
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: Thevertical and horizontal asymptote of the function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 10RE
The Horizontal asymptote is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
If the degree of the numerator is less than the denominator, thehorizontal asymptote is
If the denominator has no zeroes then there has no vertical asymptotes
Or
To get Vertical asymptote function should be rational and denominator must contain some variable otherwise there has no vertical asymptote.
Calculation:
Accordingto the laws of asymptotes:
If the degree of the numerator is more than the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote.
If the denominator has no zeroes then there has no vertical asymptotes/.
Here the numerator of the function has degree 1 and denominator has degree of 2.
the horizontal asymptote is
Vertical asymptote is at
Hence, the Horizontal asymptote is
(b)
To find: TheInterval of increasing or decreasing of the function.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10RE
The Interval of increasing or decreasing of the function is
Decreasing at interval of
Increasing at interval of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
Increasing or decreasing function can be calculated by equating first derivative of the function to 0.
Zeroes of x can be calculatedafter that the increasing and decreasing can be measured.
Calculation:
Increasing or decreasing function can be calculated by equating first derivative of the function to 0.
Hence the Interval of increasing or decreasing of the function is
Decreasing at interval of
Increasing at interval of
(c)
To find: The
(c)
Answer to Problem 10RE
the point of inflection at
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
The local maxima and minima can be calculated by firstly equating the double differentiation to 0.
1.
2.If
3.
Calculation:
At
Hence,
Local minima.
the point of inflection at
(d)
To find: The interval of concavity and the inflection point.
(d)
Answer to Problem 10RE
Concave downward in the interval of
Concave upward in the interval of
These points are point of inflection
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
The second derivative of function is calculated first.
Set the second derivative equal to zero and solve.
Check whether the second derivative undefined for any values of x.
Plot the number on number line and test the regions with the second derivative.
Plug these 3 values for obtain three inflection points.
The graph of
The graph of
If the graph of
Calculation:
This two are the point of inflection.
By putting the values in the equation.
The interval will be
Hence,
Concave downward in the interval of
Concave upward in the interval of
These points are point of inflection
(e)
To Sketch:the graph of the function using graphing device.
(e)
Answer to Problem 10RE
Through the graph it’s easily verified the point of local maxima and minima, function is increasing or decreasing, concavity down or up and point of inflection.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept used:
Desmos graphing calculator is used her to plot the graph and it can easily verify the maxima, minima and point of inflection etc.
Calculation:
The graph of
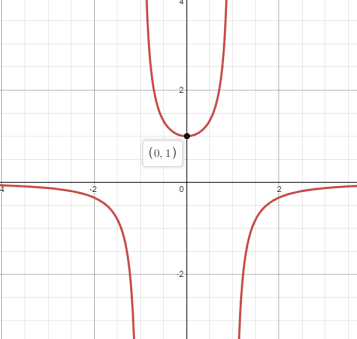
Hence, through the graph it’s easily verified the point of local maxima and minima, function is increasing or decreasing, concavity down or up and point of inflection.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Concepts and Contexts, Enhanced Edition
- Evaluate the triple integral 3' 23 HIG 2 +3 f(x, y, z)dxdydz where f(x, y, z) = x + 2x-y ม u = v = and w = 2 2 3 Triple Integral Region R -2 x N 2 y 3arrow_forwardFind the volume of the solid bounded below by the circular cone z = 2.5√√√x² + y² and above by the sphere x² + y²+z² = 6.5z.arrow_forwardElectric charge is distributed over the triangular region D shown below so that the charge density at (x, y) is σ(x, y) = 4xy, measured in coulumbs per square meter (C/m²). Find the total charge on D. Round your answer to four decimal places. 1 U 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 5 7 coulumbsarrow_forward
- Let E be the region bounded cone z = √√/6 - (x² + y²) and the sphere z = x² + y² + z² . Provide an answer accurate to at least 4 significant digits. Find the volume of E. Triple Integral Spherical Coordinates Cutout of sphere is for visual purposes 0.8- 0.6 z 04 0.2- 0- -0.4 -0.2 04 0 0.2 0.2 x -0.2 04 -0.4 Note: The graph is an example. The scale and equation parameters may not be the same for your particular problem. Round your answer to 4 decimal places. Hint: Solve the cone equation for phi. * Oops - try again.arrow_forwardThe temperature at a point (x,y,z) of a solid E bounded by the coordinate planes and the plane 9.x+y+z = 1 is T(x, y, z) = (xy + 8z +20) degrees Celcius. Find the average temperature over the solid. (Answer to 4 decimal places). Average Value of a function using 3 variables z 1- y Hint: y = -a·x+1 * Oops - try again. xarrow_forwardFind the saddle pointsarrow_forward
- For the curve defined by r(t) = (e** cos(t), et sin(t)) find the unit tangent vector, unit normal vector, normal acceleration, and tangential acceleration at t = πT 3 T (1) N Ň (1) 133 | aN = 53 ar = = =arrow_forwardFind the tangential and normal components of the acceleration vector for the curve - F(t) = (2t, −3t³, −3+¹) at the point t = 1 - ā(1) = T + Ñ Give your answers to two decimal placesarrow_forwardFind the unit tangent vector to the curve defined by (t)=(-2t,-4t, √√49 - t²) at t = −6. T(−6) =arrow_forward
- An airplane flies due west at an airspeed of 428 mph. The wind blows in the direction of 41° south of west at 50 mph. What is the ground speed of the airplane? What is the bearing of the airplane? 428 mph 41° 50 mph a. The ground speed of the airplane is b. The bearing of the airplane is mph. south of west.arrow_forwardRylee's car is stuck in the mud. Roman and Shanice come along in a truck to help pull her out. They attach one end of a tow strap to the front of the car and the other end to the truck's trailer hitch, and the truck starts to pull. Meanwhile, Roman and Shanice get behind the car and push. The truck generates a horizontal force of 377 lb on the car. Roman and Shanice are pushing at a slight upward angle and generate a force of 119 lb on the car. These forces can be represented by vectors, as shown in the figure below. The angle between these vectors is 20.2°. Find the resultant force (the vector sum), then give its magnitude and its direction angle from the positive x-axis. 119 lb 20.2° 377 lb a. The resultant force is (Tip: omit degree notations from your answers; e.g. enter cos(45) instead of cos(45°)) b. It's magnitude is lb. c. It's angle from the positive x-axis isarrow_forwardFind a plane containing the point (3, -3, 1) and the line of intersection of the planes 2x + 3y - 3z = 14 and -3x - y + z = −21. The equation of the plane is:arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





