
Concept explainers
Cervical Cancer Incidence in HPV-Positive Women
A persistent infection with one of about 10 strains of genital HPV (human papillomavirus) is the main risk factor for cervical cancer. The virus spreads easily by sexual contact, but vaccines that prevent infection have been available since 2006. The vaccines consist of viral proteins that self-assemble into virus-like particles. The particles are not infectious (they contain no viral DNA), but their component proteins trigger an immune response that can prevent HPV infection and the cervical cancer it causes.
In 2003, Michelle Khan and her coworkers published results of their 10-year study correlating HPV status with cervical cancer incidence in women (FIGURE 37.23). All 20,514 participants were free of cervical cancer when the study began.
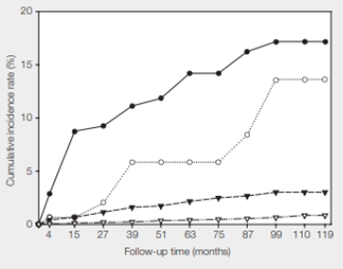
FIGURE 37.23 Cumulative incidence rate of cervical cancer correlated with HPV status.
● HPV16 positive
○ HPV16 negative and HPV18 positive
▾ All other cancer-causing HPV types combined
▿ No cancer-causing HPV types was detected.
At 110 months into the study, what percentage of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV had cervical cancer? What percentage of women who were infected with HPV16 also had cancer?
To determine: The percentage of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV, but had cervical cancer.
Introduction: The researchers in the given study attempted to make a connection between the presence of various HPV viral infections and the incidence of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer arises from the cervix, which occurs due to the abnormal growth of the cells that have the capability to invade or spread to other body parts.
Explanation of Solution
The given study showed that approximately one percent of the women who had no cancer-causing HPV infections developed cervical cancer. The study shows that the infection with the genital HPV is the main risk factor for cervical cancer. The women who have not been infected with cancer-causing HPV have a small chance of having cervical cancer. HPV is not the only cause of cervical cancer. It can also be caused due to a weakened immune system, long-term mental stress, giving birth at a very young age, several pregnancies, birth control pills, and so on.
In the given study, 1% of women who were not infected with any type of cancer-causing HPV had cervical cancer.
To determine: The percentage of the women who were infected with HPV16 had cancer.
Introduction: The researchers in this study attempted to make a connection between the presence of various HPV viral infections and the incidence of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer arises from the cervix, which occurs due to the abnormal growth of the cells that have the capability to invade or spread to other body parts.
Explanation of Solution
At 110 months, 17 percent of the women who tested positive for HPV16 had cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus that spreads easily by sexual contact is a risk factor for cervical cancer. The study indicates that those women who are HPV-positive have a high risk of getting cervical cancer.
The HPV positive women, who have the habit of smoking and have HIV influence, are more likely to develop cervical cancer. If the virus infection is left untreated, the pre-cancerous cells will develop to cancer cells, but it will take 10 to 15 years.
In the given study, 17 percent of the women who were infected with HPV16 had cancer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
- O Macmillan Learning Glu-His-Trp-Ser-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly The pKa values for the peptide's side chains, terminal amino groups, and carboxyl groups are provided in the table. Amino acid Amino pKa Carboxyl pKa Side-chain pKa glutamate 9.60 2.34 histidine 9.17 1.82 4.25 6.00 tryptophan 9.39 2.38 serine 9.15 2.21 glycine 9.60 2.34 leucine 9.60 2.36 arginine 9.04 2.17 12.48 proline 10.96 1.99 Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 3. net charge at pH 3: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 8. net charge at pH 8: Calculate the net charge of the molecule at pH 11. net charge at pH 11: Estimate the isoelectric point (pl) for this peptide. pl:arrow_forwardBiology Questionarrow_forwardThis entire structure (Pinus pollen cone) using lifecycle terminology is called what?arrow_forward
- This entire structure using lifecycle terminology is called what? megastrobilus microstrobilus megasporophyll microsporophyll microsporangium megasporangium none of thesearrow_forwardHow much protein should Sarah add to her diet if she gets pregnant? Sarah's protein requirements during pregnancy would be higher. See Hint B2. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. In your answer, round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. _______ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardMost people, even those who exercise regularly at low to average intensity (1 hour at the gym or a 2- to 3-mile walk several times per week), do not need an increased protein intake. What would be the protein needs of a man named Josh who exercises moderately and is the same age and size as Wayne? Josh is 5 ft, 8 in tall and weighs 183 lb. Round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. Because protein requirement is a range, please enter two numbers: lower and upper range values, respectively. Separate the lower and upper range values, in that order, by a comma. ___, ___ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardIf left untreated, most HIV-infected individuals will develop AIDS. Current treatments are focused on highlyactive antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART usually consists of an orally delivered drug cocktail containingtwo different reverse transcriptase inhibitors and one other drug, such as a protease inhibitor. Question: Develop a pharmacokinetic model of HAART treatment. Consider all 3 drugs. Make sure to include adiagram that illustrates your thinking, state all assumptions, and define your variables. Whatparameters would you need to know to find the concentration of drug in the plasma? In the T cells?(You do not need to write out or solve any equations.)arrow_forwardnot use ai pleseaarrow_forward(A) 25 20 20 15 NPP (Mg C/ha/yr) 10 10 5 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 ECOLOGY 4e, Figure 20.11 (Part 1) 2017 Sinauer Associates, Inc. Average annual precipitation (mm) 8,000arrow_forwardexplain the cascade of events (starting with relaxing trade winds) that occurs during El Niño in the eastern Pacific (off the coasts of California/North America and Peru/South America) and which lead to food-chain collapse - start with changes in the physical/oceanographic conditions, andthen systematically describe the cascading effects at each level of the food chain -arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
