
Concept explainers
Patterson Company produces wafers for integrated circuits. Data for the most recent year are provided:
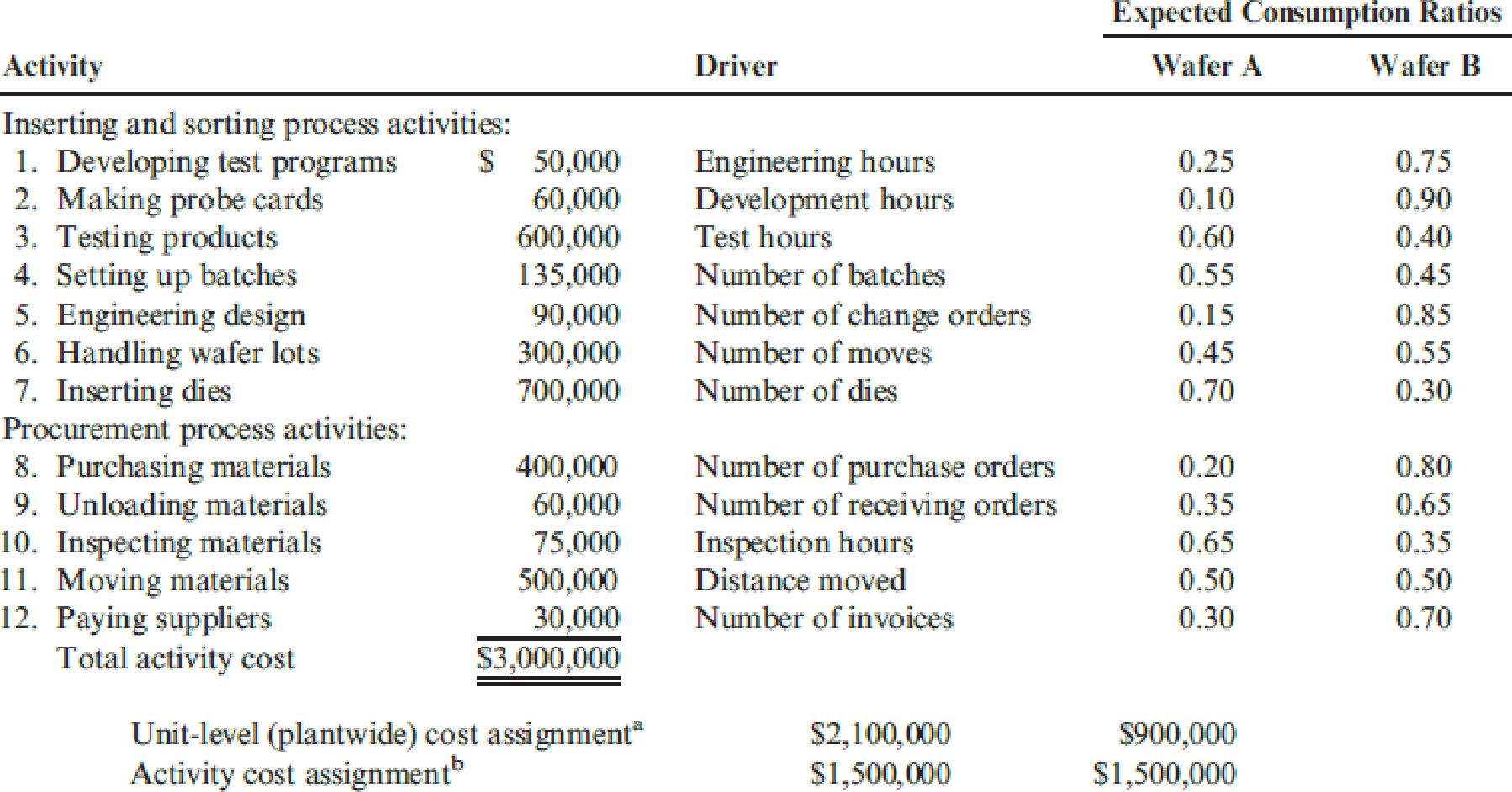
aCalculated using number of dies as the single unit-level driver.
bCalculated by multiplying the consumption ratio of each product by the cost of each activity.
