
Concept explainers
An amplifier has a gain of 15 and the input waveform shown in Fig. P4.1. Draw the output waveform.
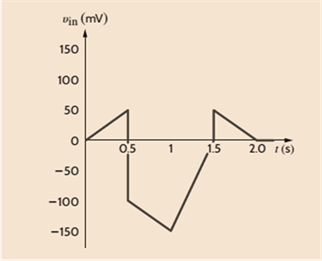
To draw:
The output waveform using input waveform and gain of the amplifier.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Amplifier has a gain of 15 and input waveform shown below.

Calculation:
For an amplifier, output voltage is product of gain and its input voltage.
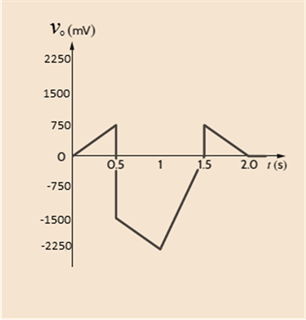
In the given figure, calculate the output voltage by the above formulae at different time to form a graph.
At
At
At
At
At
The output waveform for the given input is shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
- 6. Build the circuit shown in Figure 2 below in PSpice. Note that the power supply V1 is a VSIN power supply in the SOURCE library. Vcc is a VDC supply found in the SOURCE library. Model this circuit using the Time Domain (Transient) Analysis Type with a Run To Time of 2 ms. A. Paste your output graph showing the voltage at the base terminal, collector terminal and at the load. B. What is the voltage gain of the circuit? (Compare the voltage amplitude at the base terminal input (across Rb2) to that at the collector terminal. C. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is reduced by a factor of 10 (to 14.7 kn)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. D. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is increased by a factor of 3 (to 441 k)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. Rb1 RC 147k 1k C2 C1 Q1 Vcc 1u VOFF = 0 Q2N3904 10Vdc VAMPL = 0.1V1 1u FREQ = 2k R_load Rb2 Re AC = 0 250 40k 20 Figure…arrow_forwardThe input reactance of 1/2 dipole with radius of 1/30 is given as shown in figure below, Assuming the wire of dipole is conductor 5.6*107 S/m, determine at f=1 GHz the a-Loss resistance, b- Radiation efficiency c-Reflection efficiency when the antenna is connected to T.L shown in the figure. Rr Ro= 50 2 1/4 RL -j100 [In(l/a) - 1.5] tan(ẞl)arrow_forward6) For each independent source in this circuit calculate the amount of power being supplied or the amount of power being absorbed + 6V www +3V- www 20 ми ми 352 0.5A + 3Varrow_forward
- 2) A circuit is given as shown (a) Find and label circuit nodes. (b) Determine V, V₂, V₂, I₂ and I. + V₂ 452 m I2 6Ω www 52 t + V + 4A 노동 102 ww 1202 60 www I₂arrow_forwardA Darlington Pair consists of two transistors with the first BJT driving the base terminal of the second transistor as shown in the picture provided. What does the curve trace for a Darlington Pair of Bipolar Junction Transistors look like?arrow_forwardProvide Pen and paper solution please not using AIarrow_forward
- 5) If the current source supplies 448 watts, then what 15 the value of resistance R? ми R ↑ YA 62 ww 120 } ww 6_02 { wwarrow_forwardWhat is the equivalent resistance of this circuit between terminals A and B ? m 1852 A 7_A 122 도 www 50 ти B ww 36 Ω 201 www www 30√arrow_forward3) A circuit is given as shown. (a) Find and label the circuit nodes. (6) Determine V2, V2, I₂, I₂ and Is © For each circuit element determine how much power it Supplies 15 absorbs. m 20 + 20 www 13 + 20 Z9V H 56 +1 LOV 1/2 1 4A + 3_22 3.2 ми + V₂ I 1arrow_forward
- In this experiment, we are going to use a 2N3904 BJT. Examine the data sheet for this device carefully. In particular, make a note of the current gain (identified by hFE). 1. Obtain the curve trace for a "Darlington Pair" of Bipolar Junction Transistors. A Darlington Pair consists of two transistors with the first BJT driving the base terminal of the second transistor as shown in Figure 1 below. A. Set up the primary sweep voltages for V1 the same as shown in the lecture notes (see the Darlington pair IV curve). B. Set up the secondary sweep currents for 11 to be an order of magnitude smaller than for the single BJT. In the Sweep Type box choose linear and enter the following 3 values: Start Value: 0, End Value: 8u and Increment: 1u (see lecture notes). C. Describe the primary differences you observe between the single BJT Curve Trace and that of the Darlington Pair. Discuss what might cause each difference. Q1 11 Q2 V1 Q2N3904 Figure 1. A Darlington Pair of 2N3904 transistors in a…arrow_forward2. Using the IV plots shown in Fig. 3 (and found in the reintroduction to PSpice) design a BJT biasing circuit that results in the following parameters: VCE = 2 Vand ig = 40 μA. We also require the power supply to be fixed at 5 Volts (this is where the load line intercepts the iB =ic = 0 line). You may use the circuit shown in Example 1. Note that all resistor values in Example 1 must be recalculated. Your solution for the base to ground and base to collector resistors may not be unique.arrow_forwardA circuit is given as shown. (a) Find and label the circuit nodes. (6) Determine I, I₁, I2 and V₂ I₂ +1 I 12V ww 22 2 ти + 보통 162 - ти 4 52 12 50 602 I 1 Mwarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





