
Concept explainers
Interpretation:The common molecule that is represented nine separate times in each figure in Model 1 should be determined.
Concept introduction:Intermolecular forces are type of forces that are responsible to hold atoms together in molecule.
There are various types of intermolecular forces as follows:
1. Hydrogen bonding:
As is evident from its name, these types of forces exist if hydrogen is present. Such forces are present when hydrogen atom bonds with highly electronegative elements like N, O, F. It is of two types: intramolecular and intermolecular.
2. Ion-dipole forces:
This force exists between ion and molecules with a dipole moment in them. Attraction exists between ion and oppositely charged end of dipole.
3. Ion-induced dipole forces:
When an ion approaches non-polar molecule, it induces temporary dipole in it. Ion gets attracted towards the oppositely charged part of dipole induced in molecule.
4. Dispersion forces:
Such forces are present between various atoms and molecules. These are observed generally in non-polar molecules, halogens and noble gases.
Explanation of Solution
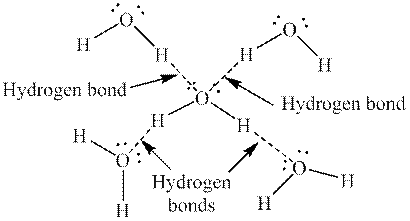
Hydrogen and oxygen are present in structure shown in model 1. Since oxygen is highly electronegative in nature, hydrogen bonding is present between water molecules. So,a hydrogen-bonded molecule is present in each figure in model 1. The hydrogen bonding in water is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