Required:
- 1. Using the five most expensive activities, calculate the
overhead cost assigned to each product. Assume that the costs of the other activities are assigned in proportion to the cost of the five activities. - 2. Calculate the error relative to the fully specified ABC product cost and comment on the outcome.
- 3. What if activities 1, 2, 5, and 8 each had a cost of $650,000 and the remaining activities had a cost of $50,000? Calculate the cost assigned to Wafer A by a fully specified ABC system and then by an approximately relevant ABC approach. Comment on the implications for the approximately relevant approach.
1.
Compute the overheads assigned to each product of P Company using the five most expensive activities assuming the cost of other activities are assigned in proportion to the cost of the five activities.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead consumption ratio: An overhead consumption ratio is a measurement tool used to calculate the proportion of the overhead activity that is consumed by a particular product.
Approximately relevant activity based costing: Approximately relevant activity based costing
Compute the overhead cost to be assigned to both products of P Company using the five most expensive activities.
| Activity |
Budgeted cost ($) | Expected consumption ratio | |
| Wafer A | Wafer B | ||
| Testing products | 720,000 (1) | 60 % | 40 % |
| Handling water lots | 360,000 (2) | 45 % | 55 % |
| Inserting dies | 840,000 (3) | 70 % | 30 % |
| Purchasing materials | 480,000 (4) | 20 % | 80 % |
| Moving materials | 600,000 (5) | 50 % | 50 % |
| Total activity cost | 3,000,000 | ||
Table (1)
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the budgeted cost for the activity of testing hours of P Company.
(2) Calculate the budgeted cost for the activity of handling water lots of P Company.
(3) Calculate the budgeted cost for the activity of testing hours of P Company.
(4) Calculate the budgeted cost for the activity of purchasing materials of P Company.
(5) Calculate the budgeted cost for the activity of purchasing materials of P Company.
Compute the total approximately relevant activity based cost for all activities by using consumption ratios.
Wafer A:
| Activity |
Consumption ratio (%) |
Budgeted activity cost ($) |
Reduced ABC system ($) |
| (a) | (b) | ||
| Testing products | 60 % | 720,000 | 432,000 |
| Handling water lots | 45 % | 360,000 | 162,000 |
| Inserting dies | 70 % | 840,000 | 588,000 |
| Purchasing materials | 20 % | 480,000 | 96,000 |
| Moving materials | 50 % | 600,000 | 300,000 |
| Total activity cost | 1,578,000 | ||
Table (2)
Wafer B:
| Activity |
Consumption ratio (%) |
Budgeted activity cost ($) |
Reduced ABC system ($) |
| (a) | (b) | ||
| Testing products | 40 % | 720,000 | 288,000 |
| Handling water lots | 55 % | 360,000 | 198,000 |
| Inserting dies | 30 % | 840,000 | 252,000 |
| Purchasing materials | 80 % | 480,000 | 384,000 |
| Moving materials | 50 % | 600,000 | 300,000 |
| Total activity cost | 1,422,000 | ||
Table (3)
2.
Compute the relative error for both products with respect to fully specified activity based costing and provide information on the result.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the relative error for both products with respect to fully specified activity based costing and provide information on the result.
Wafer A:
Wafer B:
From the above calculated result, the maximum error is 5.2 percent with respect to activity based cost assignments that indicates a positive result indicated better accuracy.
3.
Calculate the cost assigned to Wafer A by a fully specified activity based costing system and activity based costing system. Activities of developing test program, making probe cards, engineering designs, and purchasing materials costs $650,000 each and the remaining activities costs $50,000. Provide information on the implications for the relevant approach.
Explanation of Solution
Wafer A:
Compute the approximately relevant cost for the activities 1, 2, 5, and 8 of P Company.
Compute the approximately relevant cost for Wafer A.
Compute the error term of P Company with respect to the costing techniques used.
Compute the relative error between the costing techniques used by P Company.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





