
Concept explainers
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder in humans. It results from mutation of the gene on chromosome
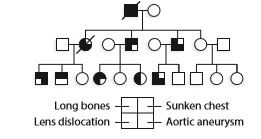
Since all cases of Marfan syndrome are caused by mutation of the fibrillin gene, and all family members with Marfan syndrome carry the same mutant allele, how do you e xplain the differences shown in the pedigree?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- Talk about the challenges involved in determining the genetic components of polygenic illnesses. Explain complementation groups and how the biochemical underpinnings of disease are determined using them. Hereditary illnesses of genomic instability include Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, XP, ataxia-telangiectasia, and Fanconi anemia. Which of these ailments has molecular mechanisms behind it? Which kind of genetic instability is connected to which disorder?.arrow_forwardGene mutations can be classified in two major ways:(1) hereditary or germline mutations that are inherited from a parent and are present throughout a person’s life in virtually every cell in the body.(2) acquired or somatic mutations that occur at some time during a person’s life and are present only in certain cells, not in every cell in the body.If there is no family history of a particular disease but a child has the disease then it may have arisen due to a(n) ________ mutation early during development. A) acquired B) inherited C) silent D) transitionarrow_forwardJunctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) is a severe skin disorder that results in blisters over the entire body. The disorder is caused by autosomal recessive mutations at any one of three loci that help to encode laminin 5, a major component in the dermal–epidermal basement membrane. Leena Pulkkinen and colleagues described a male newborn who was born with JEB and died at 2 months of age (L. Pulkkinen et al. 1997. American Journal of Human Genetics 61:611–619); the child had healthy, unrelated parents. Chromosome analysis revealed that the infant had 46 normal-appearing chromosomes. Analysis of DNA showed that his mother was heterozygous for a JEB-causing allele at the LAMB3 locus, which is on chromosome 1. The father had two normal alleles at this locus. DNA fingerprinting demonstrated that the male assumed to be the father had, in fact, conceived the child. Q. Assuming that no new mutations occurred in this family, explain the presence of an autosomal recessive disease in the child…arrow_forward
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) is a severe skin disorder that results in blisters over the entire body. The disorder is caused by autosomal recessive mutations at any one of three loci that help to encode laminin 5, a major component in the dermal–epidermal basement membrane. Leena Pulkkinen and colleagues described a male newborn who was born with JEB and died at 2 months of age (L. Pulkkinen et al. 1997. American Journal of Human Genetics 61:611–619); the child had healthy, unrelated parents. Chromosome analysis revealed that the infant had 46 normal-appearing chromosomes. Analysis of DNA showed that his mother was heterozygous for a JEB-causing allele at the LAMB3 locus, which is on chromosome 1. The father had two normal alleles at this locus. DNA fingerprinting demonstrated that the male assumed to be the father had, in fact, conceived the child. Q. How might you go about proving your explanation? Assume that a number of genetic markers are available for each chromosome.arrow_forwardLesch-Nyhan syndrome is due to a mutation in a gene that encodesa protein called hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase(HPRT). HPRT is an enzyme that functions in purine metabolism.People afflicted with this syndrome have severe neurodegenerationand loss of motor control. The pedigree below contains severalindividuals with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, shown with blacksymbols. Based on this pedigree, does this syndrome appearto be inherited by an autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant,X-linked recessive, or X-linked dominant pattern? Explainyour reasoning.arrow_forwardDuchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a disease that manifests in muscle weakness. It exhibits X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. The dystrophin gene is large and can have many different mutations along the DNA. From the following mutations between the gene sequence (DNA template strand) of a healthy male and an affected brother determine if they would affect the production of mRNA or the sequence of the protein. Base your analysis on the position of the mutation in the transcription unit, and the impact of the change on the codons. Mutation 1: Position -6 Healthy individual A Affected brother C Group of answer choices A. Normal mRNA, normal protein B. No mRNA produced (promoter affected) C. Abnormal mRNA, affected protein D. Normal mRNA, affected protein Base your analysis on the position of the mutation in the transcription unit, and the impact of the change on the codons.arrow_forward
- Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is a form of congenital blindness in humans and is known to be caused by homozygosity for recessive mutations in the RPE65 gene. Recently, a rare dominant mutation in RPE65 has been implicated as one cause of an eye disease called retinitis pigmentosa, which is characterized by retinal degeneration that can progress to blindness. The dominant RPE65 mutation is a missense mutation causing amino acid 447 in the polypeptide to change from Asp to Glu. Little is known about the nature of the mutant protein. a. Do you think that the dominant allele is more likely a loss-of-function or a gain-of-function mutation? Explain. b. Recently a group of clinicians and scientists reported that gene therapy (gene replacement therapy) for LCA has been at least partially successful. Do you think that the same kind of gene therapy can be used for patients with retinitis pigmentosa caused by the dominant mutant allele of RPE65? Explain.arrow_forwardThe dominant condition elliptocytosis causes red blood cells to become misshapen into oval-shaped cells. One of the genes responsible for the abnormal shape encodes the band 4.1 protein that together with ankyrin and other scaffold proteins creates and maintains the spherical concave shape of a normal red blood cell. The gene for band 4.1 protein, EPB41, is found on the p arm of chromosome 1. This is very close to the gene encoding the red blood cell Rhesus (Rh) blood type, either phenotype + (dominant) or - (recessive), with a recombination frequency of 2%. This means that 98% of the time alleles for these two genes are linked and are transmitted together. Diane and Jack are siblings, and both have elliptocytosis and Rh+ blood type. Due to the elliptocytosis, both had emergency splenectomies after having severe anemia. Their younger brother, Devonté, has not yet shown signs of elliptocytosis, but has Rh- blood. André, their dad, also has elliptocytosis and Rh+ blood; while their…arrow_forwardMarfan syndrome is due to a mutation in a gene that encodes aprotein called fibrillin-1. It is inherited as a dominant trait. Thefibrillin-1 protein is the main constituent of extracellular microfibrils.These microfibrils can exist as individual fibers or associatewith a protein called elastin to form elastic fibers. People with thedisorder tend to be unusually tall with long limbs, and they mayhave defects in their heart valves and aorta. Let’s suppose aphenotypically unaffected woman has a child with a man whohas Marfan syndrome.A. What is the probability this child will have the disease?B. If this couple has three children, what is the probability thatnone of them will have Marfan syndrome?arrow_forward
- Identify two genetic mechanisms whereby proto-oncogenes can become overexpressed. Select the two mechanisms. Identify two genetic mechanisms whereby proto-oncogenes can become overexpressed.Select the two mechanisms. 1) alterations in chromatin structure 2) a gain-of-function alteration 3)modification of proto-oncogenes products 4)mutations that result in an abnormal protein product 5)mutations within gene-regulatory regionsarrow_forwardTwo missense mutations in the gene that encodes an enzyme called superoxide dismutase cause a form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig disease). This disease causes loss of neurological function over a 5-year period. One mutation alters the amino acid asparagine (Asn) to lysine (Lys). The other changes an isoleucine (Ile) to a threonine (Thr). List the codons involved and describe how single-base mutations can alter the specified amino acids.arrow_forward"Changes to the p53 protein structure can be caused by differences in DNA and can affect protein function." Can you give detailed explanation why this is causation and not correlation? The explanation should be related with mutation, structure changes during protein synthesis, chemical property changes in amino acids, and functions of p53 protein.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

