor Lead Draw the phasor diagram to illustrate your calculations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Electric Charge and Electric Fields; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VFbyDCG_j18;License: Standard Youtube License