
Silven Company has identified the following
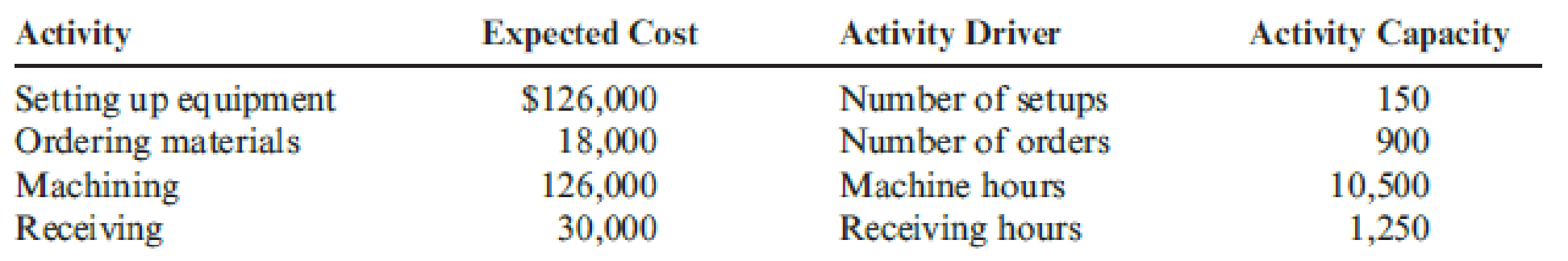
Silven produces two models of cell phones with the following expected activity demands:
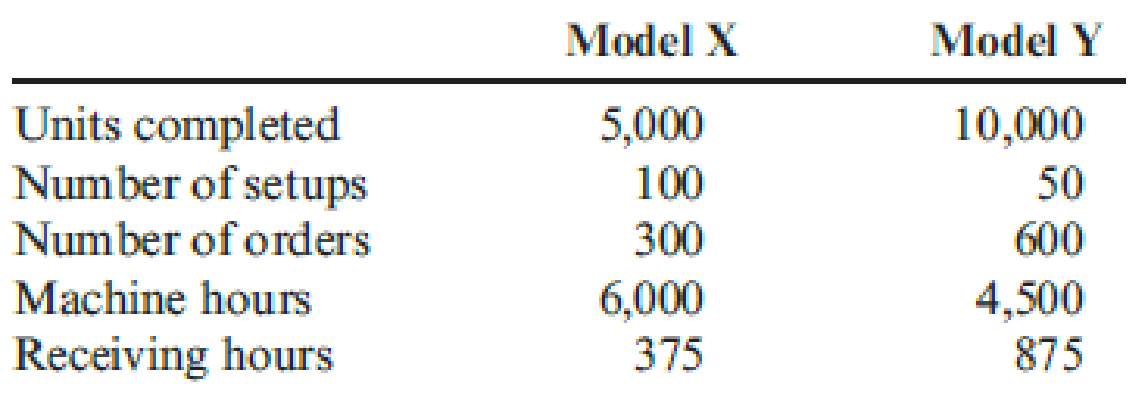
- 1. Determine the total overhead assigned to each product using the four activity drivers.
- 2. Determine the total overhead assigned to each model using the two most expensive activities. The costs of the two relatively inexpensive activities are allocated to the two expensive activities in proportion to their costs.
- 3. Using ABC as the benchmark, calculate the percentage error and comment on the accuracy of the reduced system. Explain why this approach may be desirable.
1.
Compute the predetermined overhead rates of S Company and the total overhead cost assigned to each product.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate: It is an application of estimated manufacturing overhead cost over the cost object for particular time period. Predetermined overhead rate is used to calculate the overhead used per unit of a driver.
Formula:
Compute the predetermined overheads rates for all the activities of S Company.
| Activity | Overhead rates |
| Setting up equipment | |
| Ordering materials | |
| Machining | |
| Receiving |
Table (1)
Calculate the cost assigned to be assigned to each product using the four activity drivers.
| Activity |
Model X ($) |
Model Y ($) |
| Setting up equipment | 84,000 (1) | 42,000 (2) |
| Ordering materials | 6,000 (3) | 12,000 (4) |
| Machining | 72,000 (5) | 54,000 (6) |
| Receiving | 9,000 (7) | 21,000 (8) |
| Total overhead assigned | $171,000 | $129,000 |
Table (2)
Working notes: Calculate the applied overheads for both the models of S Company
Applied overhead: Applied overhead is a cost which cannot be assigned directly to a cost object, and it is a fixed charge on a specific production department in the company.
