
Concept explainers
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis and Dr. C. Ellie Gans are performing genetic crosses on daisy plants. They self-fertilize a blue- flowered daisy and grow
a. Use the form below to calculate chi square for the
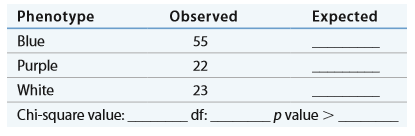
b. Use the form below to calculate chi square for the
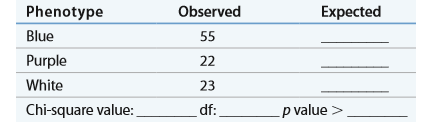
c. What is your conclusion regarding these two genetic hypotheses?
d. Using any of the
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology (10th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (11th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
- You are studying ear shape in dogs (with XY se x determination) and cross a true-breeding pointed-ear female to a true-breeding floppy-ear male and collect all pointy-ear male and female offspring. Your colleague suspects that the two phenotypes may be caused by alleles of one X-linked gene. What sort of cross would you do to determine whether this is an X-linked trait? Name it and describe it. What offspring phenotypic ratio would you expect in that cross if the green allele is a dominant X-linked allele? Make sure to label your ratio with all relevant phenotypes. How would the result of your cross (from A) be different if the trait is autosomalarrow_forwardA cross was performed using Drosophila melanogaster involving a female known to be heterozygous for both ebony body and sepia eyes and a male known to be homozygous wild type male. The resulting progeny were allowed to mate with one another to produce the data set. Three repetitions of the experiment were conducted. The following data were produced from the crosses. Test these data to determine if they are significantly different from the expected phenotypic ratio. Use the 5% level of significance. Your answer should include the hypothesized cross in genotypes, the Chi-squared value, the critical value and whether you reject or do not reject for each experiment. Wild eye Wild body – 112, Wild eye Ebony body – 40, Sepia eye Wild body – 35, Sepia eye Ebony body – 11arrow_forwardYou are trying to find a blood donor to help treat some of your patients. The C-yonce and Kay-Z have 3 children with blood types A , B, and O. The youngest with blood type O needs a transfusion and you're trying to figure out if either of the parents are a match so you test the parent genotypes. Note: Alleles for each blood type are expressed as follows: blood type A= I^A blood type B= I^B blood type O= i Hint: Remember that 2 alleles contribute to a persons blood type. Pay attention to dominant and recessive relationships among the alleles. 1-C-yonce is type B. What must her genotype be? 2-What must Kay-Z’s genotype be? 3-Which parent can give blood to their child ? 4-After running lab tests, it was discovered that the children's blood types were reported incorrectly.(This does not affect the genotypes entered for C-yonce and Kay-Z in the previous questions.) Their youngest actually has blood type AB, and still needs a blood transfusion. Which parent can donate blood to the child…arrow_forward
- A cross was performed using Drosophila melanogaster involving a female known to be heterozygous for both ebony body and sepia eyes and a male known to be homozygous for both of these recessive traits. The following data was produced from the cross. Test these data to determine if they are significantly different from the expected phenotypic ratio. Remember to use the 5% level of significance Wild eye Wild body – 102, Wild eye Ebony body – 94, Sepia eye Wild body – 100, Sepia eye Ebony body – 93. Your answer should include the hypothesized cross in genotypes, the Chi-squared value, the critical value and whether you reject or do not reject.arrow_forwardA tall pea plant (homozygous dominant) is crossed to a pea plant that is heterozygous for the gene for height. Create a Punnett Square and use it to answer the following questions: What is the genotypic ratio of the offspring? What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? Answers are written as genotype; phenotype a) 50% TT : 50% Tt; 100% tall plants b) 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1tt; 75% tall plants : 25% dwarf plants c) 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1tt; 25% tall plants : 50% medium height plants : 25% dwarf plantsarrow_forwardThe parental genotypes for a series of crosses are wild-type male fruit flies mated to females with white eyes (wh) and miniature (min) wings. The phenotypes of the F1 generation were wild-type females, and males with white eyes, and miniature wings. These flies were allowed to mate with each other and produced the following offspring: Red eyes, long wings White eyes, miniature wings Red eyes, miniature wings White eyes, long wings 770 716 401 318 Total 2205 A. Are these genes linked? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- A homozygous tomato plant with orange fruit and white flowers was crossed with a homozygous tomato plant with red fruit and red flowers. The F1 all had orange fruit and white flowers. The F1 were testcrossed by crossing them to homozygous recessive individuals and the following offspring were obtained: Orange fruit and white flowers- 64 Red fruit and red flowers- 69 Orange fruit and red flowers- 14 Red fruit and white flowers- 13 What is the recombination frequency of these two genes?arrow_forwardAs a graduate student, you join a lab and you are looking through some old notebooks. You find a linkage map someone has drawn. G--15 mu-----T----10 mu-------B If you plan to complete a test cross with a GtB/gTb male, A) What are all of the expected progeny genotypes? B.) How many of each genotype would you expect if you collected 1000 progeny?arrow_forwardYou carry out a trihybrid cross (a cross in which the parental plants differ for three characters) between a tall pea plant with round, yellow seeds (TT RR YY) and a short pea plant with wrinkled, green seeds (tt rr yy). The parental plants are homozygous for all of the three characters. They are crossed to produce the F1 generation. Tall, round, and yellow are the dominant traits for each character. What will be the phenotypes of the F1 generation?arrow_forward
- please make sure to read the question (THERE ARE OTHER VARIATIONS OF THE QUESTION ON DIFFERNT WEBSITES THAT ARE DIFFERENT THAN MINE)arrow_forwardFigure 8.10 In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea plants? How many squares would you need to complete a Punnett square analysis of this cross?arrow_forwardA genetic engineer was attempting to cross a tiger and a cheetah. She predicted a phenotypic outcome of the traits she was observing to be in the following ratio: 4 (stripes only): 3 (spots only): 9 (both stipes and spots). When the cross was performed and she counted the individuals she found 50 with stripes only, 41 with spots only and 85 with both. According to the Chi-square test, did she get the predicted outcome?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





