
Concept explainers
The following are equivalent ways of asking about the acidity of an H atom:
• What is the most acidic H on the molecule?
• Which H is associated with the published
• Which H on the molecule is easiest to remove?
• Which H on the molecule takes the least energy to remove?
• Which bond to an H is most polarized?
• For which H atom is removal least uphill in energy?
• Which bond to an H atom, when broken, results in the lowest PE conjugate base?
We will often find the last of these questions is easiest to answer. To do this, find all the different Hatoms on the molecule, and draw all possible conjugate bases.Only the lowest-energy one is the “real” conjugate base. Identify this structure, and you have found the most acidic H.
Use this strategy to find the most acidic H on each of the following molecules. Note: Each structure hasat least three different kinds of H’s, so draw at least three unique conjugate bases for each.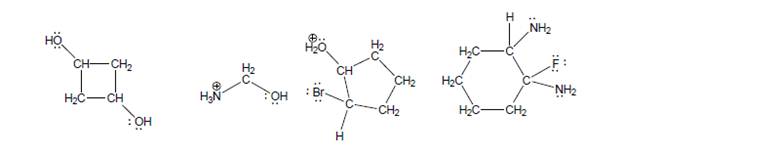
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- Answer true or false to the following statements about the mechanism of acid-base reactions. (a) The acid and base must encounter each other by a collision in order for the proton to transfer. (b) All collisions between acids and bases result in proton transfer. (c) During an acid-base reaction the lone pair on the base fills the A-H antibonding sigma orbital.arrow_forwardComplete the equation for the reaction between each Lewis acid-base pair. In each equation, label which starting material is the Lewis acid and which is the Lewis base; use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons in each reaction. In doing this problem, it is essential that you show valence electrons for all atoms participating in each reaction. (a) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forwardSeveral acids and their respective equilibrium constants are: Which is the strongest acid? Which is the weakest acid? Which acid has the weakest conjugate base? Which acid has the strongest conjugate base?arrow_forward
- For the previous four questions, label each molecule that appears in the question or your answer asstrong acid, strong base, weak acid, or weak base.arrow_forwardFor each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid or conjugate base or both if the molecule hasboth a conjugate acid and a conjugate base (e.g., water).arrow_forwardA very strong base can remove a proton from methylamine:arrow_forward
- Use Table 13-2 to order the following from the strongest to the weakest acid. HClO2,H2O,NH4+,HClO4arrow_forwardComplete a net ionic equation for each proton-transfer reaction using curved arrows to show the flow of electron pairs in each reaction. In addition, write Lewis structures for all starting materials and products. Label the original acid and its conjugate base; label the original base and its conjugate acid. If you are uncertain about which substance in each equation is the proton donor, refer to Table 4.1 for the relative strengths of proton acids. (a) NH3+HCl (b) CH3CH2O+HCl (c) HCO3+OH (d) CH3COO+NH4+arrow_forward(E) Label each of the following as strong acid, strong base, or neither.arrow_forward
- You may need Table 13-2 to answer the following questions. a. Which is the stronger base, Cl or H2O? b. Which is the stronger base, H2O or NO2? c. Which is the stronger base, CNor OC6H5?arrow_forwardIn terms of orbitals and electron arrangements, what must be present for a molecule or an ion to act as a Lewis acid? What must be present for a molecule or an ion to act as a Lewis base?arrow_forwardCalculate the [OH] of each of the following solutions at 25C. Identify each solution as neutral, acidic, or basic. a. [H+] = 1.0 107 M b. [H+] = 8.3 1016 M c. [H+] = 12 M d. [H+] = 5.4 105 M 46. Calculate the [H+] of each of the following solutions at 25C. Identify each solution as neutral, acidic, or basic. a. [OH] = 1.5 M b. [OH] = 3.6 1015 M c. [OH] = 1.0 107 M d. [OH] = 7.3 104 M 49. Calculate the pH and pOH of the solutions in Exercises 45 and 46.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