Formula:
(1) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of setting up equipment for Model X.
(2) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of setting up equipment for Model Y.
(3) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of ordering materials for Model X.
(4) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of ordering materials for Model Y.
(5) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of machining for Model X.
(6) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of machining for Model Y.
(7) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of receiving for Model X.
(8) Calculate the applied overheads for the activity of receiving for Model Y.
2.
Calculate the total overhead assigned to both the models of S Company by using the two most expensive activities.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total overhead assigned to both the models of S Company by using the two most expensive activities.
| Activity |
Model X ($) |
Model Y ($) |
| Setting up equipment | 100,000(1) | 50,000(2) |
| Machining | 85,740(3) | 64,305(4) |
| Total Overhead assigned | 185,740 | 114,305 |
Table (3)
Step 1: Calculate the new activity rates of S Company namely setting up equipment and machining activity.
Setting up equipment:
Machining:
Step 2: Compute the total applied overheads assigned to both the models of S Company.
(1) Calculate the applied overhead of setting up equipment for Model X.
(2) Calculate the applied overhead of setting up equipment for Model Y.
(3) Calculate the applied overhead of machining activity for Model X.
(4) Calculate the applied overhead of machining activity for Model Y.
Compute the new cost pools for the activities of setting up equipment and machining of S Company.
Setting up equipment:
Machining:
Compute the new activity rates for both the activities of S Company.
| Activity |
Model X ($) |
Model Y ($) |
| Setting up equipment | 100,000(1) | 50,000(2) |
| Machining | 85,740(3) | 64,305(4) |
| Total Overheads assigned | 185,740 | 114,305 |
Table (4)
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the new activity rates for setup activity.
Setting up equipment:
(2) Calculate the new activity rates for machining activity.
Machining activity:
3.
Compute the percentage of error and provide information on the accuracy of reduced costing system considering activity based costing as a benchmark.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the percentage of error for Model X of S Company.
Calculate the percentage of error for Model Yof S Company.
The degree of error is not significant in the calculated result which means the activity drivers selected to calculate overhead rates are accepted and are better accurate in contrast to activity based costing.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- need help this questionsarrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year, Many Precision Tools estimates annual overhead costs to be $1,500,000 and that 350,000 machine hours will be operated. Using machine hours as a base, what is the amount of overhead applied during the year if actual machine hours for the year was 365,000 hours?arrow_forwardI want answerarrow_forward
- The sugar shack reports net incomearrow_forwardNani Pelekai works at Halalu Building Society in Jamaica. For 2014, she received a basic pay of $65 000 per month, her commissions were $10,000 monthly and she also received a bonus of 5% of her monthly pay. Nani contributed 10% of her basic pay to a pension scheme operated by the company. Halalu pays $30,000 per month to Nani’s landlord. She drives a car owned by Halalu, which is 2 years old and was purchased at a cost of $1,200,000. It is estimated that she has up to 50% private usage of the vehicle. Each month, Nani receives lunch vouchers worth $6,000, which may be used in Halalu’s canteen or other nearby restaurants. Halalu provides Nani with a cellular phone and agrees to pay a maximum bill of $45,000 per year. For the year, Nani’s cellular phone bill was $50,000. Halalu has an approved ESOP plan. For the year 2014, the employees agreed to purchase 6% of the share capital of 10 million shares of $1 each. There are 50 employees in the plan and each employee agreed to…arrow_forwardBergson Manufacturing had a beginning work in process inventory balance of $38,500. During the year, $82,400 of direct materials were placed into production. Direct labor was $65,200, and indirect labor was $21,300. Manufacturing overhead is allocated at 125% of direct labor costs. Actual manufacturing overhead was $92,000, and jobs costing $245,700 were completed during the year. What is the ending work in process inventory balance?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





