
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation: Conjugate base for each below acid should be determined. Also, rank of conjugate bases from strongest to weakest P.E. should be determined.
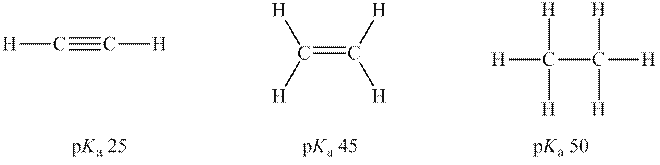
Concept introduction: According to the Bronsted-Lowry concept, a substance that donates proton is termed as acid while that accepts or gains protons is called a base. Species formed after loss of protons from acids are known as their respective conjugate bases whereas conjugate acid is produced by the addition of protons to base. The strength of conjugate acids and conjugate bases are inversely related to strengths of their respective bases and acids.
According to Lewis's concept, a substance that donates electron pair is termed as a base while that accepts or gains electron pair is called acid. For example,
According to the Arrhenius concept, substances that donate hydrogen ions in solutions are known as acids while bases are substances that release hydroxide ions in solutions.
b)
Interpretation: Type of orbital that has a lone pair of electrons in the below conjugate base should be drawn.
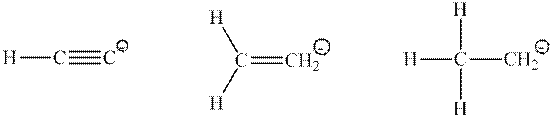
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to the different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
c)
Interpretation: Percent
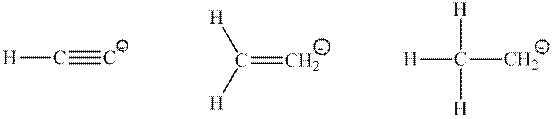
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to a different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
d)
Interpretation: Whether
Concept introduction: Orbitals are defined as regions around atomic nucleus where electrons are found. Atomic orbitals help to form covalent bonds. Atomic orbitals can be
e)
Interpretation: Reason for pattern in
Concept introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forwardHow many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forward
- Draw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forwardH 14. Draw the line angle form of the following molecule make sure you use the proper notation to indicate spatial positioning of atoms. F F H 15. Convert the following condensed form to line angle form: (CH3)3CCH2COCH2CON(CH2CH3)2arrow_forward
- In a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
