
Concept explainers
Primera Company produces two products and uses a predetermined
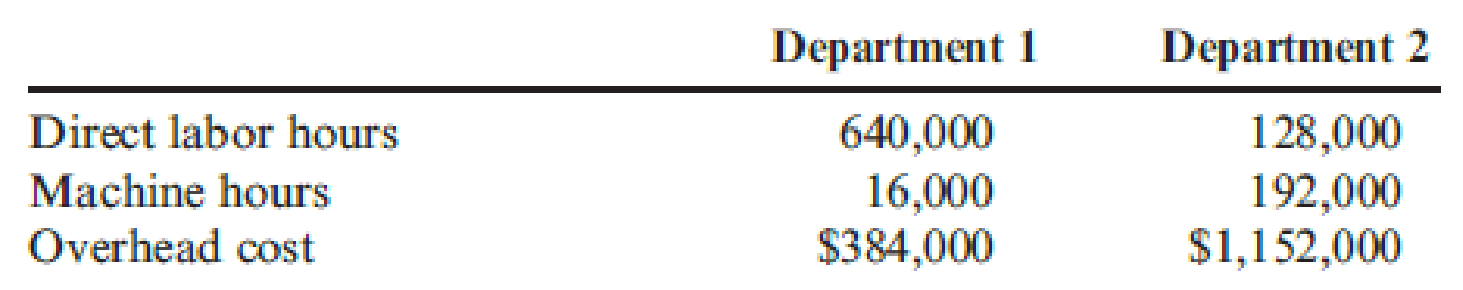
Actual results reported by department and product during the year are as follows:
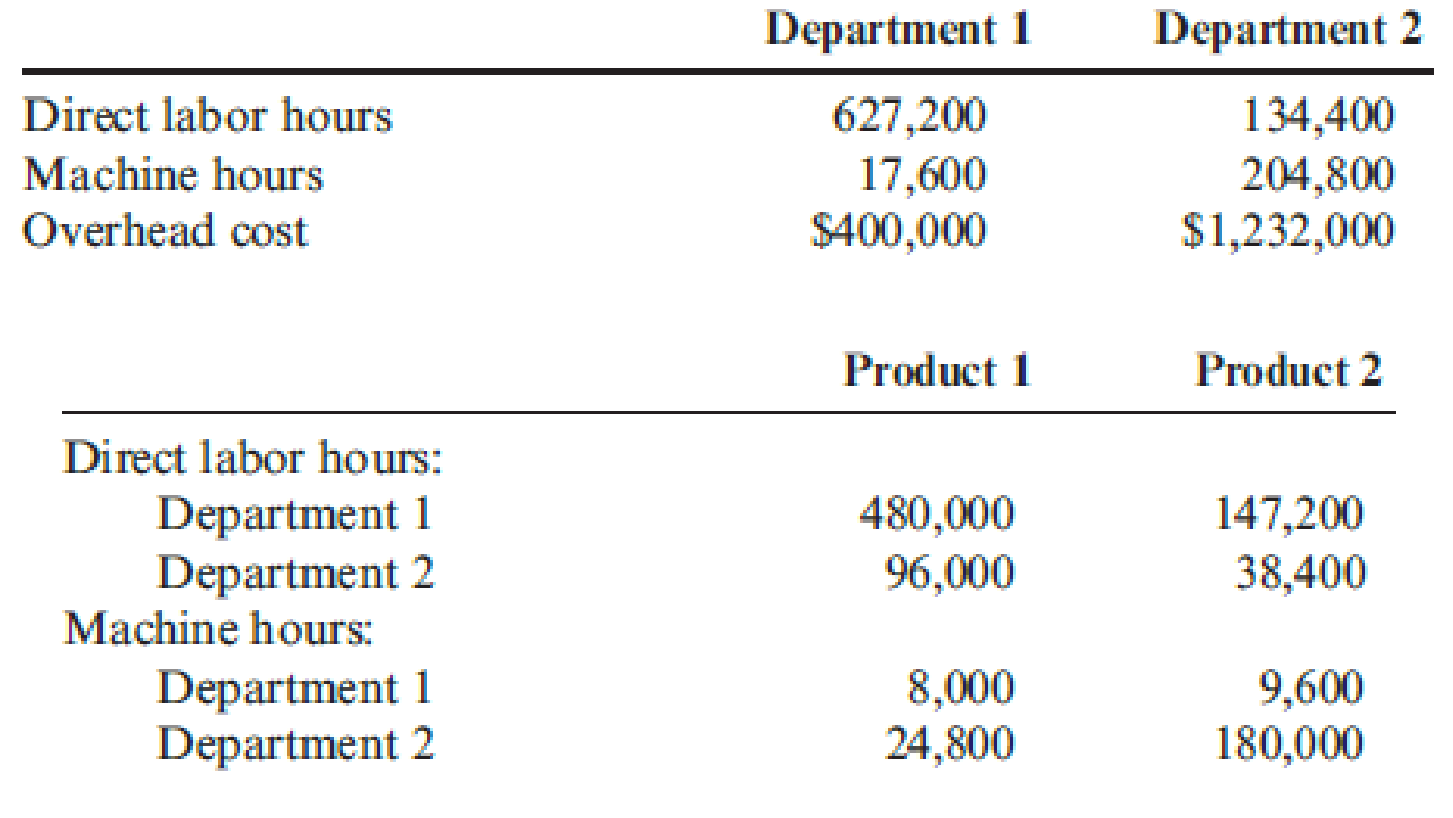
Required:
- 1. Compute the plantwide predetermined overhead rate and calculate the overhead assigned to each product.
- 2. Calculate the predetermined departmental overhead rates and calculate the overhead assigned to each product.
- 3. Using departmental rates, compute the applied overhead for the year. What is the under- or overapplied overhead for the firm?
- 4. Prepare the
journal entry that disposes of the overhead variance calculated in Requirement 3, assuming it is not material in amount. What additional information would you need if the variance is material to make the appropriate journal entry?
1.
Determine the plantwide predetermined overhead rate and identify the overhead assigned to each products of Company P.
Explanation of Solution
Plantwide predetermined overhead rate: Plantwide overhead rate is the rate a company uses to allocate its manufacturing overhead costs to products and cost centres. Predetermined overhead rate is a measure used to allocate the estimated manufacturing overhead cost to the products or job orders during a particular period. This is generally evaluated at the beginning of each reporting period. The evaluation takes into account the estimated manufacturing overhead cost and the estimated allocation base which can be direct labor hours, direct labor in dollars, machine hours or direct materials.
Compute plantwide predetermined overhead rate:
Thus, the predetermined overhead rate for Company P is $2 per direct labor hour.
Ascertain the overhead assigned to each product:
Thus, the overhead assigned to product 1 and product 2 are $1,152,000 and $371,200 respectively.
2.
Compute the predetermined departmental overhead rates and ascertain the overhead assigned to each product.
Explanation of Solution
