
Concept explainers
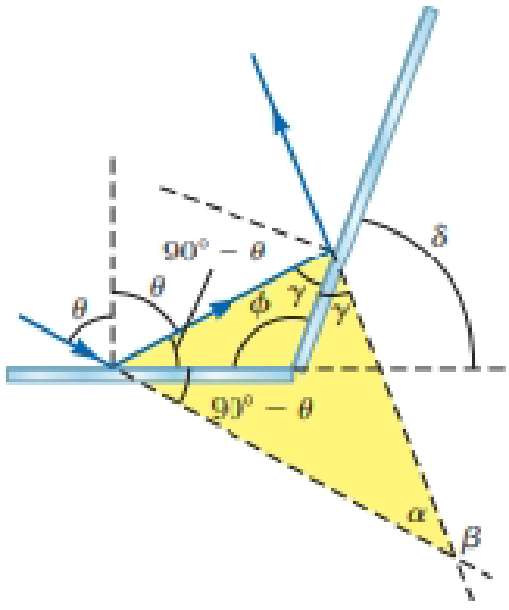
You are working for an optical research company during a summer break. Part of the apparatus in one particular experiment is shown in Figure 34.7b. In fact, the experimenter used this text book to set up this part of the experiment, and also used the result in the What If? section to determine the angular change in direction of the light beam:
The experimenter is constantly grumbling that the measuring device to determine the angle ϕ on the inside of the mirrors is constantly getting in the wav of the light beam and making his life difficult. You quickly draw Figure P34.5 and then say. “Then why don’t you use the measuring device to measure the angle δ outside the mirror, and then your device won’t get in the way of the light?”
The experimenter, who has never thought of this, tries to save face and says to you. “Well, Smarty, then tell me how angle β depends on angle δ!” You provide him the answer quickly.
Figure P34.5
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 34 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- 1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forwardPlz no chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward3.19 • Win the Prize. In a carnival booth, you can win a stuffed gi- raffe if you toss a quarter into a small dish. The dish is on a shelf above the point where the quarter leaves your hand and is a horizontal dis- tance of 2.1 m from this point (Fig. E3.19). If you toss the coin with a velocity of 6.4 m/s at an angle of 60° above the horizontal, the coin will land in the dish. Ignore air resistance. (a) What is the height of the shelf above the point where the quarter leaves your hand? (b) What is the vertical component of the velocity of the quarter just before it lands in the dish? Figure E3.19 6.4 m/s 2.1arrow_forward
- Can someone help me answer this thank you.arrow_forward1.21 A postal employee drives a delivery truck along the route shown in Fig. E1.21. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement by drawing a scale diagram. (See also Exercise 1.28 for a different approach.) Figure E1.21 START 2.6 km 4.0 km 3.1 km STOParrow_forwardhelp because i am so lost and it should look something like the picturearrow_forward
- 3.31 A Ferris wheel with radius Figure E3.31 14.0 m is turning about a horizontal axis through its center (Fig. E3.31). The linear speed of a passenger on the rim is constant and equal to 6.00 m/s. What are the magnitude and direction of the passenger's acceleration as she passes through (a) the lowest point in her circular motion and (b) the high- est point in her circular motion? (c) How much time does it take the Ferris wheel to make one revolution?arrow_forward1.56 ⚫. Three horizontal ropes pull on a large stone stuck in the ground, producing the vector forces A, B, and C shown in Fig. P1.56. Find the magnitude and direction of a fourth force on the stone that will make the vector sum of the four forces zero. Figure P1.56 B(80.0 N) 30.0 A (100.0 N) 53.0° C (40.0 N) 30.0°arrow_forward1.39 Given two vectors A = -2.00 +3.00 +4.00 and B=3.00 +1.00 -3.00k. (a) find the magnitude of each vector; (b) use unit vectors to write an expression for the vector difference A - B; and (c) find the magnitude of the vector difference A - B. Is this the same as the magnitude of B - Ä? Explain.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning





