
Autotech Manufacturing is engaged in the production of replacement parts for automobiles. One plant specializes in the production of two parts: Part #127 and Part #234. Part #127 produced the highest volume of activity, and for many years it was the only part produced by the plant. Five years ago, Part #234 was added. Part #234 was more difficult to manufacture and required special tooling and setups. Profits increased for the first three years after the addition of the new product. In the last two years, however, the plant faced intense competition, and its sales of Part #127 dropped. In fact, the plant showed a small loss in the most recent reporting period. Much of the competition was from foreign sources, and the plant manager was convinced that the foreign producers were guilty of selling the part below the cost of producing it. The following conversation between Patty Goodson, plant manager, and Joseph Fielding, divisional marketing manager, reflects the concerns of the division about the future of the plant and its products.
JOSEPH: You know, Patty, the divisional manager is real concerned about the plant’s trend. He indicated that in this budgetary environment, we can’t afford to carry plants that don’t show a profit. We shut one down just last month because it couldn’t handle the competition.
PATTY: Joe, you and I both know that Part #127 has a reputation for quality and value. It has been a mainstay for years. I don’t understand what’s happening.
JOSEPH: I just received a call from one of our major customers concerning Part #127. He said that a sales representative from another firm offered the part at $20 per unit—$11 less than what we charge. It’s hard to compete with a price like that. Perhaps the plant is simply obsolete.
PATTY: No. I don’t buy that. From my sources, I know we have good technology. We are efficient. And it’s costing a little more than $21 to produce that part. I don’t see how these companies can afford to sell it so cheaply. I’m not convinced that we should meet the price. Perhaps a better strategy is to emphasize producing and selling more of Part #234. Our margin is high on this product, and we have virtually no competition for it.
JOSEPH: You may be right. I think we can increase the price significantly and not lose business. I called a few customers to see how they would react to a 25 percent increase in price, and they all said that they would still purchase the same quantity as before.
PATTY: It sounds promising. However, before we make a major commitment to Part #234, I think we had better explore other possible explanations. I want to know how our production costs compare to those of our competitors. Perhaps we could be more efficient and find a way to earn our normal return on Part #127. The market is so much bigger for this part. I’m not sure we can survive with only Part #234. Besides, my production people hate that part. It’s very difficult to produce.
After her meeting with Joseph, Patty requested an investigation of the production costs and comparative efficiency. She received approval to hire a consulting group to make an independent investigation. After a three-month assessment, the consulting group provided the following information on the plant’s production activities and costs associated with the two products:
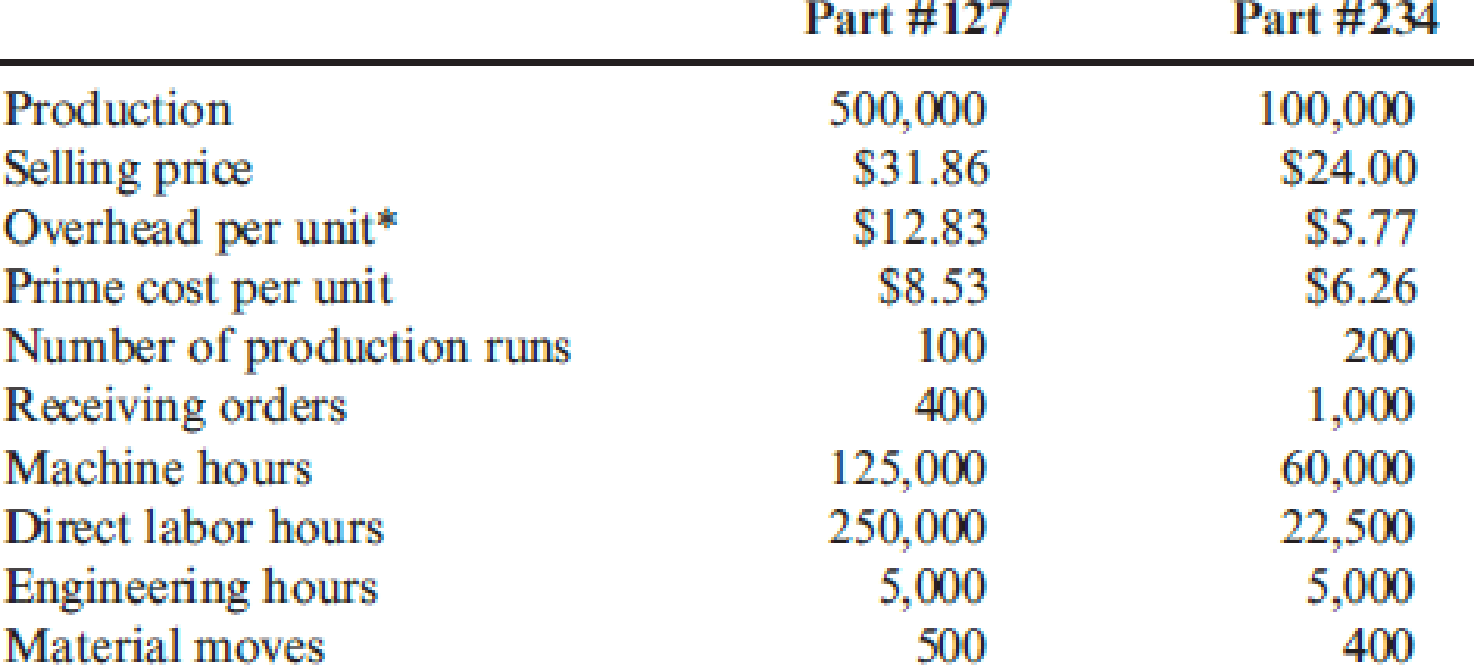
* Calculated using a plantwide rate based on direct labor hours. This is the current way of assigning the plant’s
The consulting group recommended switching the overhead assignment to an activity-based approach. It maintained that activity-based cost assignment is more accurate and will provide better information for decision making. To facilitate this recommendation, it grouped the plant’s activities into homogeneous sets with the following costs:

Required:
- 1. Verify the overhead cost per unit reported by the consulting group using direct labor hours to assign overhead. Compute the per-unit gross margin for each product.
- 2. After learning of activity-based costing, Patty asked the controller to compute the product cost using this approach. Recompute the unit cost of each product using activity-based costing. Compute the per-unit gross margin for each product.
- 3. Should the company switch its emphasis from the high-volume product to the low-volume product? Comment on the validity of the plant manager’s concern that competitors are selling below the cost of making Part #127.
- 4. Explain the apparent lack of competition for Part #234. Comment also on the willingness of customers to accept a 25 percent increase in price for Part #234.
- 5. Assume that you are the manager of the plant. Describe what actions you would take based on the information provided by the activity-based unit costs.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


