
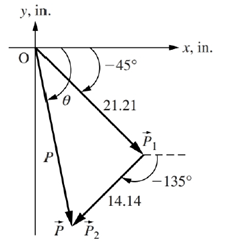
A two-link planar robot is shown in Fig. P4.28.
(a) Calculate the position of the tip
(b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the position of the robot tip. In other words, write vector
(c) Repeat part (b) using the laws of sines and cosines.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applications
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Calculate gross pay for each employee. All are paid overtime wage rates that are 1.5 times their respective regular wage rates. should be rounded to two decimal places at each calculation.arrow_forwardCalculate gross pay for each employee. All are paid overtime wage rates that are 1.5 times their respective regular wage rates. should be rounded to two decimal places at each calculation.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 1. 2. Show that the following are not logically equivalent by finding a counterexample: (p^q) →r and (db) V (d←d) Show that the following is not a contradiction by finding a counterexample: (pV-q) AqA (pv¬q Vr) 3. Here is a purported proof that (pq) ^ (q → p) = F: (db) v (bd) = (db) v (bd) =(qVp) A (g→p) = (¬¬q V ¬p) ^ (q→ p) (db) V (db) = =¬(a→p)^(a→p) = (gp) ^¬(a → p) =F (a) Show that (pq) ^ (q→p) and F are not logically equivalent by finding a counterex- ample. (b) Identify the error(s) in this proof and justify why they are errors. Justify the other steps with their corresponding laws of propositional logic.arrow_forward5 Show by multiplying matrices that the following equation represents an ellipse: 5 - -7 I (x)(3)()=30. y) 7 7)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward
- 1: Stanley Smothers receives tips from customers as a standard component of his weekly pay. He was paid $5.10/hour by his employer and received $305 in tips during the most recent 41-hour workweek. Gross Pay = $ 2: Arnold Weiner receives tips from customers as a standard component of his weekly pay. He was paid $4.40/hour by his employer and received $188 in tips during the most recent 47-hour workweek. Gross Pay = $ 3: Katherine Shaw receives tips from customers as a standard component of her weekly pay. She was paid $2.20/hour by her employer and received $553 in tips during the most recent 56-hour workweek. Gross Pay = $ 4: Tracey Houseman receives tips from customers as a standard component of her weekly pay. She was paid $3.90/hour by her employer and received $472 in tips during the most recent 45-hour workweek. Gross Pay = $arrow_forward8 √x+...∞ If, y = x + √ x + √x + √x +. then y(2) =? 00arrow_forward8 √x+...∞ If, y = x + √ x + √x + √x +. then y(2) =? 00arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


