
A ship is crossing a river at a heading of -150° with a speed of
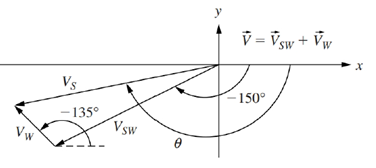
(a) Calculate the resultant velocity
(b) Determine the magnitude and direction of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applications
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward3. Consider the following theorem: Theorem: If n is an odd integer, then n³ is an odd integer. Note: There is an implicit universal quantifier for this theorem. Technically we could write: For all integers n, if n is an odd integer, then n³ is an odd integer. (a) Explore the statement by constructing at least three examples that satisfy the hypothesis, one of which uses a negative value. Verify the conclusion is true for each example. You do not need to write your examples formally, but your work should be easy to follow. (b) Pick one of your examples from part (a) and complete the following sentence frame: One example that verifies the theorem is when n = We see the hypothesis is true because and the conclusion is true because (c) Use the definition of odd to construct a know-show table that outlines the proof of the theorem. You do not need to write a proof at this time.arrow_forwardmatrix 4arrow_forward
- Please ensure that all parts of the question are answered thoroughly and clearly. Include a diagram to help explain answers. Make sure the explanation is easy to follow. Would appreciate work done written on paper. Thank you.arrow_forwardExplore this statement by constructing at least three examples, one of which must be a negative integer. Indicate if the statement is true or false for each example.arrow_forward2. Consider the following statement: For each natural number n, (3.2n+2.3n+1) is a prime number. (a) Explore this statement by completing the table below for n = 2,3 and two additional values of n of your choosing (notice n = 1 has been completed for you). One of your rows should contain a counterexample. n 1 3.2 2.3 +1 3.212.31 + 1 = 13 prime or composite? prime 2 3 (b) Write a formal counterexample argument for the statement using the template fromarrow_forward
- Please ensure that all parts of the question are answered thoroughly and clearly. Include a diagram to help explain answers. Make sure the explanation is easy to follow. Would appreciate work done written on paper. Thank you.arrow_forwardPlease ensure that all parts of the question are answered thoroughly and clearly. Include a diagram to help explain answers. Make sure the explanation is easy to follow. Would appreciate work done written on paper. Thank you.arrow_forwardmatrix 2arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