Compute predetermined departmental overhead rate:
Therefore, the predetermined departmental overhead rate of department 1 and department 2 is $0.60 per direct labor hour and $6.00 per machine hour respectively.
Ascertain the overhead assigned to each product:
Thus, the overhead assigned to product 1 and product 2 is $436,800 and $1,168,320 respectively.
3.
Calculate the applied overhead for the year and determine the under-or-overapplied overhead for the Company P.
Explanation of Solution
Applied overhead: The total overhead charged to actual production at any point of time is termed as applied overhead.
Overapplied overhead: The difference between actual and applied overheads is known as overhead variances. If the applied overhead is more than the actual overhead, then the variance is known as overapplied overhead.
Underapplied overhead: The difference between actual and applied overheads is known as overhead variances. If the applied overhead is less than the actual overhead, then the variance is known as underapplied overhead
Compute total applied overhead rate:
Therefore, the total applied overhead is $1,605,120.
Determine the under-or-overapplied overhead:
Since, the applied overhead is less than the actual overhead, the variance of $26,880 is underapplied overhead.
4.
Record the journal entry to dispose the overhead variance by assuming that it is not material in amount and identify the required additional information if the variance is material to make the appropriate journal entry.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to dispose the overhead variance:
| Date | Account title and explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 26,880 | ||
| Overhead control | 26,880 | ||
| (To record the entry to dispose of the variance at the end of the year) |
Table (1)
Therefore, if the variance is material, we would need to know the balances of following Accounts
- Work-in-progress account
- Finished goods account
- Cost of goods sold account.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning





